FE Review Handouts - Sites at Lafayette
FE Review Handouts - Sites at Lafayette
FE Review Handouts - Sites at Lafayette
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
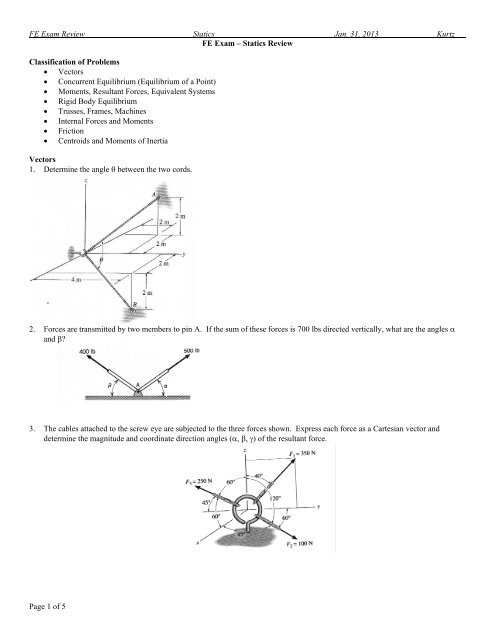
<strong>FE</strong> Exam <strong>Review</strong> St<strong>at</strong>ics Jan. 31, 2013 Kurtz<strong>FE</strong> Exam – St<strong>at</strong>ics <strong>Review</strong>Classific<strong>at</strong>ion of Problems Vectors Concurrent Equilibrium (Equilibrium of a Point) Moments, Resultant Forces, Equivalent Systems Rigid Body Equilibrium Trusses, Frames, Machines Internal Forces and Moments Friction Centroids and Moments of InertiaVectors1. Determine the angle between the two cords.2. Forces are transmitted by two members to pin A. If the sum of these forces is 700 lbs directed vertically, wh<strong>at</strong> are the angles and ?3. The cables <strong>at</strong>tached to the screw eye are subjected to the three forces shown. Express each force as a Cartesian vector anddetermine the magnitude and coordin<strong>at</strong>e direction angles () of the resultant force.Page 1 of 5
<strong>FE</strong> Exam <strong>Review</strong> St<strong>at</strong>ics Jan. 31, 2013 KurtzConcurrent Equilibrium (Equilibrium of a Point)4. Determine the unstretched length of the spring if the block has a mass of 5 kg and rests on a smooth plane5. Determine the force P th<strong>at</strong> must be applied to the cord in order to pull the post out of the ground if the post is removed by a 400-lbvertical force.Moments, Resultant Forces, Equivalent Systems6. Determine the moment of the force about point O.7. Replace the loading shown with an equivalent force and couple <strong>at</strong> point A.Page 2 of 5
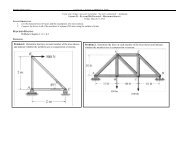
<strong>FE</strong> Exam <strong>Review</strong> St<strong>at</strong>ics Jan. 31, 2013 Kurtz8. Determine the resultant force and specify where it acts on the beam measured from A.Rigid Body Equilibrium9. Determine the tension in the cable and the horizontal and vertical components of reaction <strong>at</strong> pin A.10. Determine the tension in each supporting cable if the uniform pl<strong>at</strong>e weighs 500 lb.Trusses, Frames, Machines11. Determine the force in each member of the truss and st<strong>at</strong>e whether each is in tension or compression12. Determine the force in members BC, CF, and <strong>FE</strong> and st<strong>at</strong>e whether each is in tension or compressionPage 3 of 5
<strong>FE</strong> Exam <strong>Review</strong> St<strong>at</strong>ics Jan. 31, 2013 Kurtz13. Determine the normal force th<strong>at</strong> the 100-lb pl<strong>at</strong>e A exerts on the 30-lb pl<strong>at</strong>e B.Internal Forces and Moments14. Determine the internal normal force, shear force, and moment in the beam <strong>at</strong> B, which is loc<strong>at</strong>ed just to the left of the 800-lb force15. Determine the internal normal force, shear force, and moment in the beam <strong>at</strong> BPage 4 of 5
<strong>FE</strong> Exam <strong>Review</strong> St<strong>at</strong>ics Jan. 31, 2013 KurtzFriction16. Determine the vertical force P needed to rot<strong>at</strong>e the 200-lb spool if the coefficient of st<strong>at</strong>ic friction <strong>at</strong> all contacting surfaces is 0.4.Centroids and Moments of Inertia17. Determine the moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area of the T-beam with respect to the x’ axis passing through the centroidof the cross-section.Page 5 of 5