Scope and Sequence - Douglas County School District
Scope and Sequence - Douglas County School District
Scope and Sequence - Douglas County School District
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
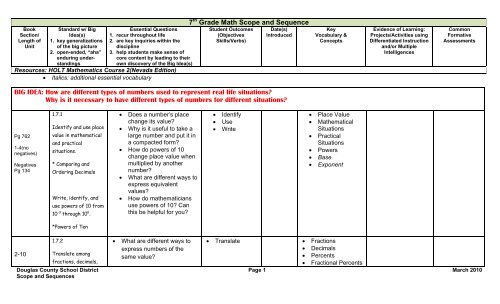
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsBIG IDEA: How are different types of numbers used to represent real life situations?Why is it necessary to have different types of numbers for different situations?Pg 7621-4(nonegatives)NegativesPg 1341.7.1Identify <strong>and</strong> use placevalue in mathematical<strong>and</strong> practicalsituations.* Comparing <strong>and</strong>Ordering DecimalsWrite, identify, <strong>and</strong>use powers of 10 from10 -3 through 10 6 .• Does a number’s placechange its value?• Why is it useful to take alarge number <strong>and</strong> put it ina compacted form?• How do powers of 10change place value whenmultiplied by anothernumber?• What are different ways toexpress equivalentvalues?• How do mathematiciansuse powers of 10? Canthis be helpful for you?• Identify• Use• Write• Place Value• MathematicalSituations• PracticalSituations• Powers• Base• Exponent*Powers of Ten2-101.7.2Translate among• What are different ways toexpress numbers of thesame value?• Translate • Fractions• Decimals• Percentsfractions, decimals,• Fractional Percents<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 1 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments6-2<strong>and</strong> percents,including fractionalpercents.• Why <strong>and</strong> how can youcalculate your grade/gradepoint average?• Integers*Fractions, Decimals<strong>and</strong> PercentsPg 7622-92-111.7.3Compare <strong>and</strong> order acombination ofrational numbers,including fractions,decimals, percents,<strong>and</strong> integers inmathematical <strong>and</strong>practical situations• What is the importance tohaving order to numbers?• Why do we expressequivalent values in differentways?• If equivalent values can beexpressed differently, whydon’t we just use one way<strong>and</strong> not have to learn therest?• Compare• Order• Simplify• Rational Numbers• Fractions• Decimals• Integers• Percents• Ratios*Comparing <strong>and</strong>Ordering Decimals*Simplifying Fractions<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 2 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments<strong>and</strong> Ratios*Ratios <strong>and</strong> Percent*Fractions, Decimals<strong>and</strong> Percents*Comparing <strong>and</strong>Ordering Fractions*Comparing <strong>and</strong>Ordering Integers2-13-13-71.7.5Identify absolutevalues of integers.*Integers1.7.6Generate a reasonableestimate for acomputation using a• Is the opposite alwayspositive?• How can numbersrepresent oppositesituations?• Can numbers representopposite situations?• When do you useestimation in daily life?• How do you clusternumbers to get a fastcalculation?• Identify• Define• Simplify• Generate• Estimate• Select• Round• Determine• Absolute Value• Integers• Estimate• Computation• Significant digits<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 3 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments6-3Pg 763variety of methods.*Estimating withDecimals*Estimating withFractions*Percent <strong>and</strong>Estimation• Since you can always use acalculator, why bother to doan estimate?• When have you roundednumbers <strong>and</strong> may not evenknow you are doing it?Select <strong>and</strong> round tothe appropriatesignificant digit.*Rounding Decimals*Determine thenumber of significantdigits in a givennumber (must containa decimal point)<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 4 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments3-33-42-22-32-43-83-93-103-116-26-46-51.7.7Calculate withintegers <strong>and</strong> otherrational numbers tosolve mathematical<strong>and</strong> practicalsituations.*Multiplying Decimals*Dividing Decimals*Adding Integers*Subtracting Integers*Multiplying Integers*Dividing Integers*Adding <strong>and</strong>Subtracting Fractions*Adding <strong>and</strong>• Are two negatives alwayspositive?• Do calculations withdecimals, percents, <strong>and</strong>fractions give you thesame results?• How has the order ofoperation change thevalue of the expression?• Why must there be anagreed order for findingthe value of anexpression?