Medical Management Guide, 2009, Version 3.0 - Tricare
Medical Management Guide, 2009, Version 3.0 - Tricare
Medical Management Guide, 2009, Version 3.0 - Tricare
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
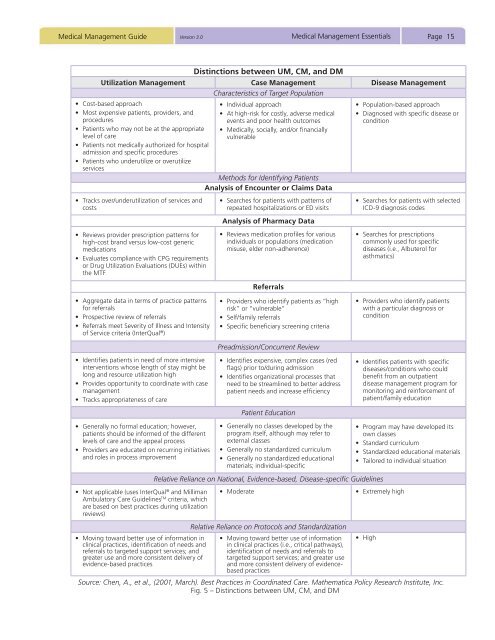
<strong>Medical</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> <strong>Version</strong> <strong>3.0</strong><strong>Medical</strong> <strong>Management</strong> EssentialsPage 15Distinctions between UM, CM, and DMUtilization <strong>Management</strong> Case <strong>Management</strong> Disease <strong>Management</strong>Characteristics of Target Population• Cost-based approach• Most expensive patients, providers, andprocedures• Patients who may not be at the appropriatelevel of care• Patients not medically authorized for hospitaladmission and specific procedures• Patients who underutilize or overutilizeservices• Tracks over/underutilization of services andcosts• Reviews provider prescription patterns forhigh-cost brand versus low-cost genericmedications• Evaluates compliance with CPG requirementsor Drug Utilization Evaluations (DUEs) withinthe MTF• Individual approach• At high-risk for costly, adverse medicalevents and poor health outcomes• <strong>Medical</strong>ly, socially, and/or financiallyvulnerableMethods for Identifying PatientsAnalysis of Encounter or Claims Data• Searches for patients with patterns ofrepeated hospitalizations or ED visitsAnalysis of Pharmacy Data• Reviews medication profiles for variousindividuals or populations (medicationmisuse, elder non-adherence)Referrals• Population-based approach• Diagnosed with specific disease orcondition• Searches for patients with selectedICD-9 diagnosis codes• Searches for prescriptionscommonly used for specificdiseases (i.e., Albuterol forasthmatics)• Aggregate data in terms of practice patternsfor referrals• Prospective review of referrals• Referrals meet Severity of Illness and Intensityof Service criteria (InterQual ® )• Identifies patients in need of more intensiveinterventions whose length of stay might belong and resource utilization high• Provides opportunity to coordinate with casemanagement• Tracks appropriateness of care• Providers who identify patients as “highrisk” or “vulnerable”• Self/family referrals• Specific beneficiary screening criteriaPreadmission/Concurrent Review• Identifies expensive, complex cases (redflags) prior to/during admission• Identifies organizational processes thatneed to be streamlined to better addresspatient needs and increase efficiencyPatient Education• Providers who identify patientswith a particular diagnosis orcondition• Identifies patients with specificdiseases/conditions who couldbenefit from an outpatientdisease management program formonitoring and reinforcement ofpatient/family education• Generally no formal education; however,patients should be informed of the differentlevels of care and the appeal process• Providers are educated on recurring initiativesand roles in process improvement• Not applicable (uses InterQual ® and MillimanAmbulatory Care <strong>Guide</strong>lines TM criteria, whichare based on best practices during utilizationreviews)• Moving toward better use of information inclinical practices, identification of needs andreferrals to targeted support services; andgreater use and more consistent delivery ofevidence-based practices• Generally no classes developed by theprogram itself, although may refer toexternal classes• Generally no standardized curriculum• Generally no standardized educationalmaterials; individual-specificRelative Reliance on National, Evidence-based, Disease-specific <strong>Guide</strong>lines• ModerateRelative Reliance on Protocols and Standardization• Moving toward better use of informationin clinical practices (i.e., critical pathways),identification of needs and referrals totargeted support services; and greater useand more consistent delivery of evidencebasedpractices• Program may have developed itsown classes• Standard curriculum• Standardized educational materials• Tailored to individual situation• Extremely high• HighSource: Chen, A., et al., (2001, March). Best Practices in Coordinated Care. Mathematica Policy Research Institute, Inc.Fig. 5 – Distinctions between UM, CM, and DM