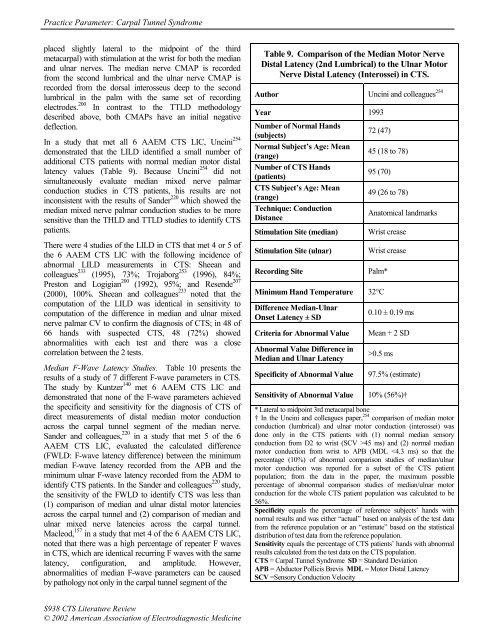
<strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Parameter</strong>: Carpal Tunnel Syndromeplaced slightly lateral to <strong>the</strong> midpoint <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> thirdmetacarpal) with stimulation at <strong>the</strong> wrist for both <strong>the</strong> median<strong>and</strong> ulnar nerves. The median nerve CMAP is recordedfrom <strong>the</strong> second lumbrical <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> ulnar nerve CMAP isrecorded from <strong>the</strong> dorsal interosseus deep to <strong>the</strong> secondlumbrical in <strong>the</strong> palm with <strong>the</strong> same set <strong>of</strong> recordingelectrodes. 200 In contrast to <strong>the</strong> TTLD methodologydescribed above, both CMAPs have an initial negativedeflection.In a study that met all 6 AAEM CTS LIC, Uncini 254demonstrated that <strong>the</strong> LILD identified a small number <strong>of</strong>additional CTS patients with normal median motor distallatency values (Table 9). Because Uncini 254 did notsimultaneously evaluate median mixed nerve palmarconduction studies in CTS patients, his results are notinconsistent with <strong>the</strong> results <strong>of</strong> S<strong>and</strong>er 220 which showed <strong>the</strong>median mixed nerve palmar conduction studies to be moresensitive than <strong>the</strong> THLD <strong>and</strong> TTLD studies to identify CTSpatients.There were 4 studies <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> LILD in CTS that met 4 or 5 <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> 6 AAEM CTS LIC with <strong>the</strong> following incidence <strong>of</strong>abnormal LILD measurements in CTS: Sheean <strong>and</strong>colleagues 233 (1995), 73%; Trojaborg 253 (1996), 84%;Preston <strong>and</strong> Logigian 200 (1992), 95%; <strong>and</strong> Resende 207(2000), 100%. Sheean <strong>and</strong> colleagues 233 noted that <strong>the</strong>computation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> LILD was identical in sensitivity tocomputation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> difference in median <strong>and</strong> ulnar mixednerve palmar CV to confirm <strong>the</strong> diagnosis <strong>of</strong> CTS; in 48 <strong>of</strong>66 h<strong>and</strong>s with suspected CTS, 48 (72%) showedabnormalities with each test <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>re was a closecorrelation between <strong>the</strong> 2 tests.Median F-Wave Latency Studies. Table 10 presents <strong>the</strong>results <strong>of</strong> a study <strong>of</strong> 7 different F-wave parameters in CTS.The study by Kuntzer 140 met 6 AAEM CTS LIC <strong>and</strong>demonstrated that none <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> F-wave parameters achieved<strong>the</strong> specificity <strong>and</strong> sensitivity for <strong>the</strong> diagnosis <strong>of</strong> CTS <strong>of</strong>direct measurements <strong>of</strong> distal median motor conductionacross <strong>the</strong> carpal tunnel segment <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> median nerve.S<strong>and</strong>er <strong>and</strong> colleagues, 220 in a study that met 5 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 6AAEM CTS LIC, evaluated <strong>the</strong> calculated difference(FWLD: F-wave latency difference) between <strong>the</strong> minimummedian F-wave latency recorded from <strong>the</strong> APB <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>minimum ulnar F-wave latency recorded from <strong>the</strong> ADM toidentify CTS patients. In <strong>the</strong> S<strong>and</strong>er <strong>and</strong> colleagues 220 study,<strong>the</strong> sensitivity <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> FWLD to identify CTS was less than(1) comparison <strong>of</strong> median <strong>and</strong> ulnar distal motor latenciesacross <strong>the</strong> carpal tunnel <strong>and</strong> (2) comparison <strong>of</strong> median <strong>and</strong>ulnar mixed nerve latencies across <strong>the</strong> carpal tunnel.Macleod, 157 in a study that met 4 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 6 AAEM CTS LIC,noted that <strong>the</strong>re was a high percentage <strong>of</strong> repeater F wavesin CTS, which are identical recurring F waves with <strong>the</strong> samelatency, configuration, <strong>and</strong> amplitude. However,abnormalities <strong>of</strong> median F-wave parameters can be causedby pathology not only in <strong>the</strong> carpal tunnel segment <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>Table 9. Comparison <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Median Motor NerveDistal Latency (2nd Lumbrical) to <strong>the</strong> Ulnar MotorNerve Distal Latency (Interossei) in CTS.Author Uncini <strong>and</strong> colleagues 254Year 1993Number <strong>of</strong> Normal H<strong>and</strong>s(subjects)72 (47)Normal Subject’s Age: Mean(range)45 (18 to 78)Number <strong>of</strong> CTS H<strong>and</strong>s(patients)95 (70)CTS Subject’s Age: Mean(range)49 (26 to 78)Technique: ConductionDistanceAnatomical l<strong>and</strong>marksStimulation Site (median)Stimulation Site (ulnar)Recording SiteWrist creaseWrist creasePalm*Minimum H<strong>and</strong> Temperature 32°CDifference Median-UlnarOnset Latency ± SDCriteria for Abnormal ValueAbnormal Value Difference inMedian <strong>and</strong> Ulnar LatencySpecificity <strong>of</strong> Abnormal Value0.10 ± 0.19 msMean + 2 SD>0.5 ms97.5% (estimate)Sensitivity <strong>of</strong> Abnormal Value 10% (56%)†* Lateral to midpoint 3rd metacarpal bone† In <strong>the</strong> Uncini <strong>and</strong> colleagues paper, 254 comparison <strong>of</strong> median motorconduction (lumbrical) <strong>and</strong> ulnar motor conduction (interossei) wasdone only in <strong>the</strong> CTS patients with (1) normal median sensoryconduction from D2 to wrist (SCV >45 ms) <strong>and</strong> (2) normal medianmotor conduction from wrist to APB (MDL
<strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Parameter</strong>: Carpal Tunnel Syndromemedian nerve, but also by pathology along <strong>the</strong> length <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>median motor nerve fibers to <strong>the</strong> APB from <strong>the</strong> spinal cordto <strong>the</strong> wrist. For all <strong>the</strong>se reasons, measurements <strong>of</strong> F-wavelatencies <strong>and</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r F-wave parameters are notrecommended for <strong>the</strong> diagnosis <strong>of</strong> CTS.Buschbacher, 35 in a study that met 5 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 6 AAEM LIC,reported <strong>the</strong> results <strong>of</strong> F-wave parameter in 195 referencesubjects. Fisher 73 (1997) used CTS as a model for analyzing<strong>the</strong> effects <strong>of</strong> focal nerve injury on F-wave parameters.Median Sensory NCSsMedian Sensory Nerve Conduction from Digit to Wrist.Table 11 presents <strong>the</strong> results <strong>of</strong> 6 studies <strong>of</strong> median sensoryNCSs <strong>of</strong> a 13 to 14 cm length <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> median nerve with <strong>the</strong>proximal portion passing through <strong>the</strong> carpal tunnel (digitwriststudies). These 6 studies that met all 6 AAEM CTSLIC determined that between 40% <strong>and</strong> 74% <strong>of</strong> patients withCTS demonstrate ei<strong>the</strong>r a prolonged median sensory peaklatency or <strong>the</strong> median SNAP was absent. In a 1972 studythat met <strong>the</strong> 6 AAEM CTS LIC, Casey <strong>and</strong> LeQuesne 39reported a 94% incidence <strong>of</strong> abnormal median digit-wristsensory conduction: 15 out <strong>of</strong> 16 CTS patient studiesabnormal with 9 out <strong>of</strong> 16 absent SNAP <strong>and</strong> 6 out <strong>of</strong> 16reduced CV.There are 4 studies listed in Table 1 that provide mediansensory nerve conduction data in normal subjects whichsupport <strong>the</strong> choice <strong>of</strong> abnormal values in <strong>the</strong> 6 studies inTable 11 for median sensory peak latency, median sensoryonset latency, <strong>and</strong> median sensory CV (calculated from <strong>the</strong>onset latency <strong>and</strong> conduction distance). 34,58,110,242There were 19 o<strong>the</strong>r median sensory NCSs <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> peaklatency, onset latency, <strong>and</strong> CV with conduction between <strong>the</strong>wrist <strong>and</strong> a digit (conduction distance <strong>of</strong> 13 to 14 cm) thatmet 4 or 5 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> AAEM CTS LIC with <strong>the</strong> followingincidence <strong>of</strong> abnormal findings (absent response, prolongedpeak or onset latency, or reduced CV) in patients with CTS:Andary <strong>and</strong> colleagues 9 (1996), 27%; Kothari <strong>and</strong>colleagues 135 (1995), D2 42% <strong>and</strong> D3 54%; White <strong>and</strong>colleagues 264 (1988), 44%, if a response could be elicited;Rosen 214 (1993), 48%; Mills 171 (1985), 53%; Sheean <strong>and</strong>colleagues 233 (1995), 55%; Stevens 243 (1987), 64%; Seror 228(1994), peak latency 61%, CV 66%; Preston <strong>and</strong>Logigian 200 (1992), 67%; Felsenthal 71 (1979), 70%;Trojaborg 253 (1996), D2 70% <strong>and</strong> D3 72%; Gunnarsson 91(1997), 77%; Melvin <strong>and</strong> colleagues 167 (1973), 79%;Marinacci 159 (1964), 83%; Monga <strong>and</strong> colleagues 174 (1985),86%; Kimura <strong>and</strong> Ayyar 131 (1985), 92%; Kemble 125 (1968),93%; Plaja 199 (1971), 98%; Merchut <strong>and</strong> colleagues 168(1990), 100%.While most authors used <strong>the</strong> index finger (Digit 2 or D2) forstimulation or recording, some prefer to use <strong>the</strong> middlefinger (Digit 3 or D3) instead <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> index finger to evaluatemedian sensory conduction in CTS. 31,117,118,173,181,192,271 Thestudies that evaluated median digit-wrist sensory conductionwith several digits noted abnormalities in CTS patients more<strong>of</strong>ten with evaluation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> middle finger compared to <strong>the</strong>index finger, <strong>and</strong> evaluation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> thumb <strong>and</strong> sometimes <strong>the</strong>ring finger studies were more <strong>of</strong>ten abnormal than both <strong>the</strong>index <strong>and</strong> middle finger studies. 135,188,189,253There are 2 studies <strong>of</strong> median sensory conduction from digitto wrist in normal subjects that met 5 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 6 AAEM CTSLIC: Stetson 242 (1994) D2 onset latency (3.0 ± 0.2 ms) <strong>and</strong>D2 sensory CV (SCV) (60.2 ± 4.9 m/s); Buschbacher 36onset (D2 = 2.6 ± 0.3 ms, D3 = 2.7 ± 0.3 ms) <strong>and</strong> peak (D2<strong>and</strong> D3 = 3.4 ± 0.3 ms) latencies, <strong>the</strong> Buschbacher 36 datapresents mean + 2 SD values higher than most <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>reference values in <strong>the</strong> 7 studies in Table 11.Median Sensory Conduction from <strong>the</strong> Palm to <strong>the</strong> Wrist.Table 12 presents <strong>the</strong> results <strong>of</strong> 7 studies <strong>of</strong> median sensory<strong>and</strong>/or mixed NCSs <strong>of</strong> an 8-cm length <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> median nervepassing through <strong>the</strong> carpal tunnel. These 7 studies that metall 6 AAEM CTS LIC determined that between 67% <strong>and</strong>84% <strong>of</strong> patients with CTS demonstrate a prolonged medianpeak latency, onset latency, or CV with a conductiondistance <strong>of</strong> 8 cm.In Table 1, <strong>the</strong>re are 4 studies <strong>of</strong> median sensory <strong>and</strong>/ormixed nerve conduction between <strong>the</strong> wrist <strong>and</strong> palm innormal subjects. Using a technique to study <strong>the</strong> conduction<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> wrist-palm median nerve segment similar toKimura, 130 Di Benedetto <strong>and</strong> colleagues 58 reported adifference in peak latency in healthy subjects <strong>of</strong> less than 2.2ms, <strong>and</strong> a difference in onset latency in healthy subjects <strong>of</strong>less than 1.8 ms, <strong>the</strong> latter value almost identical to <strong>the</strong>finding <strong>of</strong> Kimura 130 in Table 12. Cruz Martinez <strong>and</strong>colleagues 50 calculated <strong>the</strong> CV in palm-to-wrist segments <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> median nerve from <strong>the</strong> onset latency in 47 normalsubjects, aged 21 to 77 Under <strong>the</strong> age <strong>of</strong> 50, <strong>the</strong> mediansensory CV was 55 ± 5 m/s, <strong>and</strong> over <strong>the</strong> age <strong>of</strong> 50, <strong>the</strong>median sensory CV was 51 ± 5 m/s. Stetson 242 in a study <strong>of</strong>105 normal subjects noted an onset latency <strong>of</strong> 1.8 ± 0.2 ms.Buschbacher 33 in a study <strong>of</strong> 248 normal subjects reported anonset latency <strong>of</strong> 1.6 ± 0.2 ms <strong>and</strong> a peak latency <strong>of</strong> 2.1 ± 0.2ms.There were 15 additional studies that report median mixednerve conduction over a 7 cm to 8 cm distance across <strong>the</strong>carpal tunnel that met 4 or 5 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 6 AAEM CTS LIC with<strong>the</strong> following incidence <strong>of</strong> abnormal findings in patientswith CTS: Kimura 121 (1978), 45%; Andary <strong>and</strong> colleagues 9(1996), 57%; White <strong>and</strong> colleagues 264 (1988), 65%, a studythat ignored cases with absent responses; Mills 171 (1985),67%; Robinson <strong>and</strong> colleagues 211 (1998) 70%; Sheean <strong>and</strong>colleagues 233 (1995), 73%; Seror 228 (1994), 76%; Preston<strong>and</strong> Logigian 200 (1992), 82%; Stevens 243 (1987), 87%;Monga <strong>and</strong> colleagues 174 (1985), 88%; Felsenthal <strong>and</strong>Spindler 71 (1979), 100%; Wongsam 271 (1983), 100%;Muscle & Nerve Supplement X 2002 S939