Finite Element Method Magnetics
Finite Element Method Magnetics
Finite Element Method Magnetics
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
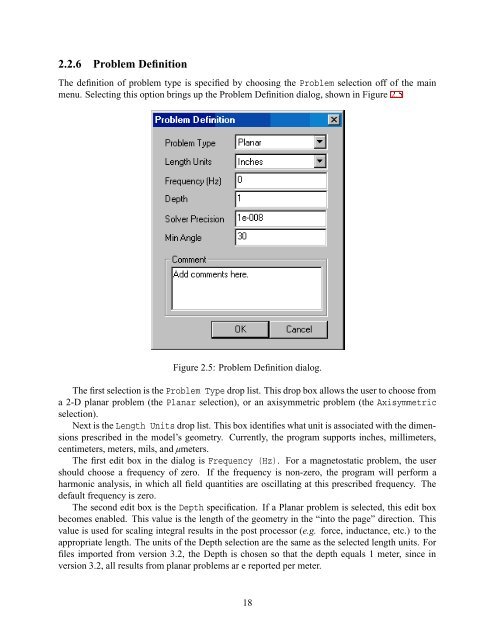
2.2.6 Problem DefinitionThe definition of problem type is specified by choosing the Problem selection off of the mainmenu. Selecting this option brings up the Problem Definition dialog, shown in Figure 2.5Figure 2.5: Problem Definition dialog.The first selection is the Problem Type drop list. This drop box allows the user to choose froma 2-D planar problem (the Planar selection), or an axisymmetric problem (the Axisymmetricselection).Next is the Length Units drop list. This box identifies what unit is associated with the dimensionsprescribed in the model’s geometry. Currently, the program supports inches, millimeters,centimeters, meters, mils, and µmeters.The first edit box in the dialog is Frequency (Hz). For a magnetostatic problem, the usershould choose a frequency of zero. If the frequency is non-zero, the program will perform aharmonic analysis, in which all field quantities are oscillating at this prescribed frequency. Thedefault frequency is zero.The second edit box is the Depth specification. If a Planar problem is selected, this edit boxbecomes enabled. This value is the length of the geometry in the “into the page” direction. Thisvalue is used for scaling integral results in the post processor (e.g. force, inductance, etc.) to theappropriate length. The units of the Depth selection are the same as the selected length units. Forfiles imported from version 3.2, the Depth is chosen so that the depth equals 1 meter, since inversion 3.2, all results from planar problems ar e reported per meter.18