- Page 1 and 2: United Nations Development Programm
- Page 4 and 5: Foreword by the Chairman of the Boa
- Page 6 and 7: Foreword by the Regional Director,U
- Page 8 and 9: Report Team(Alphabetically)Advisory
- Page 10 and 11: The knowledge society and the legit
- Page 12 and 13: Partnership with the private sector
- Page 14 and 15: LIST OF FIGURESFigure 1 Decline in
- Page 16 and 17: Table 5-12 Trade in technological p
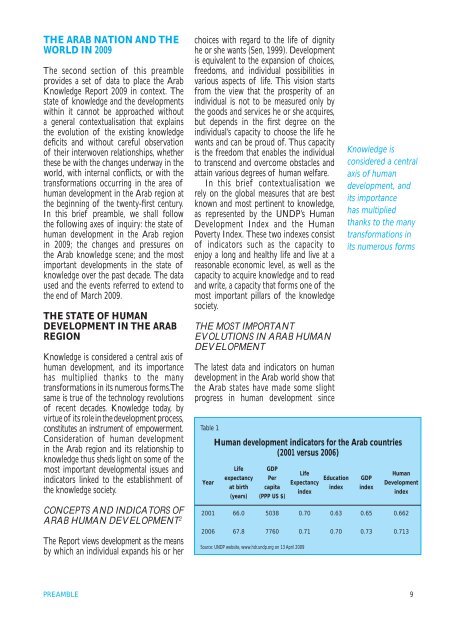
- Page 18 and 19: PREAMBLEIntroductionThe Arab Knowle
- Page 20: knowledge and from the consequences
- Page 23 and 24: Arabic istechnologicallypoor in com
- Page 25: Intercommunicationwith the self mea
- Page 29 and 30: Figure 2504540353025201510508070605
- Page 31 and 32: In the period2003-2007, morethan 83
- Page 33 and 34: Extremism negatesthe Other, haltsth
- Page 35 and 36: The reformisttendency callsfor grad
- Page 37 and 38: The current crisismay help to resto
- Page 39 and 40: On the ICT axis, theArab states hav
- Page 41 and 42: End Notes* Arberry, Arthur J. The K
- Page 44 and 45: CHAPTER ONETHE THEORETICAL FRAMEWOR
- Page 46 and 47: BOX 1-2“Knowledge” in al-Tahana
- Page 48 and 49: phrases that do not display theoret
- Page 50 and 51: enabling institutional and legal en
- Page 52 and 53: the individual and collective ident
- Page 54 and 55: services of seasoned experts and sc
- Page 56 and 57: pay too little attention to the qua
- Page 58 and 59: egion, greatest among them that the
- Page 60 and 61: the values of democratic politicalr
- Page 62 and 63: that occupy the lowest rung of the
- Page 64 and 65: the Middle Ages, as if all that has
- Page 66 and 67: of various ethnic, religious, and o
- Page 68 and 69: infrastructure, effort, energy, and
- Page 70 and 71: value to the lexicon of ethics, but
- Page 72 and 73: limit knowledge exclusively to the
- Page 74: CHAPTER TWOARAB KNOWLEDGE PERFORMAN
- Page 77 and 78:
Freedom is the basisof development.
- Page 79 and 80:
FIGURE 2-1Press freedom in the Arab
- Page 81 and 82:
Stringent legislativeand institutio
- Page 83 and 84:
Arab creativeproduction,especially
- Page 85 and 86:
The Arab countriesmost preparedto p
- Page 87 and 88:
TABLE 2-1Arab Countries that realis
- Page 89 and 90:
BOX 2-1The Contradictory Nature of
- Page 91 and 92:
External pressure,restrictions impo
- Page 93 and 94:
The Arab poorsuffer from socialmarg
- Page 95 and 96:
Arab countries havebeen absent from
- Page 97 and 98:
TABLE 2-3Rights and responsibilitie
- Page 99 and 100:
The current state ofknowledge-enabl
- Page 101 and 102:
To build andimplementan enablingenv
- Page 103 and 104:
Oman’s WorldStudies Instituteaims
- Page 105 and 106:
BOX 2-3The communications market in
- Page 107 and 108:
The desiredArab index willtranscend
- Page 109 and 110:
End Notes1The index divides the Ara
- Page 112:
CHAPTER THREEEDUCATION AND THE FORM
- Page 115 and 116:
In the last quarterof a century, Ar
- Page 117 and 118:
Knowledge is morethan the informati
- Page 119 and 120:
Although thelaws in most Arabcountr
- Page 121 and 122:
FIGURE 3-2: 19Basic knowledge capit
- Page 123 and 124:
Arab educationalcurricula in genera
- Page 125 and 126:
While Arab countriesvary greatly in
- Page 127 and 128:
FIGURE 3-390Advanced knowledge capi
- Page 129 and 130:
BOX 3-4The Commission for the Delib
- Page 131 and 132:
BOX 3-6Higher education in the Arab
- Page 133 and 134:
The available dataon the fields ofe
- Page 135 and 136:
Literacy ratesamong adults havenot
- Page 137 and 138:
Eight Arab countrieshave a critical
- Page 139 and 140:
Most Arab countrieshave been unable
- Page 141 and 142:
Statistical analysesshow a definite
- Page 143 and 144:
FIGURE 3-7Science performance of ei
- Page 145 and 146:
BOX 3-9Human Capital Formation to M
- Page 147 and 148:
BOX 3-10The Lebanese Association fo
- Page 149 and 150:
Clearly, the “lightsof knowledge
- Page 151 and 152:
End Notes1“Adult” is defined he
- Page 153 and 154:
40Accurate statistics are not avail
- Page 155 and 156:
level or the equivalent, post-secon
- Page 158:
CHAPTER FOURINFORMATION AND COMMUNI
- Page 161 and 162:
Over the last tenyears the Arabcoun
- Page 163 and 164:
FIGURE 4-3Internet users - Arab wor
- Page 165 and 166:
FIGURE 4-5Price basket for internet
