Convergent meshfree approximation schemes of arbitrary order and ...
Convergent meshfree approximation schemes of arbitrary order and ...
Convergent meshfree approximation schemes of arbitrary order and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
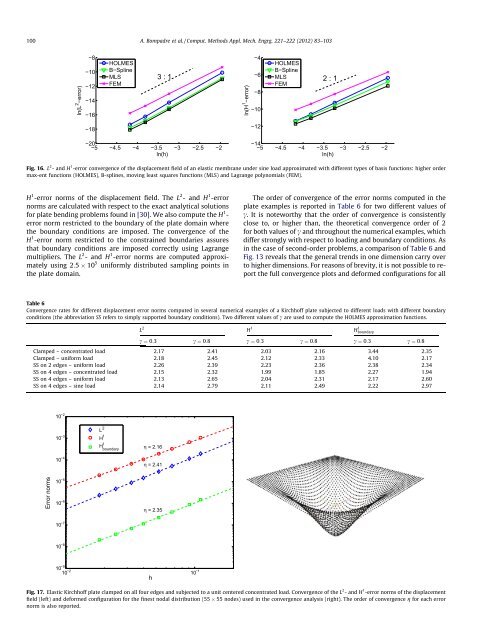
100 A. Bompadre et al. / Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 221–222 (2012) 83–103ln(L 2 −error)−8−10−12−14−16HOLMESB−SplineMLSFEM3 : 1ln(H 1 −error)−4−6−8−10HOLMESB−SplineMLSFEM2 : 1−18−12−20−5 −4.5 −4 −3.5 −3 −2.5 −2ln(h)−14−5 −4.5 −4 −3.5 −3 −2.5 −2ln(h)Fig. 16. L 2 - <strong>and</strong> H 1 -error convergence <strong>of</strong> the displacement field <strong>of</strong> an elastic membrane under sine load approximated with different types <strong>of</strong> basis functions: higher <strong>order</strong>max-ent functions (HOLMES), B-splines, moving least squares functions (MLS) <strong>and</strong> Lagrange polynomials (FEM).H 1 -error norms <strong>of</strong> the displacement field. The L 2 - <strong>and</strong> H 1 -errornorms are calculated with respect to the exact analytical solutionsfor plate bending problems found in [30]. We also compute the H 1 -error norm restricted to the boundary <strong>of</strong> the plate domain wherethe boundary conditions are imposed. The convergence <strong>of</strong> theH 1 -error norm restricted to the constrained boundaries assuresthat boundary conditions are imposed correctly using Lagrangemultipliers. The L 2 - <strong>and</strong> H 1 -error norms are computed approximatelyusing 2:5 10 5 uniformly distributed sampling points inthe plate domain.The <strong>order</strong> <strong>of</strong> convergence <strong>of</strong> the error norms computed in theplate examples is reported in Table 6 for two different values <strong>of</strong>c. It is noteworthy that the <strong>order</strong> <strong>of</strong> convergence is consistentlyclose to, or higher than, the theoretical convergence <strong>order</strong> <strong>of</strong> 2for both values <strong>of</strong> c <strong>and</strong> throughout the numerical examples, whichdiffer strongly with respect to loading <strong>and</strong> boundary conditions. Asin the case <strong>of</strong> second-<strong>order</strong> problems, a comparison <strong>of</strong> Table 6 <strong>and</strong>Fig. 13 reveals that the general trends in one dimension carry overto higher dimensions. For reasons <strong>of</strong> brevity, it is not possible to reportthe full convergence plots <strong>and</strong> deformed configurations for allTable 6Convergence rates for different displacement error norms computed in several numerical examples <strong>of</strong> a Kirchh<strong>of</strong>f plate subjected to different loads with different boundaryconditions (the abbreviation SS refers to simply supported boundary conditions). Two different values <strong>of</strong> c are used to compute the HOLMES <strong>approximation</strong> functions.L 2 H 1 H 1 boundaryc ¼ 0:3 c ¼ 0:8 c ¼ 0:3 c ¼ 0:8 c ¼ 0:3 c ¼ 0:8Clamped – concentrated load 2.17 2.41 2.03 2.16 3.44 2.35Clamped – uniform load 2.18 2.45 2.12 2.33 4.10 2.17SS on 2 edges – uniform load 2.26 2.39 2.23 2.36 2.38 2.34SS on 4 edges – concentrated load 2.15 2.32 1.99 1.85 2.27 1.94SS on 4 edges – uniform load 2.13 2.65 2.04 2.31 2.17 2.60SS on 4 edges – sine load 2.14 2.79 2.11 2.49 2.22 2.9710 −2 h10 −3L 2H 1H 1 boundary η = 2.1610 −4η = 2.41Error norms10 −510 −6η = 2.3510 −710 −810 −910 −2 10 −1Fig. 17. Elastic Kirchh<strong>of</strong>f plate clamped on all four edges <strong>and</strong> subjected to a unit centered concentrated load. Convergence <strong>of</strong> the L 2 - <strong>and</strong> H 1 -error norms <strong>of</strong> the displacementfield (left) <strong>and</strong> deformed configuration for the finest nodal distribution (55 55 nodes) used in the convergence analysis (right). The <strong>order</strong> <strong>of</strong> convergence g for each errornorm is also reported.