Impact Vibration Absorber of Pendulum Type
Impact Vibration Absorber of Pendulum Type
Impact Vibration Absorber of Pendulum Type
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
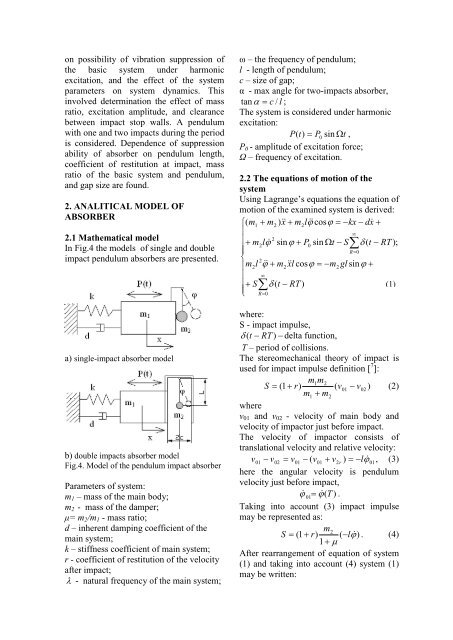
on possibility <strong>of</strong> vibration suppression <strong>of</strong>the basic system under harmonicexcitation, and the effect <strong>of</strong> the systemparameters on system dynamics. Thisinvolved determination the effect <strong>of</strong> massratio, excitation amplitude, and clearancebetween impact stop walls. A pendulumwith one and two impacts during the periodis considered. Dependence <strong>of</strong> suppressionability <strong>of</strong> absorber on pendulum length,coefficient <strong>of</strong> restitution at impact, massratio <strong>of</strong> the basic system and pendulum,and gap size are found.2. ANALITICAL MODEL OFABSORBER2.1 Mathematical modelIn Fig.4 the models <strong>of</strong> single and doubleimpact pendulum absorbers are presented.a) single-impact absorber modelb) double impacts absorber modelFig.4. Model <strong>of</strong> the pendulum impact absorberParameters <strong>of</strong> system:m 1 – mass <strong>of</strong> the main body;m 2 - mass <strong>of</strong> the damper;μ= m 2 /m 1 - mass ratio;d – inherent damping coefficient <strong>of</strong> themain system;k – stiffness coefficient <strong>of</strong> main system;r - coefficient <strong>of</strong> restitution <strong>of</strong> the velocityafter impact;λ - natural frequency <strong>of</strong> the main system;ω – the frequency <strong>of</strong> pendulum;l - length <strong>of</strong> pendulum;c – size <strong>of</strong> gap;α - max angle for two-impacts absorber,tan α = c / l ;The system is considered under harmonicexcitation:P( t)= P0 sin Ωt,P 0 - amplitude <strong>of</strong> excitation force;Ω – frequency <strong>of</strong> excitation.2.2 The equations <strong>of</strong> motion <strong>of</strong> thesystemUsing Lagrange’s equations the equation <strong>of</strong>motion <strong>of</strong> the examined system is derived:⎧(m1+ m2) x + m2l ϕ cosϕ= −kx− dx+⎪∞⎪ 2+ m2l ϕ sinϕ+ P0sin Ωt− S∑δ( t − RT );⎪R=0⎨ 2⎪m2l ϕ + m 2xl cosϕ= −m2gl sinϕ+⎪ ∞⎪+S −∑δ( t RT )(1)⎩ R=0where:S - impact impulse,δ ( t − RT ) − delta function,T – period <strong>of</strong> collisions.The stereomechanical theory <strong>of</strong> impact isused for impact impulse definition [ 7 ]:m1m2S = ( 1+r)( v01− v02) (2)m1+ m2wherev 01 and v 02 - velocity <strong>of</strong> main body andvelocity <strong>of</strong> impactor just before impact.The velocity <strong>of</strong> impactor consists <strong>of</strong>translational velocity and relative velocity:v01 − v02= v01− ( v01+ v2r ) = −lϕ01,(3)here the angular velocity is pendulumvelocity just before impact, ϕ01= ϕ(T ) .Taking into account (3) impact impulsemay be represented as:m2 S = (1 + r)( −l ϕ). (4)1+µAfter rearrangement <strong>of</strong> equation <strong>of</strong> system(1) and taking into account (4) system (1)may be written: