Simplified Occlusal Plane Analyzer Instruction Manual - Whip Mix
Simplified Occlusal Plane Analyzer Instruction Manual - Whip Mix
Simplified Occlusal Plane Analyzer Instruction Manual - Whip Mix
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
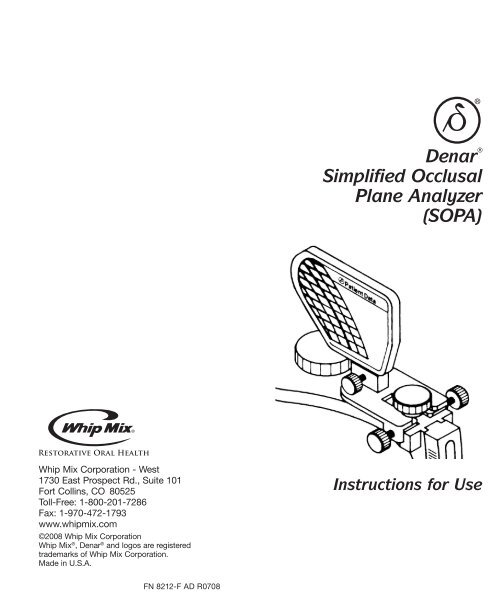
Step OneRemove the upper cast from the articulator.Step TwoInsert a flag onto the SOPA base (Figure 1).Each flag has two sides (patient’s right andleft) and space for patient information suchas name, date and other data. The graph is inmillimeter increments. Tighten lock screw.Figure 1Step FourThe compass has a standard radius of 4”. Thissetting is standard for evaluating the finalcusp tip heights on an ideal lower occlusalplane. Note: Millimeter adjustments(+ or -10mm). Use these only for measuringthe amount of tooth reduction desired whenplanning restorative cases.Step FiveTouch the compass lead (C) to the tip of thelower cuspid. Position the compass point(D) on the center line (for the 4” radius) ofthe SOPA flag (Figure 4). This automaticallyestablishes the position for the compass pointin correct relation to the condyle. Note: If thecuspid is missing, it should be waxed in. Keepthe height in harmony with the remaininganterior teeth.Step SixArc the compass lead to the back molar(Figure 5). This establishes the optimumocclusal plane height for the posterior teeth.Note: If the molar is missing, the occlusalplane can be scribed on a wax rim.Step ThreePlace the SOPA on the upper bow slidingthe key into the articulator slot (Figure 2) asshown (Figure 3-A & B). Tighten the thumbscrews.Figure 2SlotBack toSecureBFigure 4DCFigure 5If the back of the occlusal plane needs to beraised or lowered, return the compass leadto the cuspid tip. Holding that position, arcthe compass point forward or backward onthe SOPA flag along the same horizontal linewhile using the compass lead as the pivot.(Move the compass point anterior for ahigher occlusal plane or posterior for a lowerocclusal plane.)As long as the pointer maintains contact onthe width of the flag, the occlusal plane willbe acceptable. If an acceptable plane cannotbe established, the casts may not be properlymounted in relation to the condylar axis.AForwardinto SlotFigure 3