An Introduction to Evolutionary Game Theory: Lecture 2 - School of ...
An Introduction to Evolutionary Game Theory: Lecture 2 - School of ...
An Introduction to Evolutionary Game Theory: Lecture 2 - School of ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
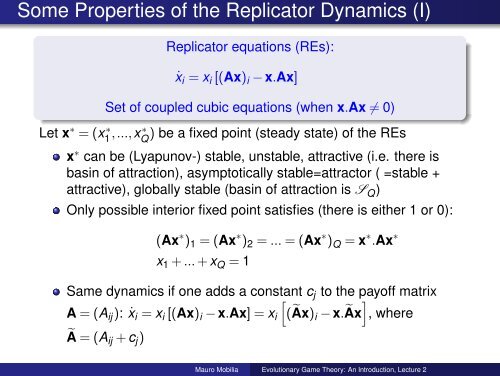
Some Properties <strong>of</strong> the Replica<strong>to</strong>r Dynamics (I)Replica<strong>to</strong>r equations (REs):ẋ i = x i [(Ax) i − x.Ax]Set <strong>of</strong> coupled cubic equations (when x.Ax ≠ 0)Let x ∗ = (x1 ∗,...,x Q ∗ ) be a fixed point (steady state) <strong>of</strong> the REsx ∗ can be (Lyapunov-) stable, unstable, attractive (i.e. there isbasin <strong>of</strong> attraction), asymp<strong>to</strong>tically stable=attrac<strong>to</strong>r ( =stable +attractive), globally stable (basin <strong>of</strong> attraction is S Q )Only possible interior fixed point satisfies (there is either 1 or 0):(Ax ∗ ) 1 = (Ax ∗ ) 2 = ... = (Ax ∗ ) Q = x ∗ .Ax ∗x 1 + ... + x Q = 1Same dynamics if one adds a constant[c j <strong>to</strong> the pay<strong>of</strong>f matrixA = (A ij ): ẋ i = x i [(Ax) i − x.Ax] = x i (Ãx) i −], x.Ãx whereà = (A ij + c j )Mauro Mobilia <strong>Evolutionary</strong> <strong>Game</strong> <strong>Theory</strong>: <strong>An</strong> <strong>Introduction</strong>, <strong>Lecture</strong> 2