pediatric-ALS-AHA-guidelines-circulation_11-2010 - SSM Cardinal ...
pediatric-ALS-AHA-guidelines-circulation_11-2010 - SSM Cardinal ...
pediatric-ALS-AHA-guidelines-circulation_11-2010 - SSM Cardinal ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
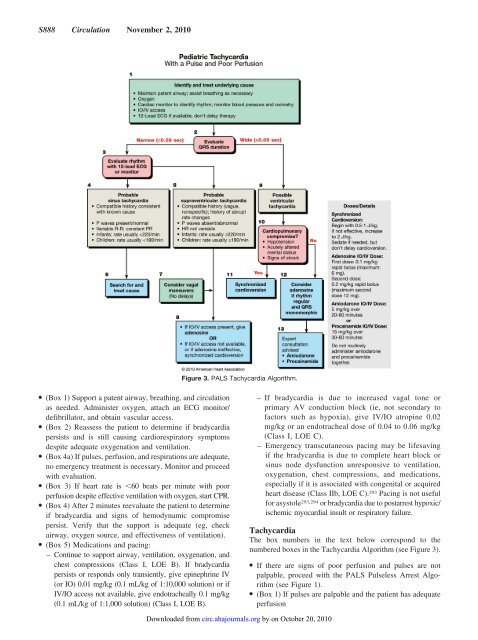
S888 Circulation November 2, <strong>2010</strong>Figure 3. P<strong>ALS</strong> Tachycardia Algorithm.● (Box 1) Support a patent airway, breathing, and <strong>circulation</strong>as needed. Administer oxygen, attach an ECG monitor/defibrillator, and obtain vascular access.● (Box 2) Reassess the patient to determine if bradycardiapersists and is still causing cardiorespiratory symptomsdespite adequate oxygenation and ventilation.● (Box 4a) If pulses, perfusion, and respirations are adequate,no emergency treatment is necessary. Monitor and proceedwith evaluation.● (Box 3) If heart rate is 60 beats per minute with poorperfusion despite effective ventilation with oxygen, start CPR.● (Box 4) After 2 minutes reevaluate the patient to determineif bradycardia and signs of hemodynamic compromisepersist. Verify that the support is adequate (eg, checkairway, oxygen source, and effectiveness of ventilation).● (Box 5) Medications and pacing:– Continue to support airway, ventilation, oxygenation, andchest compressions (Class I, LOE B). If bradycardiapersists or responds only transiently, give epinephrine IV(or IO) 0.01 mg/kg (0.1 mL/kg of 1:10,000 solution) or ifIV/IO access not available, give endotracheally 0.1 mg/kg(0.1 mL/kg of 1:1,000 solution) (Class I, LOE B).– If bradycardia is due to increased vagal tone orprimary AV conduction block (ie, not secondary tofactors such as hypoxia), give IV/IO atropine 0.02mg/kg or an endotracheal dose of 0.04 to 0.06 mg/kg(Class I, LOE C).– Emergency transcutaneous pacing may be lifesavingif the bradycardia is due to complete heart block orsinus node dysfunction unresponsive to ventilation,oxygenation, chest compressions, and medications,especially if it is associated with congenital or acquiredheart disease (Class IIb, LOE C). 293 Pacing is not usefulfor asystole 293,294 or bradycardia due to postarrest hypoxic/ischemic myocardial insult or respiratory failure.TachycardiaThe box numbers in the text below correspond to thenumbered boxes in the Tachycardia Algorithm (see Figure 3).● If there are signs of poor perfusion and pulses are notpalpable, proceed with the P<strong>ALS</strong> Pulseless Arrest Algorithm(see Figure 1).● (Box 1) If pulses are palpable and the patient has adequateperfusionDownloaded from circ.ahajournals.org by on October 20, <strong>2010</strong>