Medical Management Guide, 2009, Version 3.0 - Tricare
Medical Management Guide, 2009, Version 3.0 - Tricare
Medical Management Guide, 2009, Version 3.0 - Tricare
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
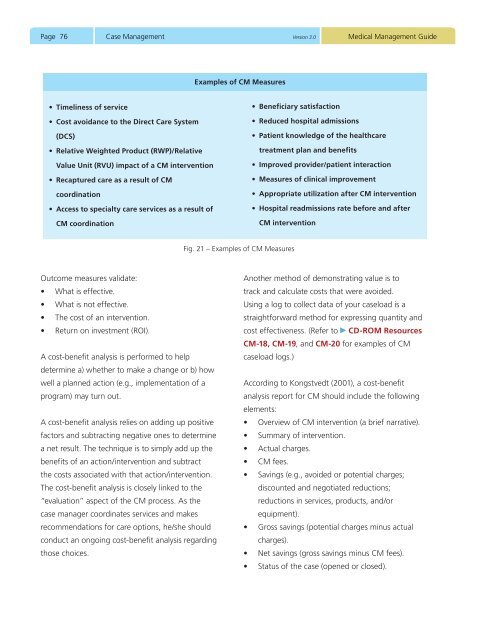
Page 76Case <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Version</strong> <strong>3.0</strong><strong>Medical</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Guide</strong>Examples of CM Measures• Timeliness of service• Cost avoidance to the Direct Care System(DCS)• Relative Weighted Product (RWP)/RelativeValue Unit (RVU) impact of a CM intervention• Recaptured care as a result of CMcoordination• Access to specialty care services as a result ofCM coordination• Beneficiary satisfaction• Reduced hospital admissions• Patient knowledge of the healthcaretreatment plan and benefits• Improved provider/patient interaction• Measures of clinical improvement• Appropriate utilization after CM intervention• Hospital readmissions rate before and afterCM interventionFig. 21 – Examples of CM MeasuresOutcome measures validate:• What is effective.• What is not effective.• The cost of an intervention.• Return on investment (ROI).A cost-benefit analysis is performed to helpdetermine a) whether to make a change or b) howwell a planned action (e.g., implementation of aprogram) may turn out.A cost-benefit analysis relies on adding up positivefactors and subtracting negative ones to determinea net result. The technique is to simply add up thebenefits of an action/intervention and subtractthe costs associated with that action/intervention.The cost-benefit analysis is closely linked to the“evaluation” aspect of the CM process. As thecase manager coordinates services and makesrecommendations for care options, he/she shouldconduct an ongoing cost-benefit analysis regardingthose choices.Another method of demonstrating value is totrack and calculate costs that were avoided.Using a log to collect data of your caseload is astraightforward method for expressing quantity andcost effectiveness. (Refer to CD-ROM ResourcesCM-18, CM-19, and CM-20 for examples of CMcaseload logs.)According to Kongstvedt (2001), a cost-benefitanalysis report for CM should include the followingelements:• Overview of CM intervention (a brief narrative).• Summary of intervention.• Actual charges.• CM fees.• Savings (e.g., avoided or potential charges;discounted and negotiated reductions;reductions in services, products, and/orequipment).• Gross savings (potential charges minus actualcharges).• Net savings (gross savings minus CM fees).• Status of the case (opened or closed).