3.091 â Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 2 ...
3.091 â Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 2 ...
3.091 â Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 2 ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
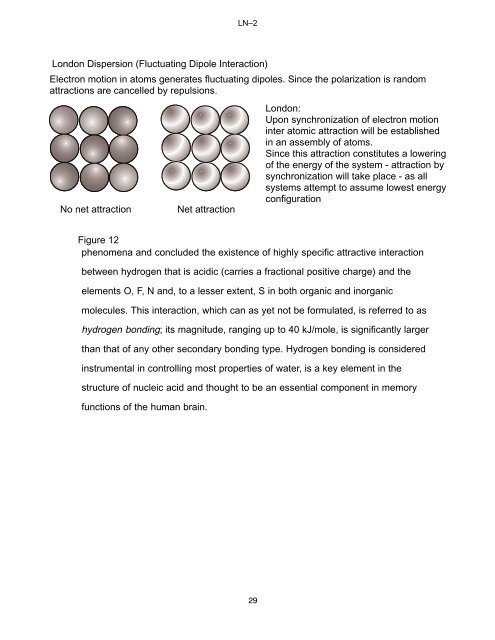
LN–2London Dispersion (Fluctuating Dipole Interaction)Electron motion in a<strong>to</strong>ms generates fluctuating dipoles. Since the polarization is randomattractions are cancelled by repulsions.<strong>No</strong> net attractionNet attractionLondon:Upon synchronization of electron motioninter a<strong>to</strong>mic attraction will be establishedin an assembly of a<strong>to</strong>ms.Since this attraction constitutes a loweringof the energy of the system - attraction bysynchronization will take place - as allsystems attempt <strong>to</strong> assume lowest energyconfigurationFigure 12phenomena and concluded the existence of highly specific attractive interactionbetween hydrogen that is acidic (carries a fractional positive charge) and theelements O, F, N and, <strong>to</strong> a lesser extent, S in both organic and inorganicmolecules. This interaction, which can as yet not be formulated, is referred <strong>to</strong> ashydrogen bonding; its magnitude, ranging up <strong>to</strong> 40 kJ/mole, is significantly largerthan that of any other secondary bonding type. Hydrogen bonding is consideredinstrumental in controlling most properties of water, is a key element in thestructure of nucleic acid and thought <strong>to</strong> be an essential component in memoryfunctions of the human brain.29


![18.03 Class 21, April 3 Fun with Fourier series [1] If f(t) is any decent ...](https://img.yumpu.com/51148985/1/190x245/1803-class-21-april-3-fun-with-fourier-series-1-if-ft-is-any-decent-.jpg?quality=85)