• What is the differencebetween <strong>and</strong> expression<strong>and</strong> an equation?• Can a trip be planned(Vacation) without solvingany math problems?• How do you take knownrelationships with numbersto solve for unknownvalues?• What does a mathexpression represent?• Calculate• Solve• Use• Compute• Evaluate• Simplify• Integers• Rational Numbers• Order of Operations• Expressions• One-step Equations• Decimals• Mixed Numbers• Fractions• Percents• Proportions<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 5 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsSubtracting MixedNumbers• What does a mathequation represent?*Multiplying Fractions<strong>and</strong> MixedNumbers*Dividing Fractions<strong>and</strong> MixedNumbers*Percents <strong>and</strong>Fractions*Percents <strong>and</strong>Decimals*Percents GreaterThan 100% <strong>and</strong>Percents Less Than1%<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 6 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments*Percent of a Number*The PercentProportion1-51-71-101-111-12Use order ofoperations to evaluateexpressions <strong>and</strong> solveone-step equations(containing rationalnumbers).*Order of Operations(4-stepproblems)*Variables <strong>and</strong>Expressions,Evaluating<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 7 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsExpressions*Solving Equations1-61.7.8Identify <strong>and</strong> apply thedistributive,commutative, <strong>and</strong>associative propertiesof rational numbers tosolve problems.• How does regrouping getyou the same answer?• How do math propertiesallow us to solve problemsusing mental math?• Identify• Apply• Simplify• DistributiveProperty• CommutativeProperty• AssociativeProperty• Rational Numbers*Properties 1-6BIG IDEA: How do you represent everyday experiences using algebraic expressions, patterns, <strong>and</strong> functions?4-42.7.1Use <strong>and</strong> create tables,charts, <strong>and</strong> graphs toextend a pattern inorder to describe a• What are somemathematical techniquesto predict data in real life?• Use• Create• Extend• Describe• Predict• Tables• Charts• Graphs• Pattern• Linear rule• Integer Values• Functions<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 8 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments4-5linear rule, includinginteger values.• Equations• Linear function4-6*Making Predictions*Functions <strong>and</strong>Equations1-91-102-52.7.2Evaluate formulas <strong>and</strong>algebraic expressionsfor given integer values.*Variables <strong>and</strong>ExpressionsEvaluating Expressions• What are the goals ofsolving equations?• How can expressionshave different values?• Does the inverse alwaysequal 1?• Is there an output (result)for every input?• Evaluate• Solve• Graphicallyrepresent• Formulas• AlgebraicExpressions• Integer values• Equations• Inequalities• Variable• Integer solutions• Two-stepequations*Solving Equations1-111-1212-1Solve <strong>and</strong> graphicallyrepresent equations <strong>and</strong><strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 9 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsinequalities in onevariable with integersolutions.12-412-512-612-7*Solving Equations*Solving Addition <strong>and</strong>SubtractionEquations*Solving MultiplicationEquations*Solving 2-StepEquations*Inequalities1-92.7.3Simplify algebraicexpressions bycombining like terms.• What makes things alike? • Simplify• Combine liketerms• Algebraicexpressions• Like term• Variableexpressions<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 10 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments*Simplifying VariableExpressions4-24-44-54-62.7.4Generate <strong>and</strong> graph aset of ordered pairs torepresent a linearequation.Why is there an output (result) forevery input?• Generate• Graph• Represent• Ordered pairs• Linear equations• Functions• Equations*Functions <strong>and</strong>Equations1-81-102.7.5Identify linearequations <strong>and</strong>inequalities.*Writing Expressions<strong>and</strong> Equations• How do signs affectresults?• Identify• Model• Solve• Writingexpressions<strong>and</strong> equations• Linear equations• Inequalities• Expression• Equation• Function*Inequalities<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 11 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsBIG IDEA: How is geometry used to represent the physical world?8-58-68-74.7.1Identify, classify,compare, <strong>and</strong> drawregular <strong>and</strong> irregularpolygons.