MISR: In-Flight Radiometric Calibration and Characterization Plan
MISR: In-Flight Radiometric Calibration and Characterization Plan
MISR: In-Flight Radiometric Calibration and Characterization Plan
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
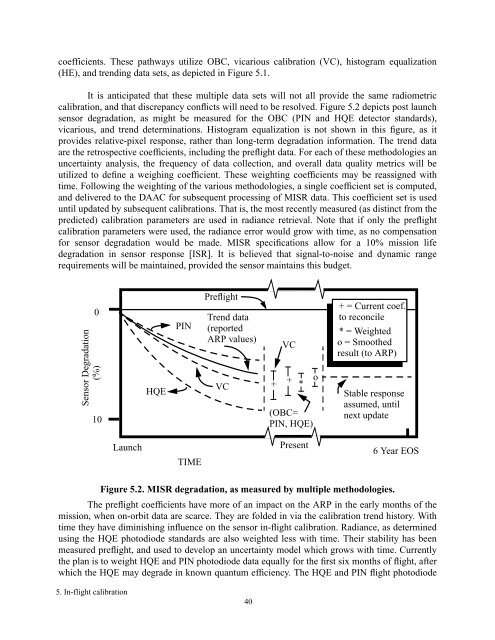
coefficients. These pathways utilize OBC, vicarious calibration (VC), histogram equalization(HE), <strong>and</strong> trending data sets, as depicted in Figure 5.1.It is anticipated that these multiple data sets will not all provide the same radiometriccalibration, <strong>and</strong> that discrepancy conflicts will need to be resolved. Figure 5.2 depicts post launchsensor degradation, as might be measured for the OBC (PIN <strong>and</strong> HQE detector st<strong>and</strong>ards),vicarious, <strong>and</strong> trend determinations. Histogram equalization is not shown in this figure, as itprovides relative-pixel response, rather than long-term degradation information. The trend dataare the retrospective coefficients, including the preflight data. For each of these methodologies anuncertainty analysis, the frequency of data collection, <strong>and</strong> overall data quality metrics will beutilized to define a weighing coefficient. These weighting coefficients may be reassigned withtime. Following the weighting of the various methodologies, a single coefficient set is computed,<strong>and</strong> delivered to the DAAC for subsequent processing of <strong>MISR</strong> data. This coefficient set is useduntil updated by subsequent calibrations. That is, the most recently measured (as distinct from thepredicted) calibration parameters are used in radiance retrieval. Note that if only the preflightcalibration parameters were used, the radiance error would grow with time, as no compensationfor sensor degradation would be made. <strong>MISR</strong> specifications allow for a 10% mission lifedegradation in sensor response [ISR]. It is believed that signal-to-noise <strong>and</strong> dynamic rangerequirements will be maintained, provided the sensor maintains this budget.0Sensor Degradation(%)10HQEPINPreflightTrend data(reportedARP values)VCVC*(OBC=PIN, HQE)o+ = Current coef.to reconcile* = Weightedo = Smoothedresult (to ARP)+ + 6 Year EOSStable responseassumed, untilnext updateLaunchTIMEPresentFigure 5.2. <strong>MISR</strong> degradation, as measured by multiple methodologies.The preflight coefficients have more of an impact on the ARP in the early months of themission, when on-orbit data are scarce. They are folded in via the calibration trend history. Withtime they have diminishing influence on the sensor in-flight calibration. Radiance, as determinedusing the HQE photodiode st<strong>and</strong>ards are also weighted less with time. Their stability has beenmeasured preflight, <strong>and</strong> used to develop an uncertainty model which grows with time. Currentlythe plan is to weight HQE <strong>and</strong> PIN photodiode data equally for the first six months of flight, afterwhich the HQE may degrade in known quantum efficiency. The HQE <strong>and</strong> PIN flight photodiode5. <strong>In</strong>-flight calibration40