thermal stress analysis using finite element method in area
thermal stress analysis using finite element method in area
thermal stress analysis using finite element method in area
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
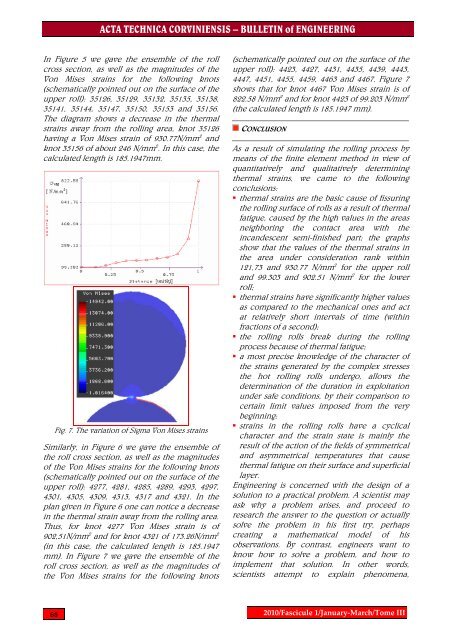
ACTA TECHNICA CORVINIENSIS – BULLETIN of ENGINEERINGIn Figure 5 we gave the ensemble of the rollcross section, as well as the magnitudes of theVon Mises stra<strong>in</strong>s for the follow<strong>in</strong>g knots(schematically po<strong>in</strong>ted out on the surface of theupper roll): 35126, 35129, 35132, 35135, 35138,35141, 35144, 35147, 35150, 35153 and 35156.The diagram shows a decrease <strong>in</strong> the <strong>thermal</strong>stra<strong>in</strong>s away from the roll<strong>in</strong>g <strong>area</strong>, knot 35126hav<strong>in</strong>g a Von Mises stra<strong>in</strong> of 930.77N/mm 2 andknot 35156 of about 246 N/mm 2 . In this case, thecalculated length is 185.1947mm.Fig. 7. The variation of Sigma Von Mises stra<strong>in</strong>sSimilarly, <strong>in</strong> Figure 6 we gave the ensemble ofthe roll cross section, as well as the magnitudesof the Von Mises stra<strong>in</strong>s for the follow<strong>in</strong>g knots(schematically po<strong>in</strong>ted out on the surface of theupper roll): 4277, 4281, 4285, 4289, 4293, 4297,4301, 4305, 4309, 4313, 4317 and 4321. In theplan given <strong>in</strong> Figure 6 one can notice a decrease<strong>in</strong> the <strong>thermal</strong> stra<strong>in</strong> away from the roll<strong>in</strong>g <strong>area</strong>.Thus, for knot 4277 Von Mises stra<strong>in</strong> is of902,51N/mm 2 and for knot 4321 of 173.26N/mm 2(<strong>in</strong> this case, the calculated length is 185.1947mm). In Figure 7 we gave the ensemble of theroll cross section, as well as the magnitudes ofthe Von Mises stra<strong>in</strong>s for the follow<strong>in</strong>g knots(schematically po<strong>in</strong>ted out on the surface of theupper roll): 4423, 4427, 4431, 4435, 4439, 4443,4447, 4451, 4455, 4459, 4463 and 4467. Figure 7shows that for knot 4467 Von Mises stra<strong>in</strong> is of822.58 N/mm 2 and for knot 4423 of 99.203 N/mm 2(the calculated length is 185.1947 mm).CONCLUSIONAs a result of simulat<strong>in</strong>g the roll<strong>in</strong>g process bymeans of the <strong>f<strong>in</strong>ite</strong> <strong>element</strong> <strong>method</strong> <strong>in</strong> view ofquantitatively and qualitatively determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<strong>thermal</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s, we came to the follow<strong>in</strong>gconclusions:• <strong>thermal</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s are the basic cause of fissur<strong>in</strong>gthe roll<strong>in</strong>g surface of rolls as a result of <strong>thermal</strong>fatigue, caused by the high values <strong>in</strong> the <strong>area</strong>sneighbor<strong>in</strong>g the contact <strong>area</strong> with the<strong>in</strong>candescent semi-f<strong>in</strong>ished part; the graphsshow that the values of the <strong>thermal</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong>the <strong>area</strong> under consideration rank with<strong>in</strong>121,73 and 930.77 N/mm 2 for the upper rolland 99.303 and 902.51 N/mm 2 for the lowerroll;• <strong>thermal</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s have significantly higher valuesas compared to the mechanical ones and actat relatively short <strong>in</strong>tervals of time (with<strong>in</strong>fractions of a second);• the roll<strong>in</strong>g rolls break dur<strong>in</strong>g the roll<strong>in</strong>gprocess because of <strong>thermal</strong> fatigue;• a most precise knowledge of the character ofthe stra<strong>in</strong>s generated by the complex <strong>stress</strong>esthe hot roll<strong>in</strong>g rolls undergo, allows thedeterm<strong>in</strong>ation of the duration <strong>in</strong> exploitationunder safe conditions, by their comparison tocerta<strong>in</strong> limit values imposed from the verybeg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g;• stra<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> the roll<strong>in</strong>g rolls have a cyclicalcharacter and the stra<strong>in</strong> state is ma<strong>in</strong>ly theresult of the action of the fields of symmetricaland asymmetrical temperatures that cause<strong>thermal</strong> fatigue on their surface and superficiallayer.Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g is concerned with the design of asolution to a practical problem. A scientist mayask why a problem arises, and proceed toresearch the answer to the question or actuallysolve the problem <strong>in</strong> his first try, perhapscreat<strong>in</strong>g a mathematical model of hisobservations. By contrast, eng<strong>in</strong>eers want toknow how to solve a problem, and how toimplement that solution. In other words,scientists attempt to expla<strong>in</strong> phenomena,682010/Fascicule 1/January‐March/Tome III