- Page 1 and 2: Biography of the Venerable Mahather
- Page 3 and 4: 44. Virati-silavinicchaya Dipani. 4
- Page 5 and 6: PREFACE The fact that a reliable co
- Page 7 and 8: The Vipassana Dipani Or The Exposit
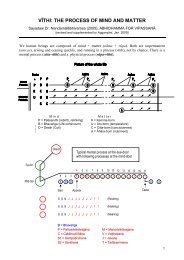
- Page 9 and 10: The views "My Body!" and "My Soul!"
- Page 11 and 12: Among the innumerable ordinary bein
- Page 13 and 14: existence to another; and as the wa
- Page 15: There are also pots and cups made o
- Page 19 and 20: 9. Jivita means the life of mental
- Page 21 and 22: them in the doing of good deeds. It
- Page 23 and 24: Jivita-Rupa or Material Quality of
- Page 25 and 26: 89. Santati-rupa means continuance.
- Page 27 and 28: Two things are necessary for the ar
- Page 29 and 30: The Three Parinnas Parinna means pr
- Page 31 and 32: 116. Anicce niccanti dihttivippalla
- Page 33 and 34: Nata-parianna is relevant to Tirana
- Page 35 and 36: What has just been expounded is the
- Page 37 and 38: These "Ills" or Dukkhas are very nu
- Page 39 and 40: ecomes evident that phenomena do no
- Page 41 and 42: In Buddhist ethics, there are three
- Page 43 and 44: The Patthanuddesa Dipani The Buddhi
- Page 45 and 46: The well-known Ledi Sayadaw Mahathe
- Page 47 and 48: mental concomitants happy and joyfu
- Page 49 and 50: In what sense is arammana to be und
- Page 51 and 52: In one existence of a being, the re
- Page 53 and 54: esolutions made. When the preceding
- Page 55 and 56: continuum, and so on with the rest,
- Page 57 and 58: A large variety of concepts or name
- Page 59 and 60: arisen, or present, inasmuch as the
- Page 61 and 62: 13. Kamma-Paccaya or the Relationsh
- Page 63 and 64: End of Vipaka-Relation. 15. Ahara-P
- Page 65 and 66: 17. Jhana-Paccaya or the Relation O
- Page 67 and 68:
qualities produced by mind. Again a
- Page 69 and 70:
Therefore, how can there be any ess
- Page 71 and 72:
only the eighteen relations do--in
- Page 73 and 74:
cittujukata, (rectitude of mind), s
- Page 75 and 76:
There are twenty-three groups of ma
- Page 77 and 78:
sahajatas only. The material qualit
- Page 79 and 80:
unspecified. The abyakatadhammas ar
- Page 81 and 82:
3. Ahetu-apaccaya-ditthi. 4. Pubbek
- Page 83 and 84:
"Monks, indeed, in the minds of tho
- Page 85 and 86:
In the minds of these samanas and b
- Page 87 and 88:
The Buddha, in a general manner, de
- Page 89 and 90:
14. Majjhimatita-kammamulakatika--t
- Page 91 and 92:
that when the Buddha declared: "Kam
- Page 93 and 94:
This issaranimmana view exists in t
- Page 95 and 96:
that everything in the world comes
- Page 97 and 98:
. Kamma and the above example. We n
- Page 99 and 100:
Here, I shall explain this with an
- Page 101 and 102:
the planes of the Brahmas who have
- Page 103 and 104:
Ones)--they are ariya (Noble Ones).
- Page 105 and 106:
conventional term of 'bowl' cannot
- Page 107 and 108:
dawn upon them that these five cons
- Page 109 and 110:
Inhabitants of Ariya-bhumi (the Pla
- Page 111 and 112:
Ati-olarika-ditthi And Ditthi-visud
- Page 113 and 114:
The bowl on which rust has accumula
- Page 115 and 116:
35. because of mind and matter, con
- Page 117 and 118:
The expression 'became perfect by t
- Page 119 and 120:
germinal, it is called bija-niyama
- Page 121 and 122:
'What is the cessation of the world
- Page 123 and 124:
nerves, sinews, bone, etc.; the nam
- Page 125 and 126:
when those steps are stepped by him
- Page 127 and 128:
numbers of years by grains of sand
- Page 129 and 130:
If it be insisted on the contrary t
- Page 131 and 132:
The drifting course of the result o
- Page 133 and 134:
this highest scale they may be rebo
- Page 135 and 136:
10. material-stage (rupa-bhumi), 11
- Page 137 and 138:
Here indeed something should be sai
- Page 139 and 140:
germs, mango-trees from mango-germs
- Page 141 and 142:
upon jhanic interest (jhanapiti). T
- Page 143 and 144:
Name is that which bends towards (n
- Page 145 and 146:
42. Existence (bhava). By dogmatism
- Page 147 and 148:
'But how does the fact of prolonged
- Page 149 and 150:
'There is no world-lord, no creator
- Page 151 and 152:
think it is not necessary. lt may c
- Page 153 and 154:
Now I have dealt enough with, to re
- Page 155 and 156:
Before we proceed any further, we s
- Page 157 and 158:
[36] 'Just as if, brother, there we
- Page 159 and 160:
monks, there be an arising of Tatha
- Page 161 and 162:
Ear Sound Nose Odour Tongue Taste B
- Page 163 and 164:
IV. 4. On account of the tongue and
- Page 165 and 166:
The four inherent characteristics o
- Page 167 and 168:
Anything that is performed compulso
- Page 169 and 170:
Here the explanation given by the S
- Page 171 and 172:
feeling associated with seeing, hea
- Page 173 and 174:
A question may be raised at this po
- Page 175 and 176:
mental formations) and vinnana-kkha
- Page 177 and 178:
greater and greater. So too are the
- Page 179 and 180:
faith, good actions and sense pleas
- Page 181 and 182:
Noble Truths and who desire to hono
- Page 183 and 184:
This neyya class of individuals can
- Page 185 and 186:
the future Metteyya Buddha. And, af
- Page 187 and 188:
acquisition a good insight into the
- Page 189 and 190:
16. bahusacca (great learning) 17.
