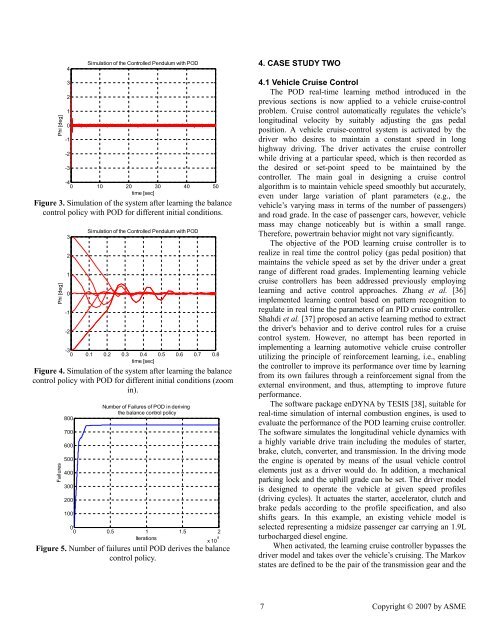
“neural-fuzzy BOXES” control system by neural networks <strong>and</strong>utilized rein<strong>for</strong>cement learning <strong>for</strong> the training. Jeen-Shing etal. [33] proposed a defuzzification method incorporating agenetic algorithm to learn the defuzzification factors. Mustaphaet al. [34] developed an actor-critic rein<strong>for</strong>cement learningalgorithm represented by two adaptive neural-fuzzy systems. Siet al. [35] proposed a generic on-line learning control systemsimilar to Anderson’s utilizing neural networks <strong>and</strong> evaluated itthrough its application to both a single <strong>and</strong> double cart-polebalancing problem. The system utilizes two neural networks,<strong>and</strong> employs the action- dependent heuristic dynamicprogramming to adapt the weights of the networks.In the implementation of the POD on the single invertedpendulum presented here, two major variations are considered:(a) a single look-up table-based representation is employed <strong>for</strong>the controller to develop the mapping from the system’sMarkov states to optimal actions, <strong>and</strong> (b) two system’s statevariables are selected to represent the Markov state. The latterintroduces uncertainty <strong>and</strong> thus a conditional probabilitydistribution associating the state transitions with respect to theactions taken. Consequently, the POD method is evaluated inderiving the optimal policy (balance control policy) in asequential decision making problem under uncertainty.The governing equations, derived from the free bodydiagram of the system, shown in Figure 2, are:2( M + m) x + bx + mLϕcosϕ− mL ϕ sin ϕ = U , (19)2mLx cos ϕ+ ( I + mL ) ϕ+ mgL sinϕ= 0, (20)N secwhere M = 0.5 kg, m = 0.2 kg, b=0.1m2 mI = 0.006 kg m , g = 9.81 ,<strong>and</strong> L = 0.3 m.2secThe goal of the learning controller is to realize in real timethe <strong>for</strong>ce, U, of a fixed magnitude to be applied either to theright or the left direction so that the pendulum st<strong>and</strong>s balancedwhen released from any angle, φ, between 3° <strong>and</strong> -3°. Thesystem is simulated by numerically solving the nonlineardifferential equations (19) <strong>and</strong> (20) employing the explicitRunge-Kutta method with a time step of τ =0.02 sec. Thesimulation is conducted by observing the system’s states <strong>and</strong>executing actions (control <strong>for</strong>ce U) with a sample rate T =0.02sec (50 Hz). This sample rate defines a sequence of decisionmakingepochs, T = 0,1, 2,..., M,M ∈N .The system is fully specified by four state variables: (a) theposition of the cart on the track, x()t ; (b) the cart velocity,x() t ; (c) the pendulum’s angle with respect to the verticalposition, ϕ () t ; <strong>and</strong> (d) the angular velocity, ϕ () t . However, toincorporate uncertainty, the Markov states are selected to beonly the pair of the pendulum’s angle <strong>and</strong> angular velocity,namely, the finite state space S, in Eq. (1) is defined asS = { s | s = ( ϕ, ϕ)}.(21)iiUN HN VMxxbxIϕ 2LϕmgN HFigure 2. Free body diagram of the system.IϕmI,Consequently, at state si∈S <strong>and</strong> executing a control <strong>for</strong>cevalue, U(s i ), the system will end up at state s j∈S with aconditional probably ps (j| si, Us (i)). The control <strong>for</strong>ce, U(s i ),selects values from the finite set A, defined asA = As (i) = [ − 3 N,3 N], where i= 1, 2,..., N, N=| S | . (22)The decision-making process occurs at each of a sequence ofepochs T = 0,1, 2,..., M,M ∈ N . At each decision epoch, thelearning controller observes the system’s state s i∈S , <strong>and</strong>executes a control <strong>for</strong>ce value U( si) ∈ A( si). At the nextdecision epoch, the system transits to another statesj∈S imposed by the conditional probabilitiesps (j| si, Us (i)), <strong>and</strong> receives a numerical reward (thependulum’s angle φ).The inverted pendulum is simulated repeatedly <strong>for</strong>different initial angles, φ, between 3° <strong>and</strong> -3° utilizing the PODlearning method. The simulation lasts <strong>for</strong> 50 sec <strong>and</strong> eachcomplete simulation defines one iteration. If at any instantduring the simulation, the pendulum’s angle, φ, becomesgreater than 3° or less than -3°, this constitutes a failure,denoted by stating that there was one iteration associated with afailure. If, however, no failure occurs during the simulation,this is denoted by stating that there was one iteration associatedwith no failure.3.2 Simulation ResultsAfter completing the learning process, the controller employingthe POD learning method realizes the balance control policy ofthe pendulum, as illustrated in Figure 3. In some instances,however, the system’s response demonstrates some overshootsor delays during the transient period, shown in Figure 4. Thiscan be h<strong>and</strong>led by a denser parameterization of the state-spaceor adding a penalty in long transient responses. The efficiencyof the POD learning method in deriving the optimal balancecontrol policy that stabilizes the system is illustrated in Figure5. It is noted that after POD realizes the optimal policy in 749failures <strong>and</strong>, afterwards, as the number of iterations continuesno further failures occur.N Vx6 Copyright © 2007 by ASME