*Polygons• Why do we have specificnames for geometricshapes?• How did the names ofgeometric shapes come tobe?• How many different,closed figures with straightlines can be made <strong>and</strong> putin groups?• Identify• Classify• Compare• Draw• Find• Verify• Regularpolygons• Measures ofinterior angles ofpolygons• Triangles• Quadrilaterals8-8Find <strong>and</strong> verify the sumof the measures ofinterior angles oftriangles <strong>and</strong>quadrilaterals.*Angles of a Polygon5-94.7.2Make scale drawingsusing ratios <strong>and</strong>• How are models similar toreal things?• What makes a smallpicture of a car look like a• Make • Scale drawings• Ratios• Proportions<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 15 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsExtension8-108-11proportions.*Scale Drawings4.7.3Demonstratetranslation, reflection,<strong>and</strong> rotation usingcoordinate geometry<strong>and</strong> models.Describe the locationof the original figure<strong>and</strong> its transformationon a coordinate plane.real car?• What do you do to drawsomething like a large caron a small piece of paper?• How can you change thelocation <strong>and</strong> orientation onobjects <strong>and</strong> show thechange on a grid?• Demonstrate• Describe• Transform• Translation• Reflection• Rotation• Coordinategeometry <strong>and</strong>models• Coordinate plane• Transformation• Original <strong>and</strong>transformedfigures*GraphingTransformations*Translations*Reflections<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 16 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsH<strong>and</strong>s onLab 10-14.7.4Make a model of a 3-Dfigure from a 2-Ddrawing.• How do you make adrawing look 3-D?• Make a model • 3-D Figure• 2-D Drawing• Nets• Surface Area*Drawing Three-Dimensional figuresMake a 2-D drawing ofa 3-D figure.*Nets <strong>and</strong> SurfaceArea5-34.7.5Determine slope of aline, midpoint of asegment, <strong>and</strong> thehorizontal <strong>and</strong> verticaldistance between twopoints using coordinategeometry.• What is steepness?• What is the opposite ofsteepness?• How do you describehalfway?• Determine • Slope of a line• Midpoint of asegment• Horizontaldistance• Vertical distance• Points• CoordinateGeometry<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 17 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsH<strong>and</strong>s onLab 8-38-54.7.6Describe the geometricrelationships of parallellines, perpendicularlines, triangles,quadrilaterals, <strong>and</strong>bisectors.*Angles*Perpendicular ParallelLines• In what ways can a treeprovide examples of thegeometric concepts ofparallel lines,perpendicular lines, <strong>and</strong>triangles?• How does <strong>and</strong> arrowrepresent a bisector?• Describe • Geometricrelationships• Parallel lines• Perpendicularlines• Triangles• Quadrilaterals• Bisectors• Polygons*PolygonsH<strong>and</strong>s onLab 9-89-84.7.7Model the PythagoreanTheorem <strong>and</strong> solve forthe hypotenuse.*Pythagorean Theorem*The PythagoreanTheorem• Who <strong>and</strong> why are peopleusing <strong>and</strong> being affectedby the PythagoreanTheorem, whether theyknow it or not?• What Greekphilosopher/mathematician is famous for workingwith right triangles?• Model• Solve• PythagoreanTheorem• Hypotenuse<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 18 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsH<strong>and</strong>s onLab 8-38-34.7.8Construct <strong>and</strong> identifycongruent angles,parallel lines, <strong>and</strong>perpendicular lines.• What are examplesaround theschool/neighborhood thatcan be named with mathterms <strong>and</strong> put in groups?• Construct• Identify• Measure• Congruentangles• Parallel lines• Perpendicularlines*Measuring Angles*Perpendicular <strong>and</strong>Parallel LinesCh. 14.7.9Make <strong>and</strong> testconjectures to explainobserved mathematicalrelationships <strong>and</strong> todevelop logicalarguments to justifyconclusions.• Can you make statementsabout a person’s healthwho only eats junk food,watches TV, plays videogames, <strong>and</strong> never goes tobed before midnight?