X86 Computer Bus Subsystems IBM PC/XT Architecture ('82, '83)
X86 Computer Bus Subsystems IBM PC/XT Architecture ('82, '83)
X86 Computer Bus Subsystems IBM PC/XT Architecture ('82, '83)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
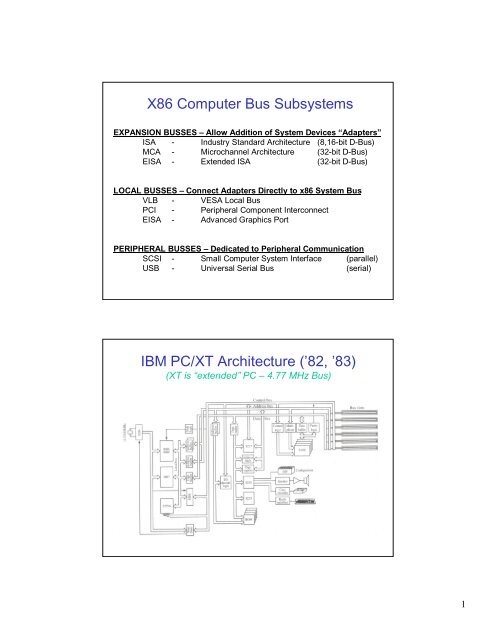
<strong>X86</strong> <strong>Computer</strong> <strong>Bus</strong> <strong>Subsystems</strong><br />
EXPANSION BUSSES – Allow Addition of System Devices “Adapters”<br />
ISA - Industry Standard <strong>Architecture</strong> (8,16-bit D-<strong>Bus</strong>)<br />
MCA - Microchannel <strong>Architecture</strong> (32-bit D-<strong>Bus</strong>)<br />
EISA - Extended ISA (32-bit D-<strong>Bus</strong>)<br />
LOCAL BUSSES – Connect Adapters Directly to x86 System <strong>Bus</strong><br />
VLB - VESA Local <strong>Bus</strong><br />
<strong>PC</strong>I - Peripheral Component Interconnect<br />
EISA - Advanced Graphics Port<br />
PERIPHERAL BUSSES – Dedicated to Peripheral Communication<br />
SCSI - Small <strong>Computer</strong> System Interface (parallel)<br />
USB - Universal Serial <strong>Bus</strong> (serial)<br />
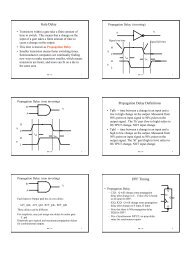
<strong>IBM</strong> <strong>PC</strong>/<strong>XT</strong> <strong>Architecture</strong> (’82, ’83)<br />
(<strong>XT</strong> is “extended” <strong>PC</strong> – 4.77 MHz <strong>Bus</strong>)<br />
1
ISA (8-bit Version)<br />
(Typical 4.77 MHz <strong>Bus</strong> – <strong>IBM</strong> <strong>PC</strong>, <strong>IBM</strong> <strong>XT</strong>)<br />
<strong>IBM</strong> AT <strong>Architecture</strong> (’84)<br />
(AT is “advanced technology” – 6 MHz)<br />
ISA “Standard” was Modified to 16-bit <strong>Bus</strong><br />
2
ISA (16-bit Version)<br />
(aka The “AT <strong>Bus</strong>”)<br />
AT <strong>Bus</strong> Standard<br />
Due to “clones” became so common it is a “standard”<br />
• 16-bit Data <strong>Bus</strong><br />
• 24-bit Address <strong>Bus</strong><br />
• 11 Interrupt Request Lines<br />
– IRQ2-7, IRQ10-12, IRQ14, IRQ15<br />
• 7 DMA Channels<br />
• 8.33 MHz Max. <strong>Bus</strong> Frequency<br />
3
Plug and Play<br />
– Each New Adapter May Require:<br />
• DMA Channels<br />
• IRQ Lines<br />
• Parallel I/O Addresses<br />
– Adding New Adapter to ISA <strong>Bus</strong> Can Cause Conflicts<br />
1) User Must MANUALLY Change DIP Switch<br />
2) Automatic Configuration<br />
– “Plug and Play”<br />
• “Standard” Developed by Intel/Microsoft<br />
• Adapters Contain Special Registers for OS Query<br />
• Adapters Accept Commands to Change Values or Deselect<br />
• Need a PnP Aware ROM-BIOS (sequence during boot-time)<br />
Microchannel <strong>Architecture</strong> (MCA)<br />
Proprietary <strong>IBM</strong> Adapter <strong>Bus</strong> - 1987<br />
• 8.33 MHz, 16-bit AT <strong>Bus</strong> Causes Sever I/O Bottleneck<br />
– Lots’ of Graphics versus Character Mode Data<br />
– 25 MHz 80386DX Available – CPU BW Far Exceeds <strong>Bus</strong> BW<br />
• MCA – 10 MHz at Selectable 8, 16, 32 bits<br />
• Totally Incompatible with ISA<br />
• <strong>IBM</strong> Proprietary – Must License to Use<br />
– Pay <strong>IBM</strong> $$$$ to Make Adapters<br />
• 9 Popular <strong>Computer</strong> Manufacturers Form Consortium<br />
– “Gang of Nine” – EISA is Born!<br />
• MCA is no longer popularly used<br />
4
EISA<br />
• Compatible With ISA and an OPEN Standard<br />
• 32-bit Address and Data <strong>Bus</strong> Width<br />
