Modeling of Mechanical (Lumped Parameter) Elements
Modeling of Mechanical (Lumped Parameter) Elements
Modeling of Mechanical (Lumped Parameter) Elements
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
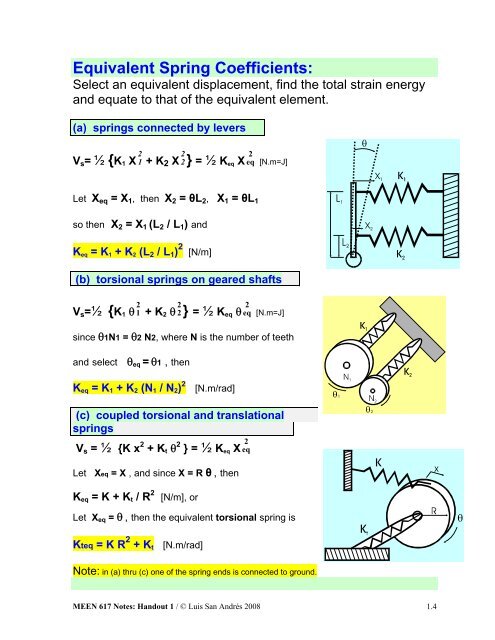
Equivalent Spring Coefficients:Select an equivalent displacement, find the total strain energyand equate to that <strong>of</strong> the equivalent element.(a) springs connected by leversV s = ½ {K 1 X 2 1 + K 2 X 2 22} = ½ K eq X eq[N.m=J]Let X eq = X 1 , then X 2 = θL 2 , X 1 = θL 1so then X 2 = X 1 (L 2 / L 1 ) andK eq = K 1 + K 2 (L 2 / L 1 ) 2 [N/m](b) torsional springs on geared shaftsV s =½ {K 1 θ 1 2 + K 2 θ 2 2 } = ½ K eq θ eq 2[N.m=J]since θ1N1 = θ2 N2, where N is the number <strong>of</strong> teethand select θ eq = θ1 , thenK eq = K 1 + K 2 (N 1 / N 2 ) 2[N.m/rad](c) coupled torsional and translationalspringsV s = ½ {K x 2 + K t θ 2 } = ½ K eq X eqLet Xeq = X , and since X = R θ , then2K eq = K + K t / R 2[N/m], orLet X eq = θ , then the equivalent torsional spring isKteq = K R 2 + K t [N.m/rad]Note: in (a) thru (c) one <strong>of</strong> the spring ends is connected to ground.MEEN 617 Notes: Handout 1 / © Luis San Andrés 2008 1.4