Phi [deg]43210-1-2-3Simulation of the Controlled Pendulum with POD-40 10 20 30 40 50time [sec]Figure 3. Simulation of the system after learning the balancecontrol policy with POD <strong>for</strong> different initial conditions.Phi [deg]3210-1-2Simulation of the Controlled Pendulum with POD-30 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8time [sec]Figure 4. Simulation of the system after learning the balancecontrol policy with POD <strong>for</strong> different initial conditions (zoomin).Failures800700600500400300200100Number of Failures of POD in derivingthe balance control policy00 0.5 1 1.5 2Iterationsx 10 4Figure 5. Number of failures until POD derives the balancecontrol policy.4. CASE STUDY TWO4.1 Vehicle Cruise ControlThe POD real-time learning method introduced in theprevious sections is now applied to a vehicle cruise-controlproblem. Cruise control automatically regulates the vehicle’slongitudinal velocity by suitably adjusting the gas pedalposition. A vehicle cruise-control system is activated by thedriver who desires to maintain a constant speed in longhighway driving. The driver activates the cruise controllerwhile driving at a particular speed, which is then recorded asthe desired or set-point speed to be maintained by thecontroller. The main goal in designing a cruise controlalgorithm is to maintain vehicle speed smoothly but accurately,even under large variation of plant parameters (e.g., thevehicle’s varying mass in terms of the number of passengers)<strong>and</strong> road grade. In the case of passenger cars, however, vehiclemass may change noticeably but is within a small range.There<strong>for</strong>e, powertrain behavior might not vary significantly.The objective of the POD learning cruise controller is torealize in real time the control policy (gas pedal position) thatmaintains the vehicle speed as set by the driver under a greatrange of different road grades. Implementing learning vehiclecruise controllers has been addressed previously employinglearning <strong>and</strong> active control approaches. Zhang et al. [36]implemented learning control based on pattern recognition toregulate in real time the parameters of an PID cruise controller.Shahdi et al. [37] proposed an active learning method to extractthe driver's behavior <strong>and</strong> to derive control rules <strong>for</strong> a cruisecontrol system. However, no attempt has been reported inimplementing a learning automotive vehicle cruise controllerutilizing the principle of rein<strong>for</strong>cement learning, i.e., enablingthe controller to improve its per<strong>for</strong>mance over time by learningfrom its own failures through a rein<strong>for</strong>cement signal from theexternal environment, <strong>and</strong> thus, attempting to improve futureper<strong>for</strong>mance.The software package enDYNA by TESIS [38], suitable <strong>for</strong>real-time simulation of internal combustion engines, is used toevaluate the per<strong>for</strong>mance of the POD learning cruise controller.The software simulates the longitudinal vehicle dynamics witha highly variable drive train including the modules of starter,brake, clutch, converter, <strong>and</strong> transmission. In the driving modethe engine is operated by means of the usual vehicle controlelements just as a driver would do. In addition, a mechanicalparking lock <strong>and</strong> the uphill grade can be set. The driver modelis designed to operate the vehicle at given speed profiles(driving cycles). It actuates the starter, accelerator, clutch <strong>and</strong>brake pedals according to the profile specification, <strong>and</strong> alsoshifts gears. In this example, an existing vehicle model isselected representing a midsize passenger car carrying an 1.9Lturbocharged diesel engine.When activated, the learning cruise controller bypasses thedriver model <strong>and</strong> takes over the vehicle’s cruising. The Markovstates are defined to be the pair of the transmission gear <strong>and</strong> the7 Copyright © 2007 by ASME