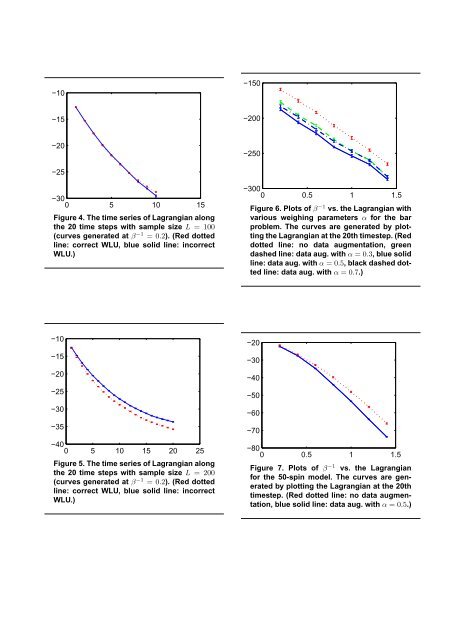
−30−40−50−60−70−80−900 0.5 1 1.5Figure 1. Plots <strong>of</strong> β −1 vs. the Lagrangian<strong>for</strong> different utilities. The curves are generatedby plotting the Lagrangian at the 20thtimestep, i.e., after 20 descents. The initialstep sizes are set to be 0.2 times the gradients.Also, L = 100 and a total <strong>of</strong> 40 simulationsare per<strong>for</strong>med. (Red dotted line: Teamgame, green dashed line: uni<strong>for</strong>m AU, bluesolid line: weighted AU.)−30−35−40−45−500 5 10 15 20 25Figure 2. The time series <strong>of</strong> Lagrangian alongthe 20 time steps (curves generated at β −1 =0.6). (Red dotted line: Team game, greendashed line: uni<strong>for</strong>m AU, blue solid line:weighted AU.)1.5magnitude <strong>of</strong> descent is halved if q i (x i ) is no longerpositive <strong>for</strong> some x ′ i .5. Repeat steps 2 to 4.Given that the utility function is reasonably smooth, itis natural to expect that the estimates aided by artificialdata points will provide an improvement. And this is indeedshown in figure 6 with varying α. The same experimentsare also per<strong>for</strong>med <strong>for</strong> the 50-spin model introduced in section4.1 but with a new metric d(x, x ′ ) = ∑ 50i=1 δ(x i − x ′ i ).The results are shown in figure 7.An immediately improvement to the scheme above is torealize that there is no need to restrict ourselves to dataavailable in that particular time step in calculating Ḡx iineq. 16. Namely, unlike step 3 above, we can accumulate“true” data from previous steps in calculating Ḡx iwhichwill certainly improve the accuracy <strong>of</strong> the estimation. To illustratethis idea, at time step t, we define S ′ to be the settrue samples drawn at time step t and with the set <strong>of</strong> truesamples drawn at time step t − 1, and we calculate Ḡx ias:Ḡ xi := 1 − α|S|+ α|A i |∑δ(x i − x ′ i)G(x) (19)x ′ ∈S∑δ(x i − x ′ i)ĜS ′(x) . (20)x ′ ∈A iThe results <strong>for</strong> the bar problem are shown in figure 8.10.500 5 10 15 20 25Figure∑ ∑3. Plots <strong>of</strong> time step versus150 i x i ∈σ iδ(L xi − 1) at different temperatures.(Red dotted line: β −1 = 0.2, bluesolid line: β −1 = 0.6.)6. Conclusion<strong>Product</strong> Distribution (PD) <strong>theory</strong> is a recently introducedbroad framework <strong>for</strong> analyzing, <strong>control</strong>ling, and optimizingdistributed <strong>systems</strong> [9, 10, 11]. Here we investigate PD <strong>theory</strong>’suse <strong>for</strong> adaptive, distributed <strong>control</strong> <strong>of</strong> a MAS. Typicallysuch <strong>control</strong> is done by having each <strong>agent</strong> run its ownrein<strong>for</strong>cement learning algorithm [4, 13, 14, 12].In this approach the utility function <strong>of</strong> each <strong>agent</strong> isbased on the world utility G(x) mapping the joint move <strong>of</strong>
−10−150−15−200−20−250−25−300 5 10 15Figure 4. The time series <strong>of</strong> Lagrangian alongthe 20 time steps with sample size L = 100(curves generated at β −1 = 0.2). (Red dottedline: correct WLU, blue solid line: incorrectWLU.)−3000 0.5 1 1.5Figure 6. Plots <strong>of</strong> β −1 vs. the Lagrangian withvarious weighing parameters α <strong>for</strong> the barproblem. The curves are generated by plottingthe Lagrangian at the 20th timestep. (Reddotted line: no data augmentation, greendashed line: data aug. with α = 0.3, blue solidline: data aug. with α = 0.5, black dashed dottedline: data aug. with α = 0.7.)−10−15−20−25−30−35−400 5 10 15 20 25Figure 5. The time series <strong>of</strong> Lagrangian alongthe 20 time steps with sample size L = 200(curves generated at β −1 = 0.2). (Red dottedline: correct WLU, blue solid line: incorrectWLU.)−20−30−40−50−60−70−800 0.5 1 1.5Figure 7. Plots <strong>of</strong> β −1 vs. the Lagrangian<strong>for</strong> the 50-spin model. The curves are generatedby plotting the Lagrangian at the 20thtimestep. (Red dotted line: no data augmentation,blue solid line: data aug. with α = 0.5.)