TNO Finger Pressure Reference Guide - Integral Process
TNO Finger Pressure Reference Guide - Integral Process
TNO Finger Pressure Reference Guide - Integral Process
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
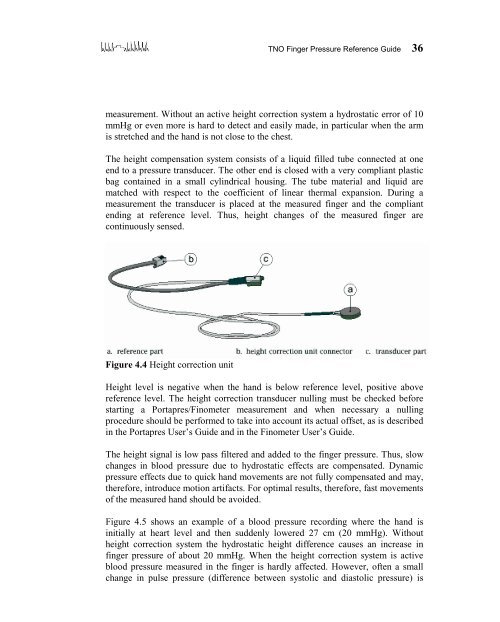
<strong>TNO</strong> <strong>Finger</strong> <strong>Pressure</strong> <strong>Reference</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> 36measurement. Without an active height correction system a hydrostatic error of 10mmHg or even more is hard to detect and easily made, in particular when the armis stretched and the hand is not close to the chest.The height compensation system consists of a liquid filled tube connected at oneend to a pressure transducer. The other end is closed with a very compliant plasticbag contained in a small cylindrical housing. The tube material and liquid arematched with respect to the coefficient of linear thermal expansion. During ameasurement the transducer is placed at the measured finger and the compliantending at reference level. Thus, height changes of the measured finger arecontinuously sensed.Figure 4.4 Height correction unitHeight level is negative when the hand is below reference level, positive abovereference level. The height correction transducer nulling must be checked beforestarting a Portapres/Finometer measurement and when necessary a nullingprocedure should be performed to take into account its actual offset, as is describedin the Portapres User’s <strong>Guide</strong> and in the Finometer User’s <strong>Guide</strong>.The height signal is low pass filtered and added to the finger pressure. Thus, slowchanges in blood pressure due to hydrostatic effects are compensated. Dynamicpressure effects due to quick hand movements are not fully compensated and may,therefore, introduce motion artifacts. For optimal results, therefore, fast movementsof the measured hand should be avoided.Figure 4.5 shows an example of a blood pressure recording where the hand isinitially at heart level and then suddenly lowered 27 cm (20 mmHg). Withoutheight correction system the hydrostatic height difference causes an increase infinger pressure of about 20 mmHg. When the height correction system is activeblood pressure measured in the finger is hardly affected. However, often a smallchange in pulse pressure (difference between systolic and diastolic pressure) is