PRIORITIES FOR EU MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETY DESIGN
priorities for eu motor vehicle safety design - ETSC
priorities for eu motor vehicle safety design - ETSC
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
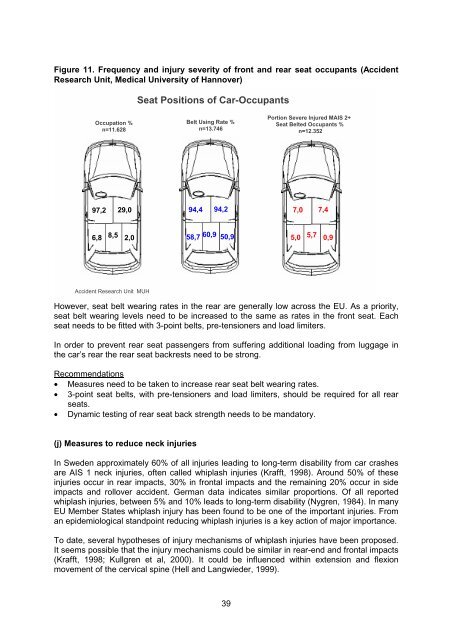
Figure 11. Frequency and injury severity of front and rear seat occupants (Accident<br />
Research Unit, Medical University of Hannover)<br />
Seat Positions of Car-Occupants<br />
Occupation %<br />
n=11.628<br />
Belt Using Rate %<br />
n=13.746<br />
Portion Severe Injured MAIS 2+<br />
Seat Belted Occupants %<br />
n=12.352<br />
97,2 29,0 94,4 94,2 7,0 7,4<br />
6,8 8,5 2,0<br />
58,7 60,9 50,9<br />
5,0 5,7 0,9<br />
Accident Research Unit MUH<br />
However, seat belt wearing rates in the rear are generally low across the <strong>EU</strong>. As a priority,<br />
seat belt wearing levels need to be increased to the same as rates in the front seat. Each<br />
seat needs to be fitted with 3-point belts, pre-tensioners and load limiters.<br />
In order to prevent rear seat passengers from suffering additional loading from luggage in<br />
the car’s rear the rear seat backrests need to be strong.<br />
Recommendations<br />
• Measures need to be taken to increase rear seat belt wearing rates.<br />
• 3-point seat belts, with pre-tensioners and load limiters, should be required for all rear<br />
seats.<br />
• Dynamic testing of rear seat back strength needs to be mandatory.<br />
(j) Measures to reduce neck injuries<br />
In Sweden approximately 60% of all injuries leading to long-term disability from car crashes<br />
are AIS 1 neck injuries, often called whiplash injuries (Krafft, 1998). Around 50% of these<br />
injuries occur in rear impacts, 30% in frontal impacts and the remaining 20% occur in side<br />
impacts and rollover accident. German data indicates similar proportions. Of all reported<br />
whiplash injuries, between 5% and 10% leads to long-term disability (Nygren, 1984). In many<br />
<strong>EU</strong> Member States whiplash injury has been found to be one of the important injuries. From<br />
an epidemiological standpoint reducing whiplash injuries is a key action of major importance.<br />
To date, several hypotheses of injury mechanisms of whiplash injuries have been proposed.<br />
It seems possible that the injury mechanisms could be similar in rear-end and frontal impacts<br />
(Krafft, 1998; Kullgren et al, 2000). It could be influenced within extension and flexion<br />
movement of the cervical spine (Hell and Langwieder, 1999).<br />
39