- Page 191 and 192:
to memory, then of contemplating on
- Page 193 and 194:
which they attain Arahatship and Ni
- Page 195 and 196:
Bodhipakkhiya Dipani The Manual of
- Page 197 and 198:
attention becomes released from its
- Page 199 and 200:
Comparisons may also be made with t
- Page 201 and 202:
The ability to keep one's attention
- Page 203 and 204:
2. let the sinews remain 3. let the
- Page 205 and 206:
course of this present life and in
- Page 207 and 208:
principles, the control can last fo
- Page 209 and 210:
The kamavacara-lokiya-sila attains
- Page 211 and 212:
The lokiya panna which puthujjana p
- Page 213 and 214:
Bodhipakkhiya Dipani The Manual of
- Page 215 and 216:
together with parikamma-samadhi (pr
- Page 217 and 218:
If any one of the pada is establish
- Page 219 and 220:
Bodhipakkhiya Dipani The Manual of
- Page 221 and 222:
no concrete results appear, and as
- Page 223 and 224:
If in the work of samatha, such as
- Page 225 and 226:
He reviews the Path in this way: 'S
- Page 227 and 228:
kingdom of saddha consisting of the
- Page 229 and 230:
incursions of lions and leopards. T
- Page 231 and 232:
118. Khuddaka-Nikaya Jataka Pali, E
- Page 233 and 234:
unequalled and unparallelled by any
- Page 235 and 236:
The definition of magga is: Kilese
- Page 237 and 238:
During the period of the proceeding
- Page 239 and 240:
and worlds they enjoy at will the p
- Page 241 and 242:
By patipada-nanadassana-visuddhi is
- Page 243 and 244:
embers. The sila, samadhi and panna
- Page 245 and 246:
A person who practises the dhammanu
- Page 247 and 248:
The meanings of the expressions 'su
- Page 249 and 250:
Those persons who do not possess an
- Page 251 and 252:
The three sasana of sila, samadhi,
- Page 253 and 254:
Magganga Dipani The Manual of the C
- Page 255 and 256:
there really exists the other world
- Page 257 and 258:
Kammassakata Samma-ditthi Sabbesatt
- Page 259 and 260:
That is, all his possessions are du
- Page 261 and 262:
In this phrase, 'refuge' means reli
- Page 263 and 264:
God has no power to give property t
- Page 265 and 266:
48. Atthi loke samanabrahmana samag
- Page 267 and 268:
Twenty-one kinds of wrong livelihoo
- Page 269 and 270:
endering of some technical Abhidham
- Page 271 and 272:
Namo tassa bhagavatto arahato samma
- Page 273 and 274:
successful existences as men or dev
- Page 275 and 276:
22. Not understanding the Law of De
- Page 277 and 278:
(samyojana), the stout bonds of Cra
- Page 279 and 280:
disappears, and the new name of 'pa
- Page 281 and 282:
The nature of Water, Wind and Fire
- Page 283 and 284:
substance whatever, not even a hund
- Page 285 and 286:
where it provides the necessary fun
- Page 287 and 288:
58. Tongue-consciousness means the
- Page 289 and 290:
of these phenomena is required for
- Page 291 and 292:
Whereas the physical phenomena in w
- Page 293 and 294:
68. the tongue sensitivity which is
- Page 295 and 296:
doing these things they cannot take
- Page 297 and 298:
The fact of the numerous vanishings
- Page 299 and 300:
Think of the law of the jungle, the
- Page 301 and 302:
eing withdrawn from the lump, and t
- Page 303 and 304:
(Phenupamam kdyamimam viditva Maric
- Page 305 and 306:
visual objects; and the images of t
- Page 307 and 308:
(End of Exposition of the Knowledge
- Page 309 and 310:
It will be observed that the pair o
- Page 311 and 312:
Those whose mothers, during their c
- Page 313 and 314:
kings, deva kings or Sakka king, th
- Page 315 and 316:
great privations. These beings rega