Targeting cyclin B1 inhibits proliferation and sensitizes breast ...
Targeting cyclin B1 inhibits proliferation and sensitizes breast ...
Targeting cyclin B1 inhibits proliferation and sensitizes breast ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
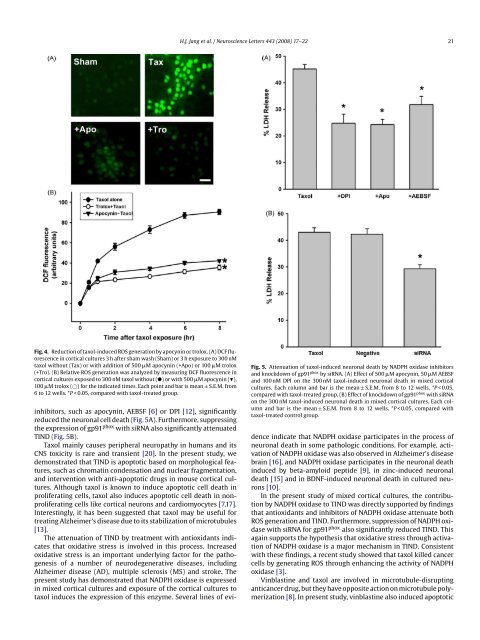
H.J. Jang et al. / Neuroscience Letters 443 (2008) 17–22 21Fig. 4. Reduction of taxol-induced ROS generation by apocynin or trolox. (A) DCF fluorescencein cortical cultures 3 h after sham wash (Sham) or 3 h exposure to 300 nMtaxol without (Tax) or with addition of 500 M apocynin (+Apo) or 100 M trolox(+Tro). (B) Relative ROS generation was analyzed by measuring DCF fluorescence incortical cultures exposed to 300 nM taxol without () or with 500 M apocynin (),100 Mtrolox(○) for the indicated times. Each point <strong>and</strong> bar is mean ± S.E.M. from6 to 12 wells. *P < 0.05, compared with taxol-treated group.inhibitors, such as apocynin, AEBSF [6] or DPI [12], significantlyreduced the neuronal cell death (Fig. 5A). Furthermore, suppressingthe expression of gp91 phox with siRNA also significantly attenuatedTIND (Fig. 5B).Taxol mainly causes peripheral neuropathy in humans <strong>and</strong> itsCNS toxicity is rare <strong>and</strong> transient [20]. In the present study, wedemonstrated that TIND is apoptotic based on morphological features,such as chromatin condensation <strong>and</strong> nuclear fragmentation,<strong>and</strong> intervention with anti-apoptotic drugs in mouse cortical cultures.Although taxol is known to induce apoptotic cell death inproliferating cells, taxol also induces apoptotic cell death in nonproliferatingcells like cortical neurons <strong>and</strong> cardiomyocytes [7,17].Interestingly, it has been suggested that taxol may be useful fortreating Alzheimer’s disease due to its stabilization of microtubules[13].The attenuation of TIND by treatment with antioxidants indicatesthat oxidative stress is involved in this process. Increasedoxidative stress is an important underlying factor for the pathogenesisof a number of neurodegenerative diseases, includingAlzheimer disease (AD), multiple sclerosis (MS) <strong>and</strong> stroke. Thepresent study has demonstrated that NADPH oxidase is expressedin mixed cortical cultures <strong>and</strong> exposure of the cortical cultures totaxol induces the expression of this enzyme. Several lines of evi-Fig. 5. Attenuation of taxol-induced neuronal death by NADPH oxidase inhibitors<strong>and</strong> knockdown of gp91 phox by siRNA. (A) Effect of 500 M apocynin, 50 M AEBSF<strong>and</strong> 100 nM DPI on the 300 nM taxol-induced neuronal death in mixed corticalcultures. Each column <strong>and</strong> bar is the mean ± S.E.M. from 8 to 12 wells. *P < 0.05,compared with taxol-treated group. (B) Effect of knockdown of gp91 phox with siRNAon the 300 nM taxol-induced neuronal death in mixed cortical cultures. Each column<strong>and</strong> bar is the mean ± S.E.M. from 8 to 12 wells. *P < 0.05, compared withtaxol-treated control group.dence indicate that NADPH oxidase participates in the process ofneuronal death in some pathologic conditions. For example, activationof NADPH oxidase was also observed in Alzheimer’s diseasebrain [16], <strong>and</strong> NADPH oxidase participates in the neuronal deathinduced by beta-amyloid peptide [9], in zinc-induced neuronaldeath [15] <strong>and</strong> in BDNF-induced neuronal death in cultured neurons[10].In the present study of mixed cortical cultures, the contributionby NADPH oxidase to TIND was directly supported by findingsthat antioxidants <strong>and</strong> inhibitors of NADPH oxidase attenuate bothROS generation <strong>and</strong> TIND. Furthermore, suppression of NADPH oxidasewith siRNA for gp91 phox also significantly reduced TIND. Thisagain supports the hypothesis that oxidative stress through activationof NADPH oxidase is a major mechanism in TIND. Consistentwith these findings, a recent study showed that taxol killed cancercells by generating ROS through enhancing the activity of NADPHoxidase [3].Vinblastine <strong>and</strong> taxol are involved in microtubule-disruptinganticancer drug, but they have opposite action on microtubule polymerization[8]. In present study, vinblastine also induced apoptotic