The Conservation and Sustainable Use of Freshwater ... - IUCN
The Conservation and Sustainable Use of Freshwater ... - IUCN
The Conservation and Sustainable Use of Freshwater ... - IUCN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
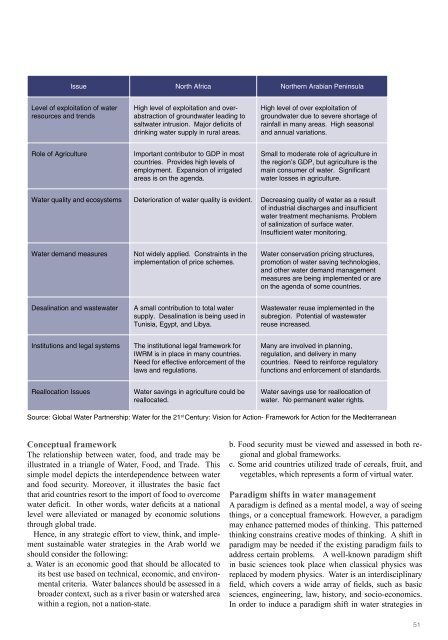
Issue North Africa Northern Arabian Peninsula<br />
Level <strong>of</strong> exploitation <strong>of</strong> water<br />
resources <strong>and</strong> trends<br />
High level <strong>of</strong> exploitation <strong>and</strong> overabstraction<br />
<strong>of</strong> groundwater leading to<br />
saltwater intrusion. Major deficits <strong>of</strong><br />
drinking water supply in rural areas.<br />
High level <strong>of</strong> over exploitation <strong>of</strong><br />
groundwater due to severe shortage <strong>of</strong><br />
rainfall in many areas. High seasonal<br />
<strong>and</strong> annual variations.<br />
Role <strong>of</strong> Agriculture<br />
Important contributor to GDP in most<br />
countries. Provides high levels <strong>of</strong><br />
employment. Expansion <strong>of</strong> irrigated<br />
areas is on the agenda.<br />
Small to moderate role <strong>of</strong> agriculture in<br />
the region’s GDP, but agriculture is the<br />
main consumer <strong>of</strong> water. Significant<br />
water losses in agriculture.<br />
Water quality <strong>and</strong> ecosystems Deterioration <strong>of</strong> water quality is evident. Decreasing quality <strong>of</strong> water as a result<br />
<strong>of</strong> industrial discharges <strong>and</strong> insufficient<br />
water treatment mechanisms. Problem<br />
<strong>of</strong> salinization <strong>of</strong> surface water.<br />
Insufficient water monitoring.<br />
Water dem<strong>and</strong> measures<br />
Not widely applied. Constraints in the<br />
implementation <strong>of</strong> price schemes.<br />
Water conservation pricing structures,<br />
promotion <strong>of</strong> water saving technologies,<br />
<strong>and</strong> other water dem<strong>and</strong> management<br />
measures are being implemented or are<br />
on the agenda <strong>of</strong> some countries.<br />
Desalination <strong>and</strong> wastewater<br />
A small contribution to total water<br />
supply. Desalination is being used in<br />
Tunisia, Egypt, <strong>and</strong> Libya.<br />
Wastewater reuse implemented in the<br />
subregion. Potential <strong>of</strong> wastewater<br />
reuse increased.<br />
Institutions <strong>and</strong> legal systems<br />
<strong>The</strong> institutional legal framework for<br />
IWRM is in place in many countries.<br />
Need for effective enforcement <strong>of</strong> the<br />
laws <strong>and</strong> regulations.<br />
Many are involved in planning,<br />
regulation, <strong>and</strong> delivery in many<br />
countries. Need to reinforce regulatory<br />
functions <strong>and</strong> enforcement <strong>of</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ards.<br />
Reallocation Issues<br />
Water savings in agriculture could be<br />
reallocated.<br />
Water savings use for reallocation <strong>of</strong><br />
water. No permanent water rights.<br />
Source: Global Water Partnership: Water for the 21 st Century: Vision for Action- Framework for Action for the Mediterranean<br />
Conceptual framework<br />
<strong>The</strong> relationship between water, food, <strong>and</strong> trade may be<br />
illustrated in a triangle <strong>of</strong> Water, Food, <strong>and</strong> Trade. This<br />
simple model depicts the interdependence between water<br />
<strong>and</strong> food security. Moreover, it illustrates the basic fact<br />
that arid countries resort to the import <strong>of</strong> food to overcome<br />
water deficit. In other words, water deficits at a national<br />
level were alleviated or managed by economic solutions<br />
through global trade.<br />
Hence, in any strategic effort to view, think, <strong>and</strong> implement<br />
sustainable water strategies in the Arab world we<br />
should consider the following:<br />
a. Water is an economic good that should be allocated to<br />
its best use based on technical, economic, <strong>and</strong> environmental<br />
criteria. Water balances should be assessed in a<br />
broader context, such as a river basin or watershed area<br />
within a region, not a nation-state.<br />
b. Food security must be viewed <strong>and</strong> assessed in both regional<br />
<strong>and</strong> global frameworks.<br />
c. Some arid countries utilized trade <strong>of</strong> cereals, fruit, <strong>and</strong><br />
vegetables, which represents a form <strong>of</strong> virtual water.<br />
Paradigm shifts in water management<br />
A paradigm is defined as a mental model, a way <strong>of</strong> seeing<br />
things, or a conceptual framework. However, a paradigm<br />
may enhance patterned modes <strong>of</strong> thinking. This patterned<br />
thinking constrains creative modes <strong>of</strong> thinking. A shift in<br />
paradigm may be needed if the existing paradigm fails to<br />
address certain problems. A well-known paradigm shift<br />
in basic sciences took place when classical physics was<br />
replaced by modern physics. Water is an interdisciplinary<br />
field, which covers a wide array <strong>of</strong> fields, such as basic<br />
sciences, engineering, law, history, <strong>and</strong> socio-economics.<br />
In order to induce a paradigm shift in water strategies in<br />
51