PHY 121 - Quiz 1 (Solution)
PHY 121 - Quiz 1 (Solution)
PHY 121 - Quiz 1 (Solution)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1<br />
Duration: 10 mins<br />
NAME:<br />
<strong>PHY</strong> <strong>121</strong> - <strong>Quiz</strong> 1 (<strong>Solution</strong>)<br />
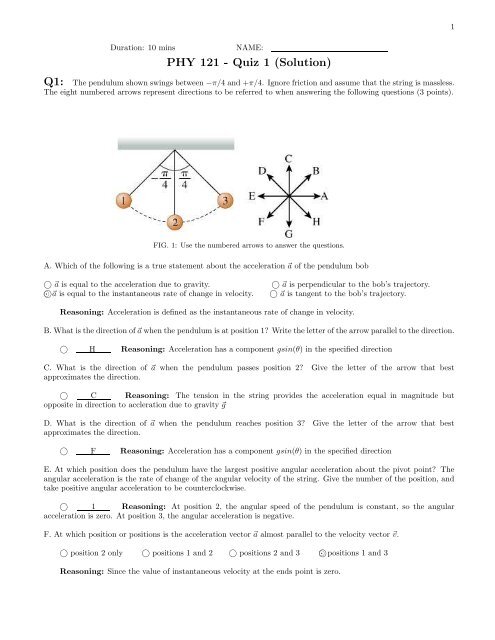
Q1: The pendulum shown swings between −π/4 and +π/4. Ignore friction and assume that the string is massless.<br />
The eight numbered arrows represent directions to be referred to when answering the following questions (3 points).<br />
FIG. 1: Use the numbered arrows to answer the questions.<br />
A. Which of the following is a true statement about the acceleration ⃗a of the pendulum bob<br />
○ ⃗a is equal to the acceleration due to gravity.<br />
○⊙ ⃗a is equal to the instantaneous rate of change in velocity.<br />
○ ⃗a is perpendicular to the bob’s trajectory.<br />
○ ⃗a is tangent to the bob’s trajectory.<br />
Reasoning: Acceleration is defined as the instantaneous rate of change in velocity.<br />
B. What is the direction of ⃗a when the pendulum is at position 1? Write the letter of the arrow parallel to the direction.<br />
○ H Reasoning: Acceleration has a component gsin(θ) in the specified direction<br />
C. What is the direction of ⃗a when the pendulum passes position 2? Give the letter of the arrow that best<br />
approximates the direction.<br />
○ C Reasoning: The tension in the string provides the acceleration equal in magnitude but<br />
opposite in direction to accleration due to gravity ⃗g<br />
D. What is the direction of ⃗a when the pendulum reaches position 3? Give the letter of the arrow that best<br />
approximates the direction.<br />
○ F Reasoning: Acceleration has a component gsin(θ) in the specified direction<br />
E. At which position does the pendulum have the largest positive angular acceleration about the pivot point? The<br />
angular acceleration is the rate of change of the angular velocity of the string. Give the number of the position, and<br />
take positive angular acceleration to be counterclockwise.<br />
○ 1 Reasoning: At position 2, the angular speed of the pendulum is constant, so the angular<br />
acceleration is zero. At position 3, the angular acceleration is negative.<br />
F. At which position or positions is the acceleration vector ⃗a almost parallel to the velocity vector ⃗v.<br />
○ position 2 only ○ positions 1 and 2 ○ positions 2 and 3 ○⊙ positions 1 and 3<br />
Reasoning: Since the value of instantaneous velocity at the ends point is zero.
2<br />
Q2: Understanding Newtons Laws (3 points)<br />
A. An object cannot remain at rest unless which of the following holds?<br />
○⊙ The net force acting on it is zero.<br />
○ There are no forces at all acting on it.<br />
○ The net force acting on it is constant.<br />
○ There is only one force acting on it.<br />
Reasoning: Newtons first law: A body will remain in a state of rest or uniform motion unless acted upon by<br />
external unbalanced force.<br />
B. If a block is moving to the left at a constant velocity, what can one conclude?<br />
○ There is exactly one force applied to the block.<br />
○ The net force applied to the block is directed to the left.<br />
○⊙ The net force applied to the block is zero.<br />
○ There must be no forces at all applied to the block.<br />
Reasoning: Same as above.<br />
C. A block of mass 2 Kg is acted upon by two forces: 3 N(directed to the left) and 4 N (directed to the right). What<br />
can you say about the block’s motion?<br />
○ It must be moving to the left.<br />
○ It must be at rest.<br />
○ It must be moving to the right.<br />
○⊙ It could be moving to the left or right or at rest.<br />
Reasoning: It could be moving to the left or right or at rest.<br />
D. A massive block is being pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface by a constant horizontal force. The block<br />
will —<br />
○ continuously change direction.<br />
○ move with constant velocity.<br />
○⊙ move with a constant nonzero acceleration.<br />
○ move with continuously increasing acceleration.<br />
Reasoning: Newtons second law: Force(F) ∝ Rate of chance of momentum (m a)<br />
E. Two forces, of magnitude 4 N and 10 N are applied to an object. The relative direction of the forces is unknown.<br />
The net force acting on the object:<br />
Circle all possible correct answers<br />
○1.<br />
cannot be equal to 5 N 2. cannot be equal to 10 N<br />
3. must be greater than 10 N 4. cannot be directed the same way as the force of 10 N<br />
Reasoning: Since force is a vector quantity deduce the smallest possible force and the largest force using different<br />
combination for orientation of the force vectors. Smallest, when the two forces are in opposite direction and largest,<br />
when they are in the same direction.