Traumatic Brain Injury and Effects of Altitude - Human Performance ...
Traumatic Brain Injury and Effects of Altitude - Human Performance ...
Traumatic Brain Injury and Effects of Altitude - Human Performance ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
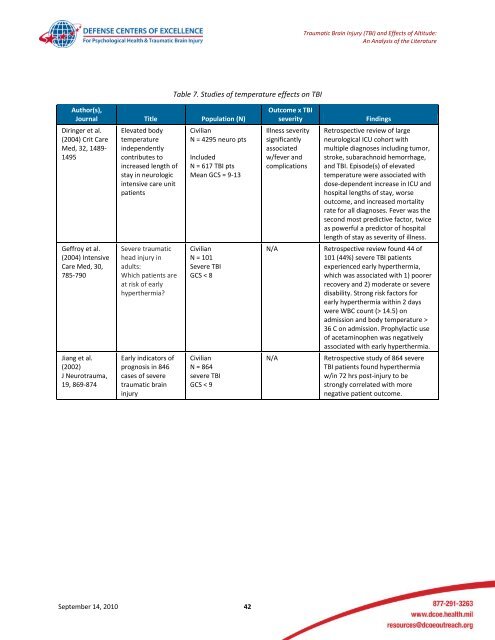
<strong>Traumatic</strong> <strong>Brain</strong> <strong>Injury</strong> (TBI) <strong>and</strong> <strong>Effects</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Altitude</strong>:An Analysis <strong>of</strong> the LiteratureTable 7. Studies <strong>of</strong> temperature effects on TBIAuthor(s),Journal Title Population (N)Diringer et al.(2004) Crit CareMed, 32, 1489-1495Geffroy et al.(2004) IntensiveCare Med, 30,785-790Jiang et al.(2002)J Neurotrauma,19, 869-874Elevated bodytemperatureindependentlycontributes toincreased length <strong>of</strong>stay in neurologicintensive care unitpatientsSevere traumatichead injury inadults:Which patients areat risk <strong>of</strong> earlyhyperthermia?Early indicators <strong>of</strong>prognosis in 846cases <strong>of</strong> severetraumatic braininjuryCivilianN = 4295 neuro ptsIncludedN = 617 TBI ptsMean GCS = 9-13CivilianN = 101Severe TBIGCS < 8CivilianN = 864severe TBIGCS < 9Outcome x TBIseverityIllness severitysignificantlyassociatedw/fever <strong>and</strong>complicationsN/AN/AFindingsRetrospective review <strong>of</strong> largeneurological ICU cohort withmultiple diagnoses including tumor,stroke, subarachnoid hemorrhage,<strong>and</strong> TBI. Episode(s) <strong>of</strong> elevatedtemperature were associated withdose-dependent increase in ICU <strong>and</strong>hospital lengths <strong>of</strong> stay, worseoutcome, <strong>and</strong> increased mortalityrate for all diagnoses. Fever was thesecond most predictive factor, twiceas powerful a predictor <strong>of</strong> hospitallength <strong>of</strong> stay as severity <strong>of</strong> illness.Retrospective review found 44 <strong>of</strong>101 (44%) severe TBI patientsexperienced early hyperthermia,which was associated with 1) poorerrecovery <strong>and</strong> 2) moderate or severedisability. Strong risk factors forearly hyperthermia within 2 dayswere WBC count (> 14.5) onadmission <strong>and</strong> body temperature >36 C on admission. Prophylactic use<strong>of</strong> acetaminophen was negativelyassociated with early hyperthermia.Retrospective study <strong>of</strong> 864 severeTBI patients found hyperthermiaw/in 72 hrs post-injury to bestrongly correlated with morenegative patient outcome.September 14, 2010 42




![Body Composition and Military [PDF] - Human Performance ...](https://img.yumpu.com/43269347/1/190x245/body-composition-and-military-pdf-human-performance-.jpg?quality=85)
![Tips for Grocery Shopping [PDF]](https://img.yumpu.com/37447379/1/190x245/tips-for-grocery-shopping-pdf.jpg?quality=85)

![Synthetic Drugs [PDF] - Human Performance Resource Center](https://img.yumpu.com/37447322/1/190x245/synthetic-drugs-pdf-human-performance-resource-center.jpg?quality=85)



