Bulk Nanostructured Materials - Foundation Coalition
Bulk Nanostructured Materials - Foundation Coalition
Bulk Nanostructured Materials - Foundation Coalition
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
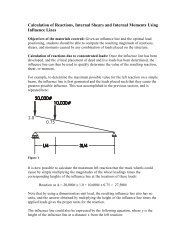
MEEN 489-500 NanoscaleIssues in ManufacturingEqual Channel AngularExtrusion (ECAE)Lecture 1 : <strong>Bulk</strong><strong>Nanostructured</strong> <strong>Materials</strong>1-ECAE 1
<strong>Bulk</strong> <strong>Nanostructured</strong><strong>Materials</strong>Theme 2: Fabrication of bulk materialsthrough severe plastic deformation andnanoparticle consolidationFabrication methods for structural materialsWhynano? ? Evidence for ultrahigh strength and ductilitywhen building blocks are in the nano range.Building blocks? Grains, layers, particles, etc.How do we make building blocks in nano range?How do we connect the building blocks?<strong>Bulk</strong>? In cm rangeProperties: bullet proof aluminum?2-ECAE 1
Theme 1 vs. Theme 2Theme 1 - Lithography: Making engineeringparts and devices smallerTheme 2 is different: Microstructural design forproperties, making building blocks submicronscale.What kind of properties we are interested in?Structural:Magnetic:Electrical (ferroelectrics)(thermoelectrics)grain size and texture isimportant3-ECAE 1
Why is texture and grain sizeimportant for functional properties?Grain size: might be asolution for brittlenessin thermoelectrics andferroelectricsMagnetizationApplied Magnetic FieldTypical thermoelectric coolerfor electronics6-ECAE 1
What is the mechanism for grainboundary strengthening innanocrystalline materials?Hall-Petch Relation:Work-hardening:τσy= σ 0+= τ 0k yd+ αGbρ7-ECAE 1
What is the mechanism for grainboundary strengthening innanocrystalline materials?Two-phase modelGrain-boundary sliding model8-ECAE 1
Top Down or Bottom Up ?Both work tomake bulknanocrystallinematerials Decreasing thegrain size ofalready bulkmaterials:Severe PlasticDeformation(SPD)Consolidationof nanograins(particles).9-ECAE 1
Top down approach to bulknanocrystalline materials fabricationMain principles of Severe PlasticDeformation (SPD):Increase dislocation density by heavilydeforming materials (uniformity! Crosssection!),form dislocation walls,transform dislocation walls into grainboundaries (high angle boundaries)Is there any intrinsic limitation?10-ECAE 1
Severe Plastic Deformation(SPD)11-ECAE 1
Why SPD?Think about materials that must be“heavily” mixed during processingConcreteBreadSamurai Sword Steel (Damascus Steel)Piano WireSuperalloyComponents in Jet EnginesSuperconductorsSheet Stock for Auto BodiesSheet Stock for Beer Cans12-ECAE 1
Why SPD?Why do this mixing?To Refine/Homogenize the MicrostructureTo Strengthen the MaterialTo Enhance the PropertiesExamplesWork HardeningGrain RefinementDevelopment of Special MicrostructuresDevelopment of Special Textures13-ECAE 1
SPD provides increase in both strengthand ductilityTrue Stress, MPa600500400300200<strong>Bulk</strong> Cu 101Tension Experiments at RTTrue stress versus true strainECAE at RT, 1AECAE at RT, 2CECAE at RT, 4CECAE at RT, 8AECAE at RT, 8EECAE at RT, 16EAnnealed Cu 101(grain size: 75µm)As received10000102030True Strain, %405014-ECAE 1
SPD provides increase in both strengthand ductility15-ECAE 1
Unconventional SPDTechniquesEqual Channel AngularExtrusionHigh Pressure TorsionAccumulative RollBondingRepetitive Corrugationand Straightening16-ECAE 1
Conventional Methods ofSPDProcess CharacteristicsLoad Change in Geometry Uniformity of Plastic StrainRolling V. High Decrease in thickness Only after SPDExtrusion High Decrease in cross- Can be with special diesectional area designDrawing Low Decrease in cross- Higher at surfacesectional areaForging V. High Usually Usually not17-ECAE 1
Bottom Up ApproachNanoparticle Consolidation (Problems withnanopowders?)Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) (good for ceramics)Cold isostatic pressing (CIP) + Sintering (good forceramics)Conventional Extrusion ConsolidationEqual Channel Angular Extrusion Consolidation (scaleup is easier)18-ECAE 1
Nanoparticle FabricationMethodsVaporization methodsFree jet expansionmethodLaser vaporizationSpark erosionElectro explosion ofwiresChemical vapordepositionetc.Mechanical Attrition19-ECAE 1
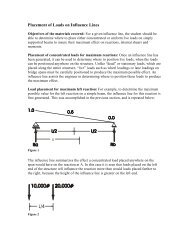
Equal Channel Angular Extrusion(ECAE)Material PropertiesImproved strength, ductility and toughnessSuperplasticityEngineered microstructuresEngineered textures<strong>Materials</strong> ExtrudedAlloysPolymersIntermetalliccompoundsComposites20-ECAE 1
Description of ECAEDie InletDieChamberChannelBilletShearZone(P)PunchDie Exit ChannelDieAngleConditions1. Inlet and outletchannels have nearlythe same dimensions2. Channel intersection isabrupt3. Lubrication and othermeans are used toreduce friction21-ECAE 1