Valves - Gustav Wahler GmbH u. Co. KG
Valves - Gustav Wahler GmbH u. Co. KG
Valves - Gustav Wahler GmbH u. Co. KG
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
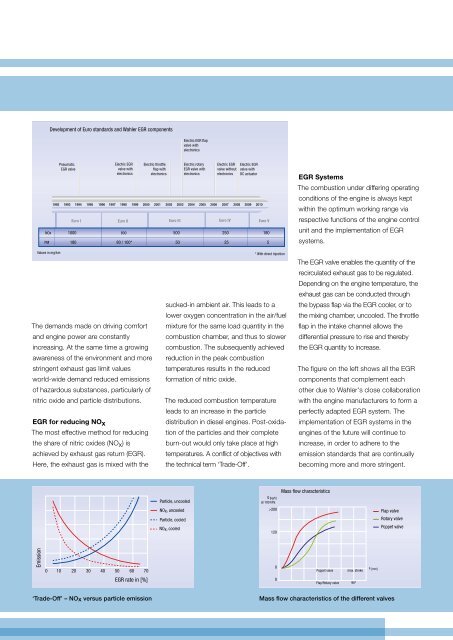
Entwicklung Development der Euro-Normen of standards und der and <strong>Wahler</strong>-AGR-Komponenten<br />
EGR components<br />
Elektrisches Electric EGR flap<br />
AGR-Klappenventil<br />
valve with<br />
mit electronics Elektronik<br />
Pneumatisches Pneumatic<br />
Electric Elektrisches EGR Electric Elektrische throttle Elektrisches Electric rotary Elektrisches Electric EGR Elektrisches Electric EGR<br />
AGR-Ventil EGR valve<br />
AGR-Ventil valve with Drosselklappe flap with AGR-Drehventil<br />
EGR valve with AGR-Ventil valve without AGR-Ventil valve with<br />
mit electronics Elektronik mit electronics Elektronik mit electronics Elektronik ohne electronics<br />
Elektronik<br />
mit DC actuator<br />
DC-Antrieb<br />
1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010<br />
Euro I Euro II Euro III Euro IV Euro V<br />
NOx 1000<br />
800 500 250<br />
180<br />
PM<br />
180 80 / 100* 50 25<br />
5<br />
EGR Systems<br />
The combustion under differing operating<br />
conditions of the engine is always kept<br />
within the optimum working range via<br />
respective functions of the engine control<br />
unit and the implementation of EGR<br />
systems.<br />
Values Werte in mg/km<br />
The demands made on driving comfort<br />
and engine power are constantly<br />
increasing. At the same time a growing<br />
awareness of the environment and more<br />
stringent exhaust gas limit values<br />
world-wide demand reduced emissions<br />
of hazardous substances, particularly of<br />
nitric oxide and particle distributions.<br />
EGR for reducing NOx<br />
The most effective method for reducing<br />
the share of nitric oxides (NOx) is<br />
achieved by exhaust gas return (EGR).<br />
Here, the exhaust gas is mixed with the<br />
* mit * With Direkteinspritzung<br />
direct injection<br />
sucked-in ambient air. This leads to a<br />
lower oxygen concentration in the air/fuel<br />
mixture for the same load quantity in the<br />
combustion chamber, and thus to slower<br />
combustion. The subsequently achieved<br />
reduction in the peak combustion<br />
temperatures results in the reduced<br />
formation of nitric oxide.<br />
The reduced combustion temperature<br />
leads to an increase in the particle<br />
distribution in diesel engines. Post-oxidation<br />
of the particles and their complete<br />
burn-out would only take place at high<br />
temperatures. A conflict of objectives with<br />
the technical term ‘Trade-Off’.<br />
The EGR valve enables the quantity of the<br />
recirculated exhaust gas to be regulated.<br />
Depending on the engine temperature, the<br />
exhaust gas can be conducted through<br />
the bypass flap via the EGR cooler, or to<br />
the mixing chamber, uncooled. The throttle<br />
flap in the intake channel allows the<br />
differential pressure to rise and thereby<br />
the EGR quantity to increase.<br />
The figure on the left shows all the EGR<br />
components that complement each<br />
other due to <strong>Wahler</strong>'s close collaboration<br />
with the engine manufacturers to form a<br />
perfectly adapted EGR system. The<br />
implementation of EGR systems in the<br />
engines of the future will continue to<br />
increase, in order to adhere to the<br />
emission standards that are continually<br />
becoming more and more stringent.<br />
Durchsatzkennlinien<br />
Mass flow characteristics<br />
Partikel, Particle, uncooled ungekühlt<br />
Q [kg/h]<br />
bei at 100 hPa<br />
NOx, ungekühlt uncooled<br />
Partikel, Particle, cooled gekühlt<br />
NOx, gekühlt cooled<br />
>200<br />
120<br />
Klappenventil<br />
Flap valve<br />
Drehventil Rotary valve<br />
Hubventil Poppet valve<br />
Emission<br />
0<br />
10 20 30 40 50 60 70<br />
AGR-Rate EGR rate in [%]<br />
0<br />
0<br />
Hubventil Poppet valve<br />
max. Hub stroke<br />
Flap/Rotary Klappen-/Drehventil valve 90°<br />
s [mm]<br />
ϕ [ ]<br />
‘Trade-Off’ – NOx versus particle emission<br />
Mass flow characteristics of the different valves