- Page 167 and 168:
The growth ratein Arabic-speakingin
- Page 169 and 170:
During the comingdecade thetechnolo
- Page 171 and 172:
Strategic decisionstaken in many Ar
- Page 173 and 174:
In general, the Arabcountries are c
- Page 175 and 176:
FIGURE 4-8Availability of e-governm
- Page 177 and 178:
Some Arab stateshave taken initiati
- Page 179 and 180:
In contradiction tothe call to rest
- Page 181 and 182:
The experiences ofboth developingan
- Page 183 and 184:
FIGURE 4-10Paper consumption worldw
- Page 185 and 186:
A system formachine parsingArabic s
- Page 187 and 188:
BOX 4-7Egypt’s Centre for Documen
- Page 189 and 190:
More research shouldbe directed tow
- Page 191 and 192:
The possession ofinformation andcom
- Page 193 and 194:
End Notes1According to the majority
- Page 195 and 196:
Technology research and development
- Page 198 and 199:
CHAPTER FIVEARAB PERFORMANCE INRESE
- Page 200 and 201:
FIGURE 5-3Per capita GDP and the in
- Page 202 and 203:
the import and consumption of ready
- Page 204 and 205:
FIGURE 5-4Arab-international cooper
- Page 206 and 207:
are characterised by flexibility to
- Page 208 and 209:
esearchers prefer to remain in univ
- Page 210 and 211:
Arab countries can be ranked in ter
- Page 212 and 213:
FIGURE 5-5Arab participation in the
- Page 214 and 215:
Institute in the USA. By analysing
- Page 216 and 217:
5-6). A tabulation of all the Arab
- Page 218 and 219:
partnerships with foreign scientifi
- Page 220 and 221:
and anthropology have decreased (Ha
- Page 222 and 223:
Arabic). Aversion to reading is con
- Page 224 and 225:
to attract a number of invested par
- Page 226 and 227:
and security conditions offered by
- Page 228 and 229:
driven economies that are in the fi
- Page 230 and 231:
• Real and deep-rooted developmen
- Page 232:
of $1.57 billion due to human capit
- Page 236 and 237:
CHAPTER SIXBUILDING THE KNOWLEDGESO
- Page 238 and 239:
This can only come about through th
- Page 240 and 241:
proposals intended to give impetus
- Page 242 and 243:
knowledge society must be considere
- Page 244 and 245:
the Arab individual’s options to
- Page 246 and 247:
and the distribution of the benefit
- Page 248 and 249:
FIGURE 6-2Priorities for action to
- Page 250 and 251:
priorities in the area of movement
- Page 252 and 253:
ACTION TO DEPLOYKNOWLEDGEAction on
- Page 254 and 255:
knowledge technologies and their me
- Page 256:
REFERENCES
- Page 259 and 260:
Maghrib (Women and Politics: politi
- Page 261 and 262:
http://www.moe.gov.ps/intifada/repo
- Page 263 and 264:
Washington, D.C. www.heritage.org/i
- Page 265 and 266:
The World Bank. 2002. “Constructi
- Page 268 and 269:
ANNEX 1. LIST OF BACKGROUNDPAPERS (
- Page 270 and 271:
ANNEX 2. PROJECT FOR ADATABASE ON K
- Page 272:
include search engines, hyperlinks
- Page 275 and 276:
is arrived at by specifying the cou
- Page 277 and 278:
the knowledge economy. On this basi
- Page 279 and 280:
FIGURE A-3Index values for the pill
- Page 281 and 282:
TABLE A-4Availability of knowledge
- Page 283 and 284:
even contradictory. For example, da
- Page 286:
STATISTICAL ANNEX
- Page 289 and 290:
Table 2: Human Development IndicesC
- Page 291 and 292:
Table 4: World Bank Knowledge Econo
- Page 293 and 294:
Table 6: Worldwide governance indic
- Page 295 and 296:
Table 8: World Bank Economic Incent
- Page 297 and 298:
Table 10: Gross enrolment ratio in
- Page 299 and 300:
Table 12: World Bank Education and
- Page 301 and 302:
Table 14: Regional literacy rates a
- Page 303 and 304:
Table 17: Gross enrolment ratios in
- Page 305 and 306:
Table 19: Time devoted to education
- Page 307 and 308:
Table 21: Time devoted to secondary
- Page 309 and 310:
Table 23: Enrolment in tertiary edu
- Page 311 and 312:
Table 25: Number of specialists in
- Page 313 and 314:
Table 27: School life expectancy in
- Page 315 and 316:
Table 29: Government expenditure on
- Page 317 and 318:
Table 31: Number of students from s
- Page 319 and 320:
Table 33: World Bank Innovation Sys
- Page 321 and 322:
Table 35: World Bank indicators for
- Page 323 and 324:
(b) The growth of fixed and mobile
- Page 325 and 326:
for example, technological under-pr
- Page 327 and 328:
Table c-2: Classification of the Ar
- Page 329:
End Notes1For example a news report