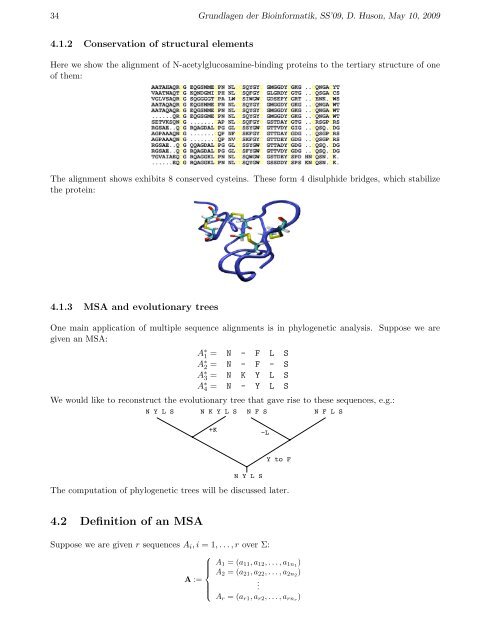
34 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS’09, D. Huson, May 10, 2009<strong>4.1</strong>.2 Conservation of structural elementsHere we show the <strong>alignment</strong> of N-acetylglucosamine-binding proteins to the tertiary structure of oneof them:The <strong>alignment</strong> shows exhibits 8 conserved cysteins. These form 4 disulphide bridges, which stabilizethe protein:<strong>4.1</strong>.3 MSA and evolutionary treesOne main application of multiple <strong>sequence</strong> <strong>alignment</strong>s is in phylogenetic analysis. Suppose we aregiven an MSA:A ∗ 1 = N - F L SA ∗ 2 = N - F - SA ∗ 3 = N K Y L SA ∗ 4 = N - Y L SWe would like to reconstruct the evolutionary tree that gave rise to these <strong>sequence</strong>s, e.g.:N Y L S N K Y L S N F S N F L S+K−LN Y L SY to FThe computation of phylogenetic trees will be discussed later.4.2 Definition of an MSASuppose we are given r <strong>sequence</strong>s A i , i = 1, . . . , r over Σ:⎧A 1 = (a 11 , a 12 , . . . , a 1n1 )⎪⎨ A 2 = (a 21 , a 22 , . . . , a 2n2 )A :=.⎪⎩A r = (a r1 , a r2 , . . . , a rnr )
Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS’09, D. Huson, May 10, 2009 35Definition 4.2.1 (MSA) A multiple <strong>sequence</strong> <strong>alignment</strong> (MSA) of A is obtained by inserting gaps(’-’) into the original <strong>sequence</strong>s such that all resulting <strong>sequence</strong>s A ∗ i have equal length L ≥ max{n i |i = 1, . . . , r}, A ∗ i = A i after removal of all gaps from A ∗ i , and no column consists of gaps only.Example:A = {apple, paper, pepper}⎧⎫⎨ - a p p l e - ⎬A∗ = p a p - - e r⎩⎭p e p p - e r⎧⎪⎨A ∗ :=⎪⎩A ∗ 1 = (a ∗ 11, a ∗ 12, . . . , a ∗ 1L )A ∗ 2 = (a ∗ 21, a ∗ 22, . . . , a ∗ 2L ).A ∗ r = (a ∗ r1, a ∗ r2, . . . , a ∗ rL ),4.3 Scoring an MSAIn the case of a linear gap penalty, if we assume independence of the different columns of an MSA,then the score α(A ∗ ) of an MSA A ∗ can be defined as a sum of column scores:α(A ∗ ) :=L∑s(a ∗ 1i, a ∗ 2i, . . . , a ∗ ri).i=1Here we assume that s(a ∗ 1i , a∗ 2i , . . . , a∗ ri ) is a function that returns a score for every combination of rsymbols (including the gap symbol).For pairwise <strong>alignment</strong>s there are three types of columns, a match, or a blank in either of the two<strong>sequence</strong>s. The following table shows the 7 possibilities for three <strong>sequence</strong>s:a 1i − a 1i a 1i − − a 1ia 2j a 2j − a 2j − a 2j −a 3k a 3k a 3k − a 3k − −For r <strong>sequence</strong>s, the number of different column types iswhere i is the number of gaps.∑r−1( r= 2i)r − 1i=04.3.1 The sum-of-pairs (SP) scoreHow to define the score s? For two protein <strong>sequence</strong>s, s is usually given by a BLOSUM or PAMmatrix. For more than two <strong>sequence</strong>s, providing such a matrix is not practical, as the number ofpossible combinations is too large.Given an MSA A ∗ , consider two <strong>sequence</strong>s A ∗ p and A ∗ q in the <strong>alignment</strong>. For two aligned symbols uand v we define:⎧⎨ match score for u and v, if u and v are residues,s(u, v) :=−dif either u or v is a gap, or⎩0 if both u and v are gaps.