Essential Revision Notes for MRCP Third Edition - PasTest
Essential Revision Notes for MRCP Third Edition - PasTest
Essential Revision Notes for MRCP Third Edition - PasTest
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
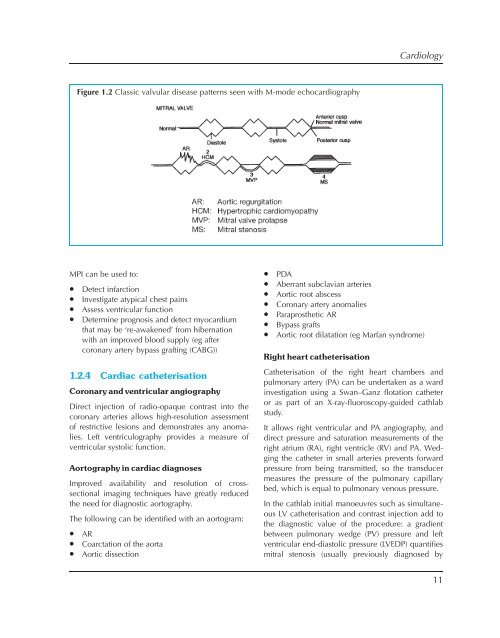
CardiologyFigure 1.2 Classic valvular disease patterns seen with M-mode echocardiographyMPI can be used to:• Detect infarction• Investigate atypical chest pains• Assess ventricular function• Determine prognosis and detect myocardiumthat may be ‘re-awakened’ from hibernationwith an improved blood supply (eg aftercoronary artery bypass grafting (CABG))1.2.4 Cardiac catheterisationCoronary and ventricular angiographyDirect injection of radio-opaque contrast into thecoronary arteries allows high-resolution assessmentof restrictive lesions and demonstrates any anomalies.Left ventriculography provides a measure ofventricular systolic function.Aortography in cardiac diagnosesImproved availability and resolution of crosssectionalimaging techniques have greatly reducedthe need <strong>for</strong> diagnostic aortography.The following can be identified with an aortogram:• AR• Coarctation of the aorta• Aortic dissection• PDA• Aberrant subclavian arteries• Aortic root abscess• Coronary artery anomalies• Paraprosthetic AR• Bypass grafts• Aortic root dilatation (eg Marfan syndrome)Right heart catheterisationCatheterisation of the right heart chambers andpulmonary artery (PA) can be undertaken as a wardinvestigation using a Swan–Ganz flotation catheteror as part of an X-ray-fluoroscopy-guided cathlabstudy.It allows right ventricular and PA angiography, anddirect pressure and saturation measurements of theright atrium (RA), right ventricle (RV) and PA. Wedgingthe catheter in small arteries prevents <strong>for</strong>wardpressure from being transmitted, so the transducermeasures the pressure of the pulmonary capillarybed, which is equal to pulmonary venous pressure.In the cathlab initial manoeuvres such as simultaneousLV catheterisation and contrast injection add tothe diagnostic value of the procedure: a gradientbetween pulmonary wedge (PV) pressure and leftventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) quantifiesmitral stenosis (usually previously diagnosed by11