Sectoral Approach
Sectoral Approach
Sectoral Approach
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
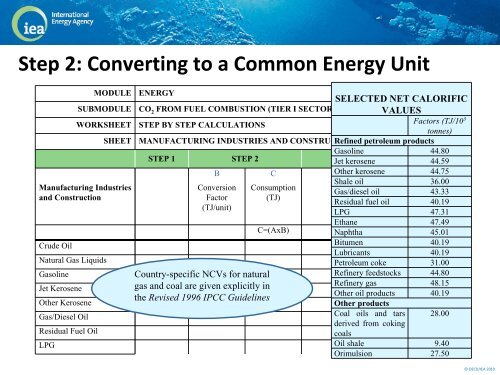
Step 2: Converting to a Common Energy UnitMODULESUBMODULEWORKSHEETSHEETManufacturing Industriesand ConstructionCrude OilNatural Gas LiquidsGasolineJet KeroseneOther KeroseneGas/Diesel OilResidual Fuel OilLPGENERGYSELECTED NET CALORIFICCO 2 FROM FUEL COMBUSTION (TIER I SECTORAL APPROACH) VALUESSTEP BY STEP CALCULATIONSFactors (TJ/10 3tonnes)MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIES AND CONSTRUCTION Refined petroleum productsSTEP 1 STEP 2Gasoline 44.80Jet kerosene STEP 3 44.59A B C D Other kerosene E 44.75 FShale oil 36.00Consumption Conversion Consumption CarbonGas/dieselCarbonoilCarbon43.33Factor (TJ) Emission Content ContentResidual fuel oil 40.19(TJ/unit)Factor (t C) (Gg C)LPG 47.31(t C/TJ)Ethane 47.49C=(AxB) Naphtha E=(CxD) F=(E 45.01 x 10-3)Bitumen 40.19Lubricants 40.19Petroleum coke 31.00Country-specific NCVs for naturalRefinery feedstocks 44.80gas and coal are given explicitly inRefinery gas 48.15Other oil products 40.19the Revised 1996 IPCC GuidelinesOther productsCoal oils and tarsderived from cokingcoals28.00Oil shale 9.40Orimulsion 27.50©OECD/IEA 2010