ION MODULATED ORGANIC TRANSISTORS - Doria
ION MODULATED ORGANIC TRANSISTORS - Doria
ION MODULATED ORGANIC TRANSISTORS - Doria
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
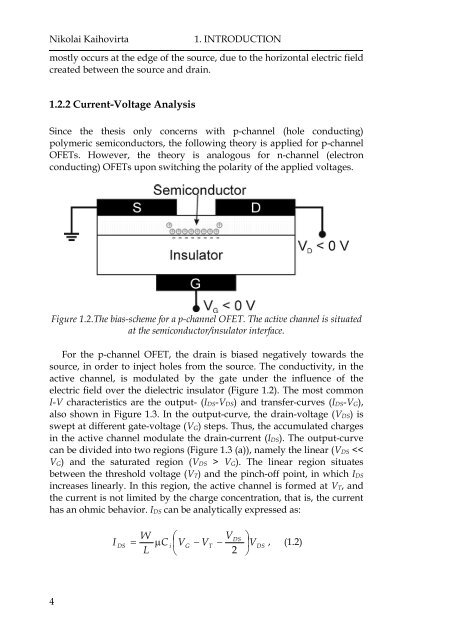
Nikolai Kaihovirta1. INTRODUCT<strong>ION</strong>mostly occurs at the edge of the source, due to the horizontal electric fieldcreated between the source and drain.1.2.2 Current-Voltage AnalysisSince the thesis only concerns with p-channel (hole conducting)polymeric semiconductors, the following theory is applied for p-channelOFETs. However, the theory is analogous for n-channel (electronconducting) OFETs upon switching the polarity of the applied voltages.Figure 1.2.The bias-scheme for a p-channel OFET. The active channel is situatedat the semiconductor/insulator interface.For the p-channel OFET, the drain is biased negatively towards thesource, in order to inject holes from the source. The conductivity, in theactive channel, is modulated by the gate under the influence of theelectric field over the dielectric insulator (Figure 1.2). The most commonI-V characteristics are the output- (I DS-V DS) and transfer-curves (I DS-V G),also shown in Figure 1.3. In the output-curve, the drain-voltage (V DS) isswept at different gate-voltage (V G ) steps. Thus, the accumulated chargesin the active channel modulate the drain-current (I DS). The output-curvecan be divided into two regions (Figure 1.3 (a)), namely the linear (V DS