Geometric theory of defects in solids
Geometric theory of defects in solids
Geometric theory of defects in solids
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
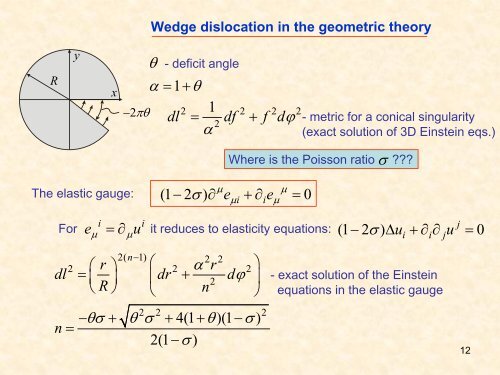
Wedge dislocation <strong>in</strong> the geometric <strong>theory</strong><br />
R<br />
y<br />
x<br />
−2πθ<br />
θ<br />
- deficit angle<br />
α = 1+<br />
θ<br />
2 1 2 2 2<br />
dl = df + f dϕ - metric for a conical s<strong>in</strong>gularity<br />
2<br />
α<br />
(exact solution <strong>of</strong> 3D E<strong>in</strong>ste<strong>in</strong> eqs.)<br />
Where is the Poisson ratio σ ???<br />
The elastic gauge:<br />
μ<br />
(1− 2 σ ) ∂ e +∂ e = 0<br />
μi<br />
i<br />
μ<br />
μ<br />
e<br />
i<br />
μ<br />
=∂<br />
u<br />
i<br />
For it reduces to elasticity equations:<br />
μ<br />
(1− 2 σ ) Δ u +∂ ∂ u = 0<br />
i i j<br />
j<br />
2( n 1) 2 2<br />
2 ⎛ r ⎞<br />
− ⎛<br />
2 α r 2⎞<br />
dl = ⎜ ⎟ ⎜dr + dϕ<br />
2 ⎟<br />
⎝R<br />
⎠ ⎝ n ⎠<br />
- exact solution <strong>of</strong> the E<strong>in</strong>ste<strong>in</strong><br />
equations <strong>in</strong> the elastic gauge<br />
n<br />
=<br />
2 2 2<br />
− θσ + θ σ + 4(1 + θ)(1 −σ)<br />
2(1 −σ<br />
)<br />
12