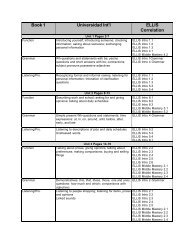
Examination Correlations With English Discoveries Online
Examination Correlations With English Discoveries Online
Examination Correlations With English Discoveries Online
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
©2002 Edusoft LTD All rights reserved Page 6 of 10<strong>English</strong> <strong>Discoveries</strong> <strong>Online</strong> – Overview of LevelsBelow is a description of the objectives, text types and content according to the three maincourse levels in <strong>English</strong> <strong>Discoveries</strong> <strong>Online</strong>. A detailed description of content and objectives foreach unit and component can be found in the Scope and Sequence section of this guide.BasicIn the Basic levels learners access and make use of oral and written information needed for dailycommunication through a variety of media and text types. Learners are exposed to and take partin oral interactions on familiar topics in everyday situations. Oral and written texts in each Basiclevel course contain simple vocabulary and basic syntactic structures relevant to that level andtext type.Section Description Topics ObjectivesReadingListeningSpeakingGrammarLearners access writteninformation through thefollowing text types:• Postcards (50-100words)• Advertisements (50-100 words)• Stories (200-250words)• Articles (200- 250words)Learners access oralinformation through thefollowing media:• Radio programs• Voice mail• TV programsLearners are exposed tooral interactions infamiliar situations suchas: street, hotel,restaurant, office, railwaystation, party, airport anddepartment store.Learners receiveexplanations of andpractice in simplegrammatical topics andThe texts are simpleand are on topicsclose to the learners’own lives andenvironment, rangingfrom family, food,shopping, to travel,sports, etc.The short passagesare simple and dealwith topics such asmusic, ordering food,ads, sports, asking forand giving informationand directions,interviews, restaurantreviews, etc.The simple shortdialogues are abouteveryday topics suchas ordering food,transportation, phonecalls, clothes, andmaking plans for theday.The structures arepracticed in shortsentences anddialogues on everydayLearners understand themain ideas and supportingdetails in texts, drawinferences from simpleinformation, understandfactual information and usethe information in the textsto fill in reports, sort itemsaccording to categories,order events in the correctsequence, and answerquestions.Learners accessinformation such as thegeneral meaning andsignificant details in apassage, understand mainideas and supportingdetails and drawinferences. They use theinformation to answerquestions, and completeads, forms, scripts andletters.Learners practice speechfunctions such as asking forand providing information,expressing opinions,making up your mind,ordering food, makingappointments, sayinggoodbye, etc.Learners learn structuresand tenses such as: theverb “Be,” present simple,present and past
©2002 Edusoft LTD All rights reserved Page 7 of 10structures relevant totheir level.topics.progressive, future,adverbs, gerunds, nouns,articles, past simple,imperatives, modals, etc.They practice using them inmultiple choice, cloze andfill in the gap exercises.IntermediateIn the Intermediate level courses learners access and make use of oral and written informationneeded for fluent communication through a variety of media and text types on a wider range oftopics. Learners are exposed to and take part in oral interactions on less familiar topics in arange of situations. Oral and written texts in each of the Intermediate courses contain richervocabulary and more complex syntactic structures relevant to the level and text type.Section Description Topics ObjectivesReadingListeningLearners access writteninformation through thefollowing text types:• Directions,instructions andnotices (80-150words)• Stories (250-300words)• Articles (250- 300words)Learners access oralinformation through thefollowing media:• Radio programs• Voice mail• TV programsThe texts are longer,written in morecomplex language,using richervocabulary, andcontain inferentialinformation. They dealwith less familiar topicssuch as: education,festivals and holidays,buying and selling,instructions anddirections, currenttrends, etc.The passages arelonger and containricher vocabulary andmore complexlanguage and containimplicit information.They deal with lessfamiliar topics such asdescribing problems,celebrity and jobinterviews, festivalsand celebrations,weather reports,quizzes, electionresults, etc.Learners understand mainideas and supportingdetails in texts, drawinferences, identify pointsof view, apply knowledge ofdiscourse markers to obtaininformation and understandlogical relationships intexts. They use theinformation to fill in reports,complete letters, emailmessages and summaries,follow instructions, andanswer questions, etc.Learners understand mainideas and supportingdetails, understand implicitand explicit information,draw inferences, identifyand understand points ofview, and apply knowledgeof discourse markers toobtain information andunderstand logicalrelationships from oraltexts. They use theinformation to fill in reports,complete letters, andsummaries, followinstructions, and answerquestions, etc.
