Geometric theory of defects in solids
Geometric theory of defects in solids
Geometric theory of defects in solids
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
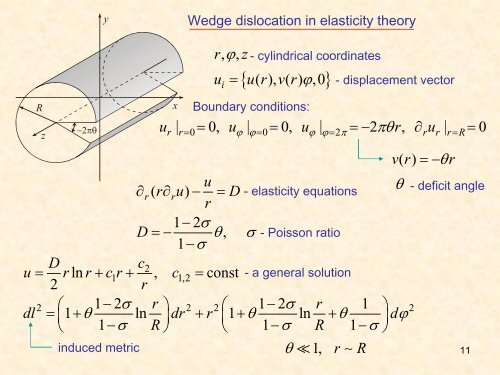
y<br />
Wedge dislocation <strong>in</strong> elasticity <strong>theory</strong><br />
R<br />
z<br />
−2πθ<br />
x<br />
r, ϕ,<br />
z<br />
ui<br />
- cyl<strong>in</strong>drical coord<strong>in</strong>ates<br />
{ u(),() r v r ϕ,0}<br />
= - displacement vector<br />
Boundary conditions:<br />
u | = 0, u | = 0, u | =−2 r, ∂ u | = 0<br />
r r= 0 ϕ ϕ= 0 ϕ ϕ= 2π πθ r r r=<br />
R<br />
vr ()<br />
u<br />
∂r( r∂ru)<br />
− = D - elasticity equations<br />
r<br />
1−<br />
2σ D =− θ , σ - Poisson ratio<br />
1 − σ<br />
D<br />
c2<br />
u = rln r+ cr 1 + , c1,2<br />
= const - a general solution<br />
2<br />
r<br />
2 ⎛ 1−2σ<br />
r ⎞ 2 2⎛ 1−2σ<br />
r 1 ⎞ 2<br />
dl = ⎜1+ θ ln ⎟dr + r ⎜1+ θ ln + θ ⎟dϕ<br />
⎝ 1−σ R⎠ ⎝ 1−σ R 1−σ<br />
⎠<br />
<strong>in</strong>duced metric θ 1, r ∼ R<br />
= −θ r<br />
θ - deficit angle<br />
11