IST-2003-507581 WINNER D2.5 v1.0 Duplex ... - Celtic-Plus
IST-2003-507581 WINNER D2.5 v1.0 Duplex ... - Celtic-Plus
IST-2003-507581 WINNER D2.5 v1.0 Duplex ... - Celtic-Plus
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
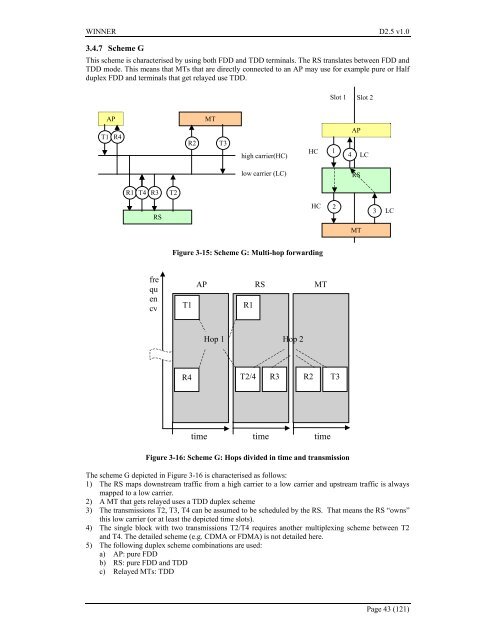
<strong>WINNER</strong> <strong>D2.5</strong> <strong>v1.0</strong>3.4.7 Scheme GThis scheme is characterised by using both FDD and TDD terminals. The RS translates between FDD andTDD mode. This means that MTs that are directly connected to an AP may use for example pure or Halfduplex FDD and terminals that get relayed use TDD.Slot 1 Slot 2APMTT1R4R2T3high carrier(HC)HC1AP4 LClow carrier (LC)RSR1 T4 R3T2RSHC23LCMTFigure 3-15: Scheme G: Multi-hop forwardingfrequencyT1AP RS MTR1Hop 1 Hop 2R4 T2/4 R3R2T3time time timeFigure 3-16: Scheme G: Hops divided in time and transmissionThe scheme G depicted in Figure 3-16 is characterised as follows:1) The RS maps downstream traffic from a high carrier to a low carrier and upstream traffic is alwaysmapped to a low carrier.2) A MT that gets relayed uses a TDD duplex scheme3) The transmissions T2, T3, T4 can be assumed to be scheduled by the RS. That means the RS “owns”this low carrier (or at least the depicted time slots).4) The single block with two transmissions T2/T4 requires another multiplexing scheme between T2and T4. The detailed scheme (e.g. CDMA or FDMA) is not detailed here.5) The following duplex scheme combinations are used:a) AP: pure FDDb) RS: pure FDD and TDDc) Relayed MTs: TDDPage 43 (121)