WUCT121 Discrete Mathematics Logic Tutorial Exercises Solutions
WUCT121 Discrete Mathematics Logic Tutorial Exercises Solutions
WUCT121 Discrete Mathematics Logic Tutorial Exercises Solutions
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
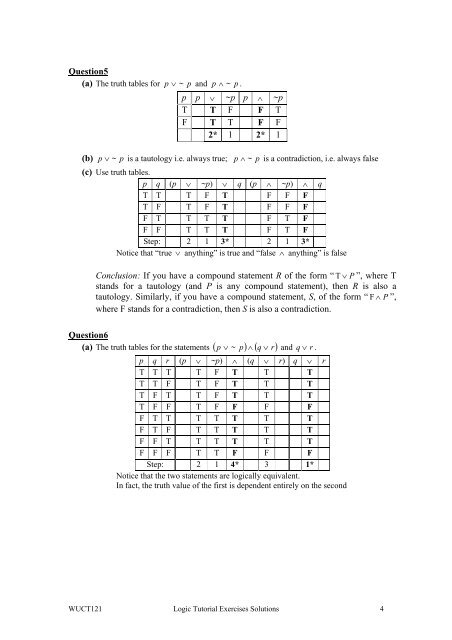
Question5(a) The truth tables for(b)p ∨ ~ p and p ∧ ~ p .p p ∨ ~p p ∧ ~pT T F F TF T T F F2* 1 2* 1p ∨ ~ p is a tautology i.e. always true; p ∧ ~ p is a contradiction, i.e. always false(c) Use truth tables.p q (p ∨ ~p) ∨ q (p ∧ ~p) ∧ qT T T F T F F FT F T F T F F FF T T T T F T FF F T T T F T FStep: 2 1 3* 2 1 3*Notice that “true ∨ anything” is true and “false ∧ anything” is falseConclusion: If you have a compound statement R of the form “ T ∨ P ”, where Tstands for a tautology (and P is any compound statement), then R is also atautology. Similarly, if you have a compound statement, S, of the form “ F ∧ P ”,where F stands for a contradiction, then S is also a contradiction.Question6(a) The truth tables for the statements ( p p) ∧ ( q ∨ r)∨ ~ and q ∨ r .p q r (p ∨ ~p) ∧ (q ∨ r) q ∨ rT T T T F T T TT T F T F T T TT F T T F T T TT F F T F F F FF T T T T T T TF T F T T T T TF F T T T T T TF F F T T F F FStep: 2 1 4* 3 1*Notice that the two statements are logically equivalent.In fact, the truth value of the first is dependent entirely on the second<strong>WUCT121</strong> <strong>Logic</strong> <strong>Tutorial</strong> <strong>Exercises</strong> <strong>Solutions</strong> 4