Numerical simulation of two-dimensional flows over a circular ...
Numerical simulation of two-dimensional flows over a circular ...
Numerical simulation of two-dimensional flows over a circular ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
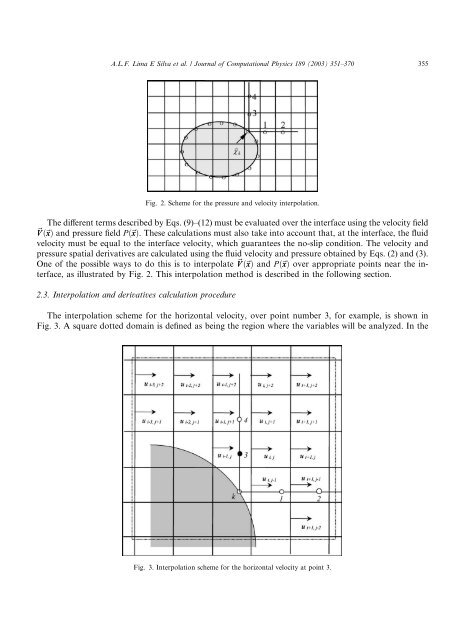
A.L.F. Lima E Silva et al. / Journal <strong>of</strong> Computational Physics 189 (2003) 351–370 355Fig. 2. Scheme for the pressure and velocity interpolation.The different terms described by Eqs. (9)–(12) must be evaluated <strong>over</strong> the interface using the velocity field~V ð~xÞ and pressure field Pð~xÞ. These calculations must also take into account that, at the interface, the fluidvelocity must be equal to the interface velocity, which guarantees the no-slip condition. The velocity andpressure spatial derivatives are calculated using the fluid velocity and pressure obtained by Eqs. (2) and (3).One <strong>of</strong> the possible ways to do this is to interpolate ~V ð~xÞ and Pð~xÞ <strong>over</strong> appropriate points near the interface,as illustrated by Fig. 2. This interpolation method is described in the following section.2.3. Interpolation and derivatives calculation procedureThe interpolation scheme for the horizontal velocity, <strong>over</strong> point number 3, for example, is shown inFig. 3. A square dotted domain is defined as being the region where the variables will be analyzed. In theFig. 3. Interpolation scheme for the horizontal velocity at point 3.