• How do you use facts tocreate a logical argument<strong>and</strong> come to a reasonableconclusion?• Make• Test• Explain• Developlogicalarguments• Justify• Conjectures• Mathematicalrelationships• Logicalarguments• Conclusions<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 19 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessmentsBIG IDEA: How does data represent real life situations?7-17-105.7.1Formulate questionsthat guide thecollection of data.Organize, display, <strong>and</strong>read data using theappropriate graphicalrepresentations (with<strong>and</strong> w/o technology).• What questions would youask if you want to knowthe different activities ofyour classmate <strong>and</strong> thenorganize the data?• Formulate• Organize• Display• Read• Data• Graphicalrepresentations• Technology• Frequency table• Line Plots• Stem <strong>and</strong> LeafPlot• Misleadingstatistics*Frequency Tables*Making Predictions*Line Plots*Stem-<strong>and</strong>-Leaf Plots*Misleading Statistics<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 20 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments4-37-25.7.2Interpret graphicalrepresentations ofdata to describepatterns, trends <strong>and</strong>data distribution*Making Predictions• How can you look at avariety of graph types <strong>and</strong>make predictions/• Interpret• Describepatterns <strong>and</strong>trends• Predict• Graphicalrepresentations• Patterns• Trends• Data distribution• Mean• Median• Mode*Mean, Median <strong>and</strong>Mode7-105.7.3Analyze the effect ofchange of scale willhave on statisticalcharts <strong>and</strong> graphs.*Misleading Statistics• Will using different scaleson graphs representingthe same data lend todifferent conclusions?• Analyze• Describe• Change of scale• Statistical charts• Statistical graphs• Misleadingstatistics5.7.4Find the number of• How many ways can thestudents in this class lineup?• Find • Permutations• Event<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 21 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments11-7permutations possiblefor an event inmathematical <strong>and</strong>practical situations.*Permutations11-111-211-411-35.7.5Find the theoreticalprobability of an eventusing differentcounting methodsincluding sample spaces<strong>and</strong> compare thatprobability withexperimental results.• Do you want to know thechance of success beforeyou do something?• How can chance bedetermined?• If everyone in your classtossed a coin 100 times,will everyone have thesame number of heads astails?• Find• Compare• Represent• Theoreticalprobability• Event• Countingmethods• Sample spaces• Experimentalresults• Tree diagrams• CountingprincipleRepresent theprobability of an eventas a number between 0<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 22 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s
BookSection/Length ofUnitSt<strong>and</strong>ard w/ BigIdea(s)1. key generalizationsof the big picture2. open-ended, “aha”enduring underst<strong>and</strong>ingsEssential Questions1. recur throughout life2. are key inquiries within thediscipline3. help students make sense ofcore content by leading to theirown discovery of the Big Idea(s)Resources: HOLT Mathematics Course 2(Nevada Edition)• Italics: additional essential vocabulary7 th Grade Math <strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>Student Outcomes(ObjectivesSkills/Verbs)Date(s)IntroducedKeyVocabulary &ConceptsEvidence of Learning:Projects/Activities usingDifferentiated Instruction<strong>and</strong>/or MultipleIntelligencesCommonFormativeAssessments<strong>and</strong> 1.*Theoretical <strong>and</strong>ExperimentalProbability*Tree Diagrams*The Counting Principle7-105.7.6Interpolate <strong>and</strong>extrapolate from datato make predictions fora given set of data.*Misleading Statistics• What are reasons tocollect data?• What can be done withdata when you have it?• What ways can data beused or organized?• How can data be used togive the wrong idea?• Interpolate• Extrapolate• Makepredictions• Data• Prediction• Set of data• Misleadingstatistics<strong>Douglas</strong> <strong>County</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>District</strong> Page 23 March 2010<strong>Scope</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sequence</strong>s