Recycling critical raw materials from waste electronic equipment
Recycling critical raw materials from waste electronic equipment
Recycling critical raw materials from waste electronic equipment
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Recycling</strong> <strong>critical</strong> <strong>raw</strong> <strong>materials</strong><br />
<strong>from</strong> <strong>waste</strong> <strong>electronic</strong> <strong>equipment</strong><br />
Table 18: Quantity of precious metals in the hard disk drive platters of a notebook<br />
Ag [mg] Au [mg] Pt [mg] Pd [mg] Rh [mg] Ru [mg]<br />
< 0.1 < 0.1 0.4 < 0.1 < 0.1 < 0.1<br />
3.2 Tantalum<br />
Assembled PCBs contain a range of other metals in addition to the precious metals. In terms<br />
of <strong>critical</strong> <strong>raw</strong> <strong>materials</strong>, tantalum is of particular importance. Tantalum is used in highcapacity<br />
capacitors. As it cannot be recovered in the refining process for precious metals,<br />
there are no data comparable to that in Table 15 and Table 16. Although some older sources<br />
specify a percent by weight of 0.0157% or 4.71 g for a desktop PC (ACRR, undated) nothing<br />
is really known about the basis for this value. Furthermore, this value relates to device<br />
generations <strong>from</strong> the 1990s and should therefore be viewed with caution.<br />
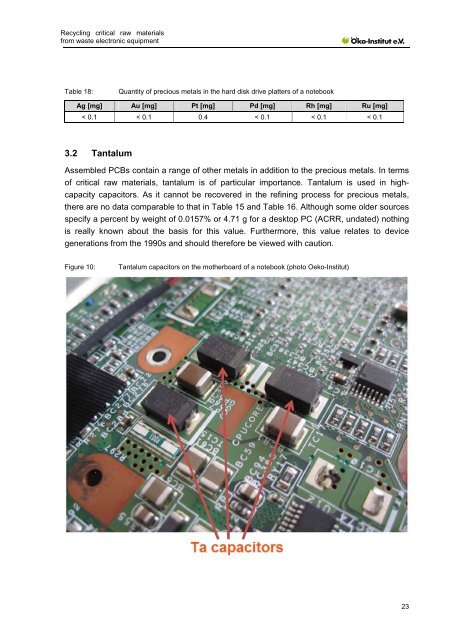
Figure 10: Tantalum capacitors on the motherboard of a notebook (photo Oeko-Institut)<br />
23