Dell Power Solutions
Dell Power Solutions
Dell Power Solutions
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
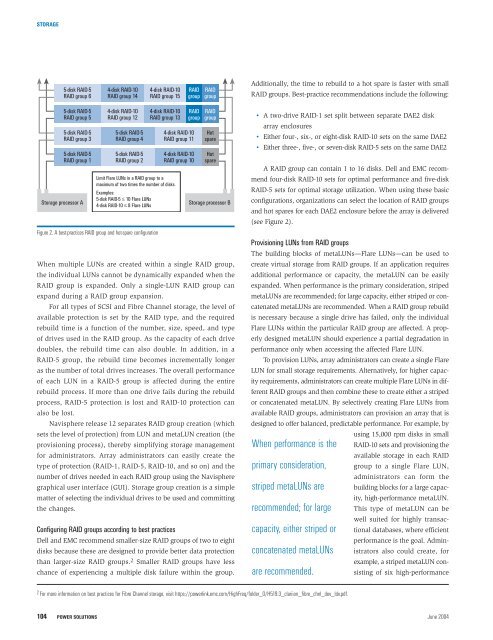
STORAGE5-disk RAID-5RAID group 64-disk RAID-10RAID group 144-disk RAID-10RAID group 15RAIDgroupRAIDgroupAdditionally, the time to rebuild to a hot spare is faster with smallRAID groups. Best-practice recommendations include the following:5-disk RAID-5RAID group 55-disk RAID-5RAID group 35-disk RAID-5RAID group 1Storage processor A4-disk RAID-10RAID group 125-disk RAID-5RAID group 45-disk RAID-5RAID group 24-disk RAID-10RAID group 13Limit Flare LUNs in a RAID group to amaximum of two times the number of disks.Examples:5-disk RAID-5 ≤ 10 Flare LUNs4-disk RAID-10 ≤ 8 Flare LUNsFigure 2. A best-practices RAID group and hot-spare configurationRAIDgroup4-disk RAID-10RAID group 114-disk RAID-10RAID group 10RAIDgroupHotspareHotspareStorage processor BWhen multiple LUNs are created within a single RAID group,the individual LUNs cannot be dynamically expanded when theRAID group is expanded. Only a single-LUN RAID group canexpand during a RAID group expansion.For all types of SCSI and Fibre Channel storage, the level ofavailable protection is set by the RAID type, and the requiredrebuild time is a function of the number, size, speed, and typeof drives used in the RAID group. As the capacity of each drivedoubles, the rebuild time can also double. In addition, in aRAID-5 group, the rebuild time becomes incrementally longeras the number of total drives increases. The overall performanceof each LUN in a RAID-5 group is affected during the entirerebuild process. If more than one drive fails during the rebuildprocess, RAID-5 protection is lost and RAID-10 protection canalso be lost.Navisphere release 12 separates RAID group creation (whichsets the level of protection) from LUN and metaLUN creation (theprovisioning process), thereby simplifying storage managementfor administrators. Array administrators can easily create thetype of protection (RAID-1, RAID-5, RAID-10, and so on) and thenumber of drives needed in each RAID group using the Navispheregraphical user interface (GUI). Storage group creation is a simplematter of selecting the individual drives to be used and committingthe changes.Configuring RAID groups according to best practices<strong>Dell</strong> and EMC recommend smaller-size RAID groups of two to eightdisks because these are designed to provide better data protectionthan larger-size RAID groups. 2 Smaller RAID groups have lesschance of experiencing a multiple disk failure within the group.• A two-drive RAID-1 set split between separate DAE2 diskarray enclosures• Either four-, six-, or eight-disk RAID-10 sets on the same DAE2• Either three-, five-, or seven-disk RAID-5 sets on the same DAE2A RAID group can contain 1 to 16 disks. <strong>Dell</strong> and EMC recommendfour-disk RAID-10 sets for optimal performance and five-diskRAID-5 sets for optimal storage utilization. When using these basicconfigurations, organizations can select the location of RAID groupsand hot spares for each DAE2 enclosure before the array is delivered(see Figure 2).Provisioning LUNs from RAID groupsThe building blocks of metaLUNs—Flare LUNs—can be used tocreate virtual storage from RAID groups. If an application requiresadditional performance or capacity, the metaLUN can be easilyexpanded. When performance is the primary consideration, stripedmetaLUNs are recommended; for large capacity, either striped or concatenatedmetaLUNs are recommended. When a RAID group rebuildis necessary because a single drive has failed, only the individualFlare LUNs within the particular RAID group are affected. A properlydesigned metaLUN should experience a partial degradation inperformance only when accessing the affected Flare LUN.To provision LUNs, array administrators can create a single FlareLUN for small storage requirements. Alternatively, for higher capacityrequirements, administrators can create multiple Flare LUNs in differentRAID groups and then combine these to create either a stripedor concatenated metaLUN. By selectively creating Flare LUNs fromavailable RAID groups, administrators can provision an array that isdesigned to offer balanced, predictable performance. For example, byusing 15,000 rpm disks in smallWhen performance is the RAID-10 sets and provisioning theavailable storage in each RAIDprimary consideration, group to a single Flare LUN,administrators can form thestriped metaLUNs are building blocks for a large capacity,high-performance metaLUN.recommended; for large This type of metaLUN can bewell suited for highly transactionaldatabases, where efficientcapacity, either striped orperformance is the goal. Administratorsalso could create, forconcatenated metaLUNsexample, a striped metaLUN consistingof six high-performanceare recommended.2 For more information on best practices for Fibre Channel storage, visit https://powerlink.emc.com/HighFreq/folder_0/H519.3_clariion_fibre_chnl_dev_ldv.pdf.104POWER SOLUTIONS June 2004