Quelques EDP simples r´esolues avec FreeFem++, Astuces et Trucs
Quelques EDP simples r´esolues avec FreeFem++, Astuces et Trucs
Quelques EDP simples r´esolues avec FreeFem++, Astuces et Trucs
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
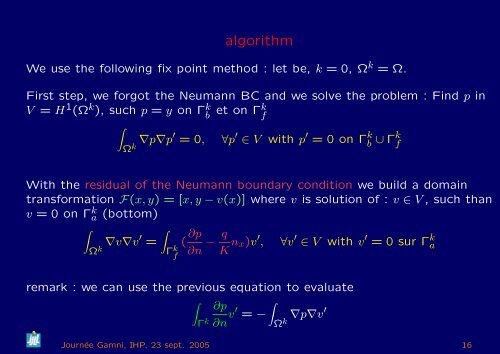
algorithm<br />
We use the following fix point m<strong>et</strong>hod : l<strong>et</strong> be, k = 0, Ω k = Ω.<br />
First step, we forgot the Neumann BC and we solve the problem : Find p in<br />
V = H 1 (Ω k ), such p = y on Γ k b <strong>et</strong> on Γk f<br />
�<br />
Ω k ∇p∇p′ = 0, ∀p ′ ∈ V with p ′ = 0 on Γ k b ∪ Γk f<br />
With the residual of the Neumann boundary condition we build a domain<br />
transformation F(x, y) = [x, y − v(x)] where v is solution of : v ∈ V , such than<br />
v = 0 on Γ k a (bottom)<br />
�<br />
Ω k ∇v∇v′ =<br />
�<br />
Γ k f<br />
( ∂p<br />
∂n<br />
− q<br />
K nx)v ′ , ∀v ′ ∈ V with v ′ = 0 sur Γ k a<br />
remark : we can use the previous equation to evaluate<br />
�<br />
Γ k<br />
∂p<br />
∂n v′ = −<br />
�<br />
∇p∇v′<br />
Ωk Journée Gamni, IHP, 23 sept. 2005 16