Chapter 11.pdf
Chapter 11.pdf
Chapter 11.pdf
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
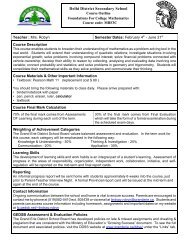
Uses for Convex MirrorsIf you were to compare a convex mirror with a plane mirror of the samesize, you would discover that more objects can be seen in the convexmirror. For this reason, convex mirrors are often used as securitymirrors in stores (Figure 11.19). A convex mirror allows you to view alarge region of the store from one location. For the same reason, convexmirrors are used in vehicles as side-view mirrors and rear-view mirrors.However, if you look in a convex mirror, it appears as if the image isoriginating from a smaller point behind the mirror. Because of thesesmaller images, convex mirrors on cars often have a warning such asthe one shown in Figure 11.20 that objects in the mirror are closer thanthey appear.You may have noticed convex mirrors used in some automatic tellermachines and computers (Figure 11.21). A convex mirror allows themachine users to see what is happening behind them while they arefacing the machine screen. Many camera phones include a convexmirror so that you can accurately aim the camera to take a self-portrait.Figure 11.19 A store security mirror Figure 11.20 A side-view mirror Figure 11.21 A security mirror on anautomatic teller machineLearning Checkpoint1. What is a real image?2. What is a virtual image?3. Name the features of the ray diagram identified as A, B, C, and D.DACBTake It FurtherThe first astronaut to walk on theMoon, Neil Armstrong, put aspecial mirror on the Moon’ssurface that was able to reflectlight directly back in the directionfrom which it came. Scientistsfrom Earth shine laser light at thismirror. Find out how this mirrorworks and what has been learnedfrom pointing a laser from Earth atthe mirror. Begin your research atScienceSource.4. Draw a ray diagram where the object is between one and two focal lengthsfrom a concave mirror with a focal length of 5 cm.5. Draw a ray diagram where the object is more than two focal lengths from aconcave mirror with a focal length of 5 cm.Ray diagrams model the behaviour of light in mirrors and lenses.427