Chapter 11.pdf
Chapter 11.pdf
Chapter 11.pdf
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
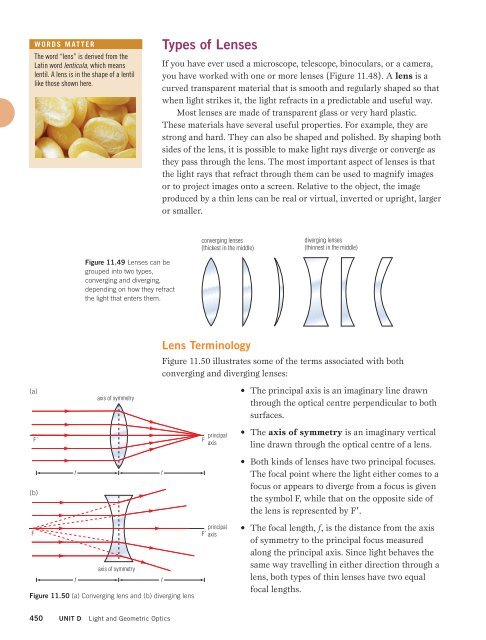
WORDS MATTERThe word “lens” is derived from theLatin word lenticula, which meanslentil. A lens is in the shape of a lentillike those shown here.Types of LensesIf you have ever used a microscope, telescope, binoculars, or a camera,you have worked with one or more lenses (Figure 11.48). A lens is acurved transparent material that is smooth and regularly shaped so thatwhen light strikes it, the light refracts in a predictable and useful way.Most lenses are made of transparent glass or very hard plastic.These materials have several useful properties. For example, they arestrong and hard. They can also be shaped and polished. By shaping bothsides of the lens, it is possible to make light rays diverge or converge asthey pass through the lens. The most important aspect of lenses is thatthe light rays that refract through them can be used to magnify imagesor to project images onto a screen. Relative to the object, the imageproduced by a thin lens can be real or virtual, inverted or upright, largeror smaller.converging lenses(thickest in the middle)diverging lenses(thinnest in the middle)Figure 11.49 Lenses can begrouped into two types,converging and diverging,depending on how they refractthe light that enters them.(a)FF´(b)ffaxis of symmetryaxis of symmetryFigure 11.50 (a) Converging lens and (b) diverging lensLens TerminologyFigure 11.50 illustrates some of the terms associated with bothconverging and diverging lenses:ffFprincipalaxisprincipalF´ axis• The principal axis is an imaginary line drawnthrough the optical centre perpendicular to bothsurfaces.• The axis of symmetry is an imaginary verticalline drawn through the optical centre of a lens.• Both kinds of lenses have two principal focuses.The focal point where the light either comes to afocus or appears to diverge from a focus is giventhe symbol F, while that on the opposite side ofthe lens is represented by F.• The focal length, f, is the distance from the axisof symmetry to the principal focus measuredalong the principal axis. Since light behaves thesame way travelling in either direction through alens, both types of thin lenses have two equalfocal lengths.450 UNIT D Light and Geometric Optics