Global plan for insecticide resistance management in malaria vectors
Global plan for insecticide resistance management in malaria vectors
Global plan for insecticide resistance management in malaria vectors
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
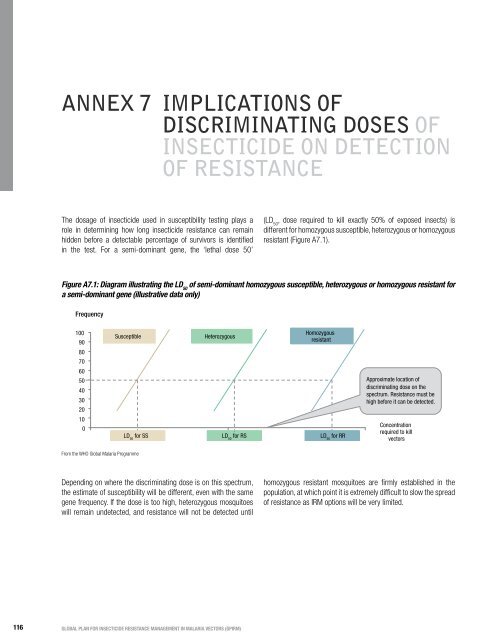
Annex 7 Implications ofdiscrim<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g doses of<strong><strong>in</strong>secticide</strong> on detectionof <strong>resistance</strong>The dosage of <strong><strong>in</strong>secticide</strong> used <strong>in</strong> susceptibility test<strong>in</strong>g plays arole <strong>in</strong> determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g how long <strong><strong>in</strong>secticide</strong> <strong>resistance</strong> can rema<strong>in</strong>hidden be<strong>for</strong>e a detectable percentage of survivors is identified<strong>in</strong> the test. For a semi-dom<strong>in</strong>ant gene, the ‘lethal dose 50’(LD 50, dose required to kill exactly 50% of exposed <strong>in</strong>sects) isdifferent <strong>for</strong> homozygous susceptible, heterozygous or homozygousresistant (Figure A7.1).Figure A7.1: Diagram illustrat<strong>in</strong>g the LD 50of semi-dom<strong>in</strong>ant homozygous susceptible, heterozygous or homozygous resistant <strong>for</strong>a semi-dom<strong>in</strong>ant gene (illustrative data only)Frequency10090SusceptibleHeterozygousHomozygousresistant80706050403020Approximate location ofdiscrim<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g dose on thespectrum. Resistance must behigh be<strong>for</strong>e it can be detected.100LD 50<strong>for</strong> SSLD 50<strong>for</strong> RSLD 50<strong>for</strong> RRConcentrationrequired to kill<strong>vectors</strong>From the WHO <strong>Global</strong> Malaria ProgrammeDepend<strong>in</strong>g on where the discrim<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g dose is on this spectrum,the estimate of susceptibility will be different, even with the samegene frequency. If the dose is too high, heterozygous mosquitoeswill rema<strong>in</strong> undetected, and <strong>resistance</strong> will not be detected untilhomozygous resistant mosquitoes are firmly established <strong>in</strong> thepopulation, at which po<strong>in</strong>t it is extremely difficult to slow the spreadof <strong>resistance</strong> as IRM options will be very limited.116GLOBAL PLAN FOR INSECTICIDE RESISTANCE MANAGEMENT IN MALARIA VECTORS (GPIRM)