Chapter 11.pdf
Chapter 11.pdf
Chapter 11.pdf
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
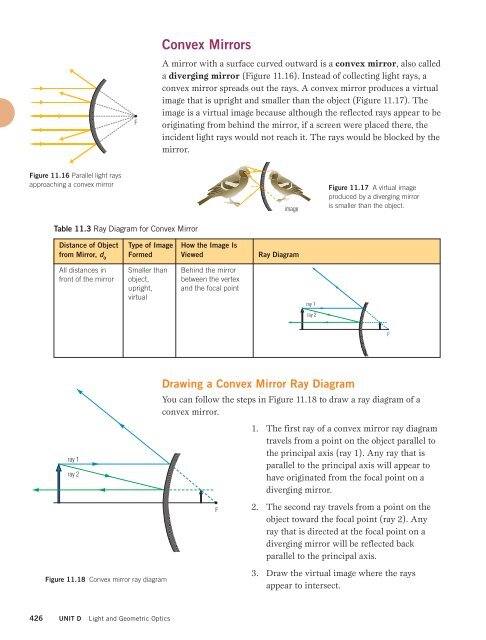
FConvex MirrorsA mirror with a surface curved outward is a convex mirror, also calleda diverging mirror (Figure 11.16). Instead of collecting light rays, aconvex mirror spreads out the rays. A convex mirror produces a virtualimage that is upright and smaller than the object (Figure 11.17). Theimage is a virtual image because although the reflected rays appear to beoriginating from behind the mirror, if a screen were placed there, theincident light rays would not reach it. The rays would be blocked by themirror.Figure 11.16 Parallel light raysapproaching a convex mirrorimageFigure 11.17 A virtual imageproduced by a diverging mirroris smaller than the object.Table 11.3 Ray Diagram for Convex MirrorDistance of Objectfrom Mirror, d oType of ImageFormedHow the Image IsViewedRay DiagramAll distances infront of the mirrorSmaller thanobject,upright,virtualBehind the mirrorbetween the vertexand the focal pointray 1ray 2Fray 1ray 2Figure 11.18 Convex mirror ray diagramDrawing a Convex Mirror Ray DiagramYou can follow the steps in Figure 11.18 to draw a ray diagram of aconvex mirror.F1. The first ray of a convex mirror ray diagramtravels from a point on the object parallel tothe principal axis (ray 1). Any ray that isparallel to the principal axis will appear tohave originated from the focal point on adiverging mirror.2. The second ray travels from a point on theobject toward the focal point (ray 2). Anyray that is directed at the focal point on adiverging mirror will be reflected backparallel to the principal axis.3. Draw the virtual image where the raysappear to intersect.426UNIT DLight and Geometric Optics