©2002 Edusoft LTD All rights reserved Page 8 of 10SpeakingLearners are exposed tooral interactions in familiarand less familiar situationssuch as: post office, mall,school, barbecue, street,gym, office, andrestaurant.The longer dialoguesare about a range oftopics: exams, beinglate, making plans forthe day, art shows,sending a parcel,buying and selling, etc.Learners practice moreadvanced speech functionssuch as: expressinguncertainty, apologizing,expressing hope,issuing/declining invitations,give a warning, etc.GrammarLearners receiveexplanations of andpractice in more complexgrammatical topics andstructures relevant to theirlevel.The structures arepracticed in longersentences anddialogues on a rangeof topics.Learners learn structuresand tenses such as:present prefect, passivevoice, relative clauses,reported speech,conditionals, past perfect,past from of modals, etc.They practice using them inmultiple choice, cloze andfill in the gap exercises.AdvancedIn the Advanced level courses learners access and make use of more in-depth oral and writteninformation needed for effective communication through a variety of media and text types.Learners are exposed to and take part in oral interactions on less familiar, more abstract topics ina wide range of situations. Oral and written texts in each of the Advanced courses contain richvocabulary and complex syntactic structures relevant to the level and text type.Section Description Topics ObjectivesReadingListeningLearners access writteninformation through thefollowing text types:• Letters (200-300words)• Stories (300-350words)• Articles (300- 350words)Learners access oralinformation through thefollowing media:• Radio programs• Voice mail• TV programsThe texts are longer,written in morecomplex language,using rich vocabulary,and contain moreinferential information.They deal with moreabstract topics suchas: culturaldifferences, alternativevs. conventionalmedicine, letters ofrequest, complaint,etc., bilingualism,working a home, etc.The passages arelonger and contain richvocabulary andcomplex language withmore implicitinformation. They dealLearners understand mainideas and supportingdetails in texts, drawinferences, understandidiomatic expressions,identify points of view andwriter’s attitude, applyknowledge of discoursemarkers to obtaininformation and understandlogical relationships intexts. They use theinformation in the texts tofill in newspaper reports,notes, complete letters ofreply and summaries, andanswer questions.Learners understand mainideas and supportingdetails, understand implicitand explicit information andidiomatic language, drawinferences from visual
©2002 Edusoft LTD All rights reserved Page 9 of 10SpeakingGrammarLearners are exposed tooral interactions in lessfamiliar and familiarsituations such as: dressshop, office, emergencyroom, cruise ship, house,department store, street,high school, grouptherapy session, anddiner.Learners receiveexplanations of andpractice in complexgrammatical topics andstructures relevant totheir level.with a wide range oftopics and situations:crime, travelogues,missing persons, indepthinterviews,banking services,instructions, andunemployment.The longer dialoguesuse complex languageand rich vocabulary totalk about a range ofmore abstract topics:being bored,describing injuries,marketing, problems atwork, descriptions, andrelationships.The structures arepracticed in longersentences anddialogues on a rangeof topics.information, infer andunderstand points of view,and apply knowledge ofdiscourse markers to obtaininformation and understandlogical relationships. Theyuse the information to fill inreports, complete letters,and summaries, followinstructions, and answerquestions, etc.Learners practice advancedspeech functions such ascomplaining, offeringsympathy, expressing anopinion, giving advice,disagreeing, expressingworry, asking for a favor,interrupting, insisting, etc.Learners learn andconsolidate knowledge ofstructures and tenses suchas: future perfect andprogressive, clauses ofresult, phrasal verbs,participles, logicalconnectors, commonerrors, subjunctive, andnegation.
©2002 Edusoft LTD All rights reserved Page 10 of 10<strong>Correlations</strong>The following were evaluated and correlated with <strong>English</strong> <strong>Discoveries</strong> <strong>Online</strong> curricula:ALTE - Association of Language Testers in Europe (http://www.alte.org/)Council of Europe - Common European Framework of Reference for languagesUCLES - University of Cambridge, Local <strong>Examination</strong>s Syndicate (http://www.cambridge-efl.org/)IELTS - International <strong>English</strong> Language Testing System (http://www.ielts.org/)TOEFL - Test of <strong>English</strong> as a Foreign Language Paper/Computer (http://www.toefl.org/)TOEIC - Test of <strong>English</strong> for International Communication (http://www.toeic-usa.com/)<strong>English</strong><strong>Discoveries</strong><strong>Online</strong>ALTECouncilofEuropeUCLES IELTS TOEFL TOEICBasic 1 Level 1 A2 KET 3.0 400/97 150Basic 2 Level 1-2A2-B1 KET/PET 3.5-4.0 450/133 350Basic 3 Level 2 B1 PET 4.5 477/153 500Intermediate 1 Level 3 B2 FCE 5.0 500/173 625Intermediate 2 Level 3 B2 FCE 5.25 513/183 700Intermediate 3 Level 3 B2 FCE 5.5 527/197 750Advanced 1 Level 4 C1 CAE 6 550/213 800Advanced 2 Level 4 C1 CAE 6.25 563/223 825Advanced 3 Level 4 C1 CAE 6.5 577/233 850Based on information from “Using <strong>English</strong> for Academic Purposes – a Guide for International Students”,Andy Gillett, Department of Inter-Faculty Studies, University of Hertfordshire, Hatfield, UK. (2002),http://www.uefap.co.uk/index.htm