The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab
The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab
The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
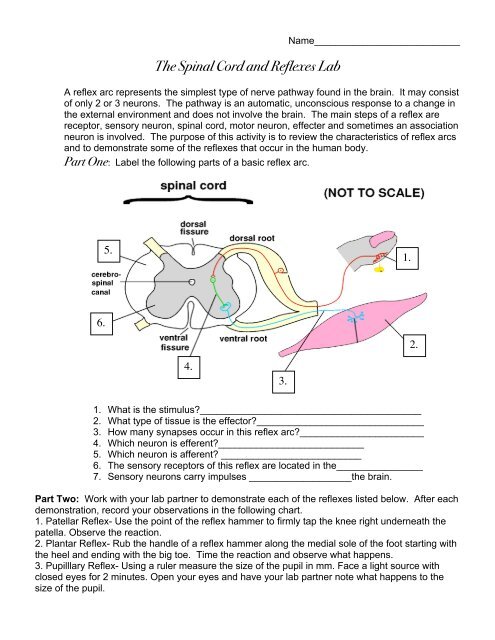
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Spinal</strong> <strong>Cord</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Reflexes</strong> <strong>Lab</strong>Name___________________________A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consistof only 2 or 3 neurons. <strong>The</strong> pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change inthe external environment <strong>and</strong> does not involve the brain. <strong>The</strong> main steps of a reflex arereceptor, sensory neuron, spinal cord, motor neuron, effecter <strong>and</strong> sometimes an associationneuron is involved. <strong>The</strong> purpose of this activity is to review the characteristics of reflex arcs<strong>and</strong> to demonstrate some of the reflexes that occur in the human body.Part One: <strong>Lab</strong>el the following parts of a basic reflex arc.5.1.____6.___ 2.4.__3.__1. What is the stimulus?__________________________________________2. What type of tissue is the effector?_______________________________3. How many synapses occur in this reflex arc?_______________________ _4. Which neuron is efferent?___________________________ _5. Which neuron is afferent? __________________________ _6. <strong>The</strong> sensory receptors of this reflex are located in the________________ _7. Sensory neurons carry impulses ___________________the brain. __Part Two: Work with your lab partner to demonstrate each of the reflexes listed below. After eachdemonstration, record your observations in the following chart._1. Patellar Reflex- Use the point of the reflex hammer to firmly tap the knee right underneath _ thepatella. Observe the reaction.2. Plantar Reflex- Rub the h<strong>and</strong>le of a reflex hammer along the medial sole of the foot starting withthe heel <strong>and</strong> ending with the big toe. Time the reaction <strong>and</strong> observe what happens.3. Pupilllary Reflex- Using a ruler measure the size of the pupil in mm. Face a light source withclosed eyes for 2 minutes. Open your eyes <strong>and</strong> have your lab partner note what happens to thesize of the pupil.
4. Accomodation Reflex- Note the size of the pupil while the subject is looking at an object acrossthe room. Now have the subject look at an object that is close by. What happens to the size of thepupil.5. Balancing Reflex- Have the subject st<strong>and</strong> on one foot while looking at the ceiling, eyes open.Notice the attempts to maintain balance. <strong>The</strong>n have the subject repeat, but with their eyes closed.Note the difference.Reflex Tested Response Observed Effector Involved1. Patellar Reflex2. Plantar Reflex “Babinski”3. Pupillary Reflex4. Accomodation Reflex5. Balancing ReflexPost <strong>Lab</strong> Questions:1. Define the terms reflex <strong>and</strong> reflex arc.2. Explain the function of each element of a reflex arc. In order, what are the five steps of areflex arc?3. Explain the importance of reflex testing in a physical examination.4. What is a monosynaptic reflex?5. What type of neurons conduct nerve impulses along an efferent pathway?6. What type of reflexes are not subject to conscious control?7. What is the effector in the papillary reflex arc?8. Where along a reflex arc would you find interneurons ( or association neurons)?9. What functions as the afferent pathway for the pupillary reflex arc?10. Describe a normal plantar reflex.11. Describe Babinski’s sign.12. How important are the eyes in balance?13. Why does the pupil size chance during accommodation?14. What is the difference between innate <strong>and</strong> acquired reflexes?15. What type of reflex is the patellar reflex?