Design of a Small Size Dielectric Loaded Helical Antenna for ...
Design of a Small Size Dielectric Loaded Helical Antenna for ...
Design of a Small Size Dielectric Loaded Helical Antenna for ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
III. A REDUCED SIZED TWO-ELEMENT BBHA ARRAY<br />
For satellite communications, usually high-gain antennas<br />
are required. To this end, we have designed a two-element<br />
array using the Macor-loaded BBHA, which is different from<br />
the conventional dielectric loaded helical antenna array [7].<br />
This is because the inter element spacing between the<br />
BBHAs <strong>of</strong> 0.2� at the operating frequency <strong>of</strong> 2.4 GHz is<br />
much smaller and there is no need <strong>for</strong> a ground plane. Hence,<br />
the overall size <strong>of</strong> the Macor-loaded BBHA array is smaller<br />
compared to the conventional dielectric loaded helical<br />
antenna array. Fig. 16 shows the coordinate system employed<br />
here <strong>for</strong> the two element BBHA.<br />
�<br />
y�<br />
2�<br />
1�<br />
Fig. 16. Coordinate system <strong>of</strong> a two element BBHA.<br />
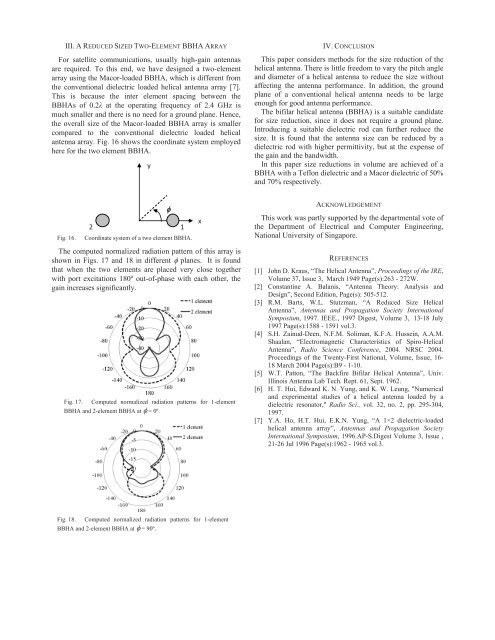
The computed normalized radiation pattern <strong>of</strong> this array is<br />
shown in Figs. 17 and 18 in different � planes. It is found<br />
that when the two elements are placed very close together<br />
with port excitations 180º out-<strong>of</strong>-phase with each other, the<br />
gain increases significantly.<br />
Fig. 17. Computed normalized radiation patterns <strong>for</strong> 1-element<br />
BBHA and 2-element BBHA at � = 0º.<br />
Fig. 18. Computed normalized radiation patterns <strong>for</strong> 1-element<br />
BBHA and 2-element BBHA at � = 90º.<br />
��<br />
x<br />
51<br />
IV. CONCLUSION<br />
This paper considers methods <strong>for</strong> the size reduction <strong>of</strong> the<br />
helical antenna. There is little freedom to vary the pitch angle<br />
and diameter <strong>of</strong> a helical antenna to reduce the size without<br />
affecting the antenna per<strong>for</strong>mance. In addition, the ground<br />
plane <strong>of</strong> a conventional helical antenna needs to be large<br />
enough <strong>for</strong> good antenna per<strong>for</strong>mance.<br />
The bifilar helical antenna (BBHA) is a suitable candidate<br />
<strong>for</strong> size reduction, since it does not require a ground plane.<br />
Introducing a suitable dielectric rod can further reduce the<br />
size. It is found that the antenna size can be reduced by a<br />
dielectric rod with higher permittivity, but at the expense <strong>of</strong><br />
the gain and the bandwidth.<br />
In this paper size reductions in volume are achieved <strong>of</strong> a<br />
BBHA with a Teflon dielectric and a Macor dielectric <strong>of</strong> 50%<br />
and 70% respectively.<br />
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT<br />
This work was partly supported by the departmental vote <strong>of</strong><br />
the Department <strong>of</strong> Electrical and Computer Engineering,<br />
National University <strong>of</strong> Singapore.<br />
REFERENCES<br />
[1] John D. Kraus, “The <strong>Helical</strong> <strong>Antenna</strong>”, Proceedings <strong>of</strong> the IRE,<br />
Volume 37, Issue 3, March 1949 Page(s):263 - 272W.<br />
[2] Constantine A. Balanis, “<strong>Antenna</strong> Theory: Analysis and<br />
<strong>Design</strong>”, Second Edition, Page(s): 505-512.<br />
[3] R.M. Barts, W.L. Stutzman, “A Reduced <strong>Size</strong> <strong>Helical</strong><br />
<strong>Antenna</strong>”, <strong>Antenna</strong>s and Propagation Society International<br />
Symposium, 1997. IEEE., 1997 Digest, Volume 3, 13-18 July<br />
1997 Page(s):1588 - 1591 vol.3.<br />
[4] S.H. Zainud-Deen, N.F.M. Soliman, K.F.A. Hussein, A.A.M.<br />
Shaalan, “Electromagnetic Characteristics <strong>of</strong> Spiro-<strong>Helical</strong><br />
<strong>Antenna</strong>”, Radio Science Conference, 2004. NRSC 2004.<br />
Proceedings <strong>of</strong> the Twenty-First National, Volume, Issue, 16-<br />
18 March 2004 Page(s):B9 - 1-10.<br />
[5] W.T. Patton, “The Backfire Bifilar <strong>Helical</strong> <strong>Antenna</strong>”, Univ.<br />
Illinois <strong>Antenna</strong> Lab Tech. Rept. 61, Sept. 1962.<br />
[6] H. T. Hui, Edward K. N. Yung, and K. W. Leung, "Numerical<br />
and experimental studies <strong>of</strong> a helical antenna loaded by a<br />
dielectric resonator," Radio Sci., vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 295-304,<br />
1997.<br />
[7] Y.A. Ho, H.T. Hui, E.K.N. Yung, “A 1×2 dielectric-loaded<br />
helical antenna array”, <strong>Antenna</strong>s and Propagation Society<br />
International Symposium, 1996.AP-S.Digest Volume 3, Issue ,<br />
21-26 Jul 1996 Page(s):1962 - 1965 vol.3.<br />
Authorized licensed use limited to: National University <strong>of</strong> Singapore. Downloaded on May 03,2010 at 14:47:24 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.