Learning Guide for Chapter 24 - Carboxylic Acid derivatives
Learning Guide for Chapter 24 - Carboxylic Acid derivatives
Learning Guide for Chapter 24 - Carboxylic Acid derivatives
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
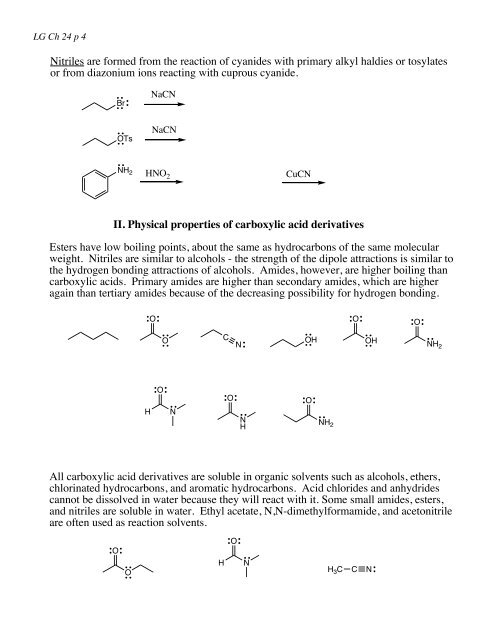
LG Ch <strong>24</strong> p 4Nitriles are <strong>for</strong>med from the reaction of cyanides with primary alkyl haldies or tosylatesor from diazonium ions reacting with cuprous cyanide.BrNaCNOTsNaCNNH 2 HNO 2CuCNII. Physical properties of carboxylic acid <strong>derivatives</strong>Esters have low boiling points, about the same as hydrocarbons of the same molecularweight. Nitriles are similar to alcohols - the strength of the dipole attractions is similar tothe hydrogen bonding attractions of alcohols. Amides, however, are higher boiling thancarboxylic acids. Primary amides are higher than secondary amides, which are higheragain than tertiary amides because of the decreasing possibility <strong>for</strong> hydrogen bonding.OOOOCOHOHNH 2NNHHONOONH 2All carboxylic acid <strong>derivatives</strong> are soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols, ethers,chlorinated hydrocarbons, and aromatic hydrocarbons. <strong>Acid</strong> chlorides and anhydridescannot be dissolved in water because they will react with it. Some small amides, esters,and nitriles are soluble in water. Ethyl acetate, N,N-dimethyl<strong>for</strong>mamide, and acetonitrileare often used as reaction solvents.OOHONH 3 C C N