Six Sigma in the call centre - CallCenter PROFI
Six Sigma in the call centre - CallCenter PROFI
Six Sigma in the call centre - CallCenter PROFI
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
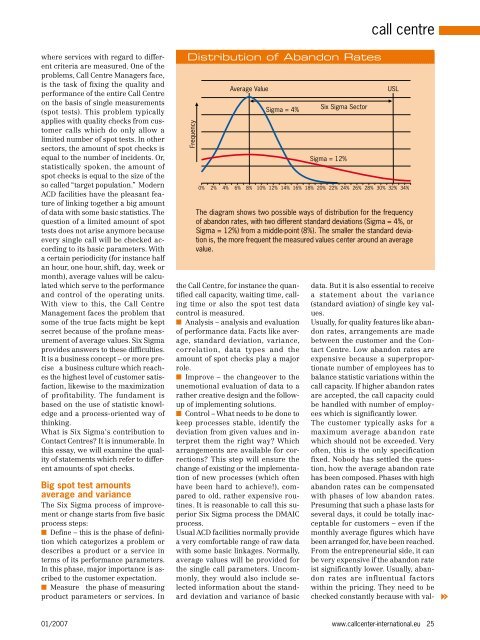
<strong>call</strong> <strong>centre</strong>where services with regard to differentcriteria are measured. One of <strong>the</strong>problems, Call Centre Managers face,is <strong>the</strong> task of fix<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> quality andperformance of <strong>the</strong> entire Call Centreon <strong>the</strong> basis of s<strong>in</strong>gle measurements(spot tests). This problem typi<strong>call</strong>yapplies with quality checks from customer<strong>call</strong>s which do only allow alimited number of spot tests. In o<strong>the</strong>rsectors, <strong>the</strong> amount of spot checks isequal to <strong>the</strong> number of <strong>in</strong>cidents. Or,statisti<strong>call</strong>y spoken, <strong>the</strong> amount ofspot checks is equal to <strong>the</strong> size of <strong>the</strong>so <strong>call</strong>ed ‘‘target population.” ModernACD facilities have <strong>the</strong> pleasant featureof l<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g toge<strong>the</strong>r a big amountof data with some basic statistics. Thequestion of a limited amount of spottests does not arise anymore becauseevery s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>call</strong> will be checked accord<strong>in</strong>gto its basic parameters. Witha certa<strong>in</strong> periodicity (for <strong>in</strong>stance halfan hour, one hour, shift, day, week ormonth), average values will be calculatedwhich serve to <strong>the</strong> performanceand control of <strong>the</strong> operat<strong>in</strong>g units.With view to this, <strong>the</strong> Call CentreManagement faces <strong>the</strong> problem thatsome of <strong>the</strong> true facts might be keptsecret because of <strong>the</strong> profane measurementof average values. <strong>Six</strong> <strong>Sigma</strong>provides answers to <strong>the</strong>se difficulties.It is a bus<strong>in</strong>ess concept – or more precisea bus<strong>in</strong>ess culture which reaches<strong>the</strong> highest level of customer satisfaction,likewise to <strong>the</strong> maximizationof profitability. The fundament isbased on <strong>the</strong> use of statistic knowledgeand a process-oriented way ofth<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g.What is <strong>Six</strong> <strong>Sigma</strong>‘s contribution toContact Centres? It is <strong>in</strong>numerable. Inthis essay, we will exam<strong>in</strong>e <strong>the</strong> qualityof statements which refer to differentamounts of spot checks.Big spot test amountsaverage and varianceThe <strong>Six</strong> <strong>Sigma</strong> process of improvementor change starts from five basicprocess steps:n Def<strong>in</strong>e – this is <strong>the</strong> phase of def<strong>in</strong>itionwhich categorizes a problem ordescribes a product or a service <strong>in</strong>terms of its performance parameters.In this phase, major importance is ascribedto <strong>the</strong> customer expectation.n Measure <strong>the</strong> phase of measur<strong>in</strong>gproduct parameters or services. InDistribution of Abandon RatesFrequencyAverage Value<strong>Sigma</strong> = 4%<strong>the</strong> Call Centre, for <strong>in</strong>stance <strong>the</strong> quantified<strong>call</strong> capacity, wait<strong>in</strong>g time, <strong>call</strong><strong>in</strong>gtime or also <strong>the</strong> spot test datacontrol is measured.n Analysis – analysis and evaluationof performance data. Facts like average,standard deviation, variance,correlation, data types and <strong>the</strong>amount of spot checks play a majorrole.n Improve – <strong>the</strong> changeover to <strong>the</strong>unemotional evaluation of data to ara<strong>the</strong>r creative design and <strong>the</strong> followupof implement<strong>in</strong>g solutions.n Control – What needs to be done tokeep processes stable, identify <strong>the</strong>deviation from given values and <strong>in</strong>terpret<strong>the</strong>m <strong>the</strong> right way? Whicharrangements are available for corrections?This step will ensure <strong>the</strong>change of exist<strong>in</strong>g or <strong>the</strong> implementationof new processes (which oftenhave been hard to achieve!), comparedto old, ra<strong>the</strong>r expensive rout<strong>in</strong>es.It is reasonable to <strong>call</strong> this superior<strong>Six</strong> <strong>Sigma</strong> process <strong>the</strong> DMAICprocess.Usual ACD facilities normally providea very comfortable range of raw datawith some basic l<strong>in</strong>kages. Normally,average values will be provided for<strong>the</strong> s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>call</strong> parameters. Uncommonly,<strong>the</strong>y would also <strong>in</strong>clude selected<strong>in</strong>formation about <strong>the</strong> standarddeviation and variance of basic<strong>Six</strong> <strong>Sigma</strong> Sector<strong>Sigma</strong> = 12%USL0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% 18% 20% 22% 24% 26% 28% 30% 32% 34%The diagram shows two possible ways of distribution for <strong>the</strong> frequencyof abandon rates, with two different standard deviations (<strong>Sigma</strong> = 4%, or<strong>Sigma</strong> = 12%) from a middle-po<strong>in</strong>t (8%). The smaller <strong>the</strong> standard deviationis, <strong>the</strong> more frequent <strong>the</strong> measured values center around an averagevalue.data. But it is also essential to receivea statement about <strong>the</strong> variance(standard aviation) of s<strong>in</strong>gle key values.Usually, for quality features like abandonrates, arrangements are madebetween <strong>the</strong> customer and <strong>the</strong> ContactCentre. Low abandon rates areexpensive because a superproportionatenumber of employees has tobalance statistic variations with<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong><strong>call</strong> capacity. If higher abandon ratesare accepted, <strong>the</strong> <strong>call</strong> capacity couldbe handled with number of employeeswhich is significantly lower.The customer typi<strong>call</strong>y asks for amaximum average abandon ratewhich should not be exceeded. Veryoften, this is <strong>the</strong> only specificationfixed. Nobody has settled <strong>the</strong> question,how <strong>the</strong> average abandon ratehas been composed. Phases with highabandon rates can be compensatedwith phases of low abandon rates.Presum<strong>in</strong>g that such a phase lasts forseveral days, it could be totally <strong>in</strong>acceptablefor customers – even if <strong>the</strong>monthly average figures which havebeen arranged for, have been reached.From <strong>the</strong> entrepreneurial side, it canbe very expensive if <strong>the</strong> abandon rateist significantly lower. Usually, abandonrates are <strong>in</strong>fluentual factorswith<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> pric<strong>in</strong>g. They need to bechecked constantly because with val-01/2007www.<strong>call</strong>center-<strong>in</strong>ternational.eu 25