Design of arsenic removal plant by coagulation, sedimentation
Design of arsenic removal plant by coagulation, sedimentation
Design of arsenic removal plant by coagulation, sedimentation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
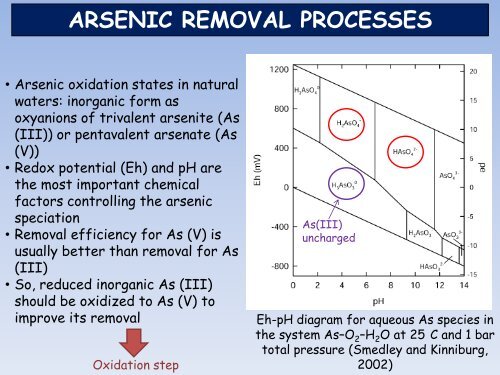
ARSENIC REMOVAL PROCESSES<br />
• Arsenic oxidation states in natural<br />
waters: inorganic form as<br />
oxyanions <strong>of</strong> trivalent arsenite (As<br />
(III)) or pentavalent arsenate (As<br />
(V))<br />
• Redox potential (Eh) and pH are<br />
the most important chemical<br />
factors controlling the <strong>arsenic</strong><br />
speciation<br />
• Removal efficiency for As (V) is<br />
usually better than <strong>removal</strong> for As<br />
(III)<br />
• So, reduced inorganic As (III)<br />
should be oxidized to As (V) to<br />
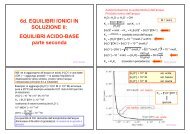
improve its <strong>removal</strong> Eh-pH diagram for aqueous As species in<br />
the system As–O 2–H 2O at 25 C and 1 bar<br />
Oxidation step<br />
As(III)<br />
uncharged<br />
total pressure (Smedley and Kinniburg,<br />
2002)