• Supports Automatic Adapter Configuration<br />
– CFG (driver file) with each Adapter<br />
– Writes Special Information in CMOS RAM for boot time<br />
• 15 IRQs Supported<br />
• 7 (32-bit) DMA Channels Supported<br />
• 8.33 MHz <strong>Bus</strong> Speed<br />
EISA Structure<br />
5
EISA<br />
ISA ISA EISA<br />
EISA Pinout<br />
Local <strong>Bus</strong>ses – VLB, <strong>PC</strong>I, AGP<br />
• EISA BW Still Too Slow For Video<br />
• Need Direct Access to x86 System <strong>Bus</strong><br />
– for VRAM write/read<br />
• VESA Developed VLB (1992)<br />
– designed to operate “with” ISA or EISA or MCA<br />
– use IRQ and DMA support of Adapter <strong>Bus</strong><br />
– VLB portion operates at system bus speed (50 or 66 MHz)<br />
– no automatic configuration support<br />
– x86 only bus<br />
• <strong>PC</strong>I<br />
– developed with ISA Compatibility in mind<br />
– New <strong>Bus</strong> – Extension in the Sense of Compatibility<br />
– Requires a “Bridge” Circuit<br />
• AGP<br />
– Advanced Graphics Port<br />
– Extension to <strong>PC</strong>I Standard 66MHz<br />
6
<strong>PC</strong>I Based <strong>Computer</strong><br />
<strong>PC</strong>I Characteristics<br />
• 0-33 MHz (0 MHz Important for Laptops)<br />
• 32-bit OR 64-bit Data <strong>Bus</strong><br />
• Burst Mode Support<br />
– Northbridge Transforms Mult. Sys. Req. into <strong>PC</strong>I Burst<br />
• <strong>Bus</strong> Master Support<br />
– Similar to DMAC Capability<br />
• Sharable IRQs<br />
– ISRs (drivers) Chained Together<br />
– Each Checks to Determine Which Should Execute<br />
7
<strong>PC</strong>I Pinout<br />
I/O (Peripheral) <strong>Bus</strong>ses<br />
• NOT System <strong>Bus</strong> Adapters<br />
• SCSI (Small <strong>Computer</strong> System Interface)<br />
- high speed, parallel<br />
- HD, Tape Drive, CD-ROM, etc.<br />
• USB (Universal Serial <strong>Bus</strong>)<br />
- medium/low speed, serial<br />
- mice, keyboard, modems<br />
8
SCSI (“scuzzy”)<br />
• Many Versions – Original:<br />
– 8-bit Data<br />
– 1-bit Parity<br />
– 9-bit Control<br />
• Intelligent – SCSI Controller Accepts High Level<br />
Commands<br />
– e.g. HD can backup to Tape Drive while CPU does “other things”<br />
• Daisy Chained with Device IDs<br />
• Must Terminate – Prevent Reflections<br />
USB<br />
• 1.5 Mb/s and 12 Mb/s Data Rates<br />
• Simplifies Task of Connecting Peripherals<br />
• Uses Notions of “Nodes” and “Hubs”<br />
• Devices Connect to Nodes present at a Hub<br />
• All Hubs Daisy-Chained to “Host Root Hub”<br />
• Host Allows upto 127 Different USB Devices<br />
9
USB<br />
Typical <strong>PC</strong>I Based x86 <strong>Computer</strong> <strong>Architecture</strong><br />
L3<br />
Cache<br />
AGP SDRAM<br />
<strong>PC</strong>I Adapter 1 <strong>PC</strong>I Adapter 2<br />
XD <strong>Bus</strong> 8-bit<br />
EIDE 1<br />
EIDE 2<br />
Flash Mem BIOS RTC and CMOS<br />
System <strong>Bus</strong> 64-bit<br />
North Bridge<br />
<strong>PC</strong>I <strong>Bus</strong> 32-bit<br />
South<br />
Bridge<br />
L2<br />
Cache<br />
L1<br />
Cache<br />
ISA <strong>Bus</strong> 16-bit<br />
x86<br />
CPU<br />
Common Package<br />
<strong>PC</strong>I Adapter 3 <strong>PC</strong>I Adapter 4<br />
USB Root Hub 1<br />
USB Root Hub 2<br />
KBD, PS/2, LPT,<br />
UART1, UART2, Floppy<br />
ISA Adapter 1 ISA Adapter 